The outsourcing of zirconia crowns and braces has emerged as a significant development in the global dental laboratory and clinic settings. The increase in labor costs, the number of cases, and the need to maintain a uniform quality have led most dental practitioners to go outside the local production. China has become the leading and most mature outsourcing destination in the world for zirconia restorations.
The guide has been authored to enable dental laboratories and clinics fully comprehend what is really meant by zirconia outsourcing, the reason why China has been the top of this area, and the ability to maintain control, predictability, and confidence of the process. As a beginner in outsourcing or as an expert who wants to streamline an existing workflow, then this article is a roadmap that is comprehensive and step by step.
1. What is Zirconia?
Zirconia, also called zirconium dioxide (ZrO2), is a high-performance ceramic, making it a popular material in contemporary dentistry as it is employed in crowns, bridges, and full-arch restoration.
Zirconia is stronger, biocompatible, and aesthetically pleasing compared to other metal-fused-to-porcelain (PFM) restorations because it is made of metal-free materials. It is very fracture-resistant and is entirely compatible with the CAD/CAM manufacturing processes.
Key Characteristics of Dental Zirconia:
- Very high flexural strength, which is why it can be used in the posterior teeth and in long-span bridges.
- The best biocompatibility reduces the possibility of an allergy.
- Reduced adhesion of plaque, which promotes oral health.
- CAD/CAM compatibility, which allows a high level of accuracy in digital production.
- Several translucency levels with a high-strength opaque zirconia at the high end and multilayer aesthetic selections at the low end.
Contemporary zirconia onlays may be either monolithic (full contoured) or porcelain overlay bonded to improve esthetics, which makes them flexible to a broad set of clinical indications.
2. Why Zirconia Is Suitable for Outsourcing?
Dental products cannot outsource everything. However, zirconia specifically can be applied well to offshore production because it is digital-friendly and it has a standard production process.
- Digital workflow interoperability: The crowns and braces made of zirconia are created using CAD files, which may be sent in real time without any decrease in accuracy.
- Repetitive manufacturing process: Milling, sintering, and finishing are highly standardized procedures and have very little variation across cases.
- Scalable manufacturing: It is also possible to produce large volumes and still have a standard level of quality for all the units.
- Controllable material process: Zirconia offers greater control and less variation compared to hand-made restorations.
- Reduced reliance on chairside adjustments; Zirconia restorations that are well designed need very few adjustments when delivering.
In cases of increased workload in labs or in cases where technicians are in short supply, outsourcing zirconia is cost-effective without affecting quality or predictability.
3. Why Outsource Zirconia to China?
China is not merely a low-cost production nation, but it has become the industry center in outsourcing dental lab services, especially in the production of zirconia restorations. Key advantages of outsourcing to China are as follows:
(1) Mature Dental Manufacturing Ecosystem
There are thousands of specialty dental factories in China, most of which have 10-20 years of experience and provide their services to clients in North America, Europe, Australia, and Japan.
(2) Strong CAD/CAM Infrastructure
The majority of Chinese laboratories have a fully digital workflow with:
- 3Shape
- Exocad
- Dental Wings
- High-precision 5-axis milling machines
This guarantees compatibility with global laboratory systems and workflows.
(3) Well-trained Technical Labor Force
China has developed a high number of professionals, such as:
- CAD designers who were experts in the anatomy of the crowns and bridges.
- Zirconia finishing technicians are exposed to a large number of cases.
- Specific quality control teams that are trained according to international standards.
(4) Cost Efficiency Without Quality Compromise
The reduced costs of labor and operations enable the Chinese laboratories to be able to provide competitive prices, as well as use branded zirconia materials and modern equipment.
(5) Export-Oriented Quality Mindset
Labs serving overseas clients are experienced in:
- Delivering quality to meet international expectations.
- Carrying out obvious English communication.
- Being responsible for remakes.
- Developing long-term alliances.

4. What Can Be Outsourced?
It is also important to know what can and cannot be outsourced to create explicit expectations and trust in your outsourcing partner. Instead of strict guidelines, it is beneficial to consider the suitability of outsourcing in the context of predictability, standardization, and compatibility of workflow.
(1) Suitable for Outsourcing
The ideal restorations to outsource are zirconia restorations that can be aspired to conform to standard, digital workflows and predictable processes:
- Single zirconia crowns (anterior & posterior)
- Zirconia bridges (short to medium span)
- Full-contour monolithic zirconia
- Layered zirconia crowns
- Implant-supported zirconia restorations
- Full-arch zirconia (for selected cases with clearly defined protocols)
(2) Less Suitable for Outsourcing
Cases that have high variability, artisticization, or urgent schedules tend to be more effectively managed in-house:
- Very complicated aesthetic anterior cases involving chairside shade artistry.
- Same-day restorations of an emergency nature.
- Unusual or experimental materials.
- Cases of missing or incomplete clinical information.
The ability to clearly define scope and boundaries would help dental labs to obtain predictable results, minimize remakes, and be confident in their outsourcing process.

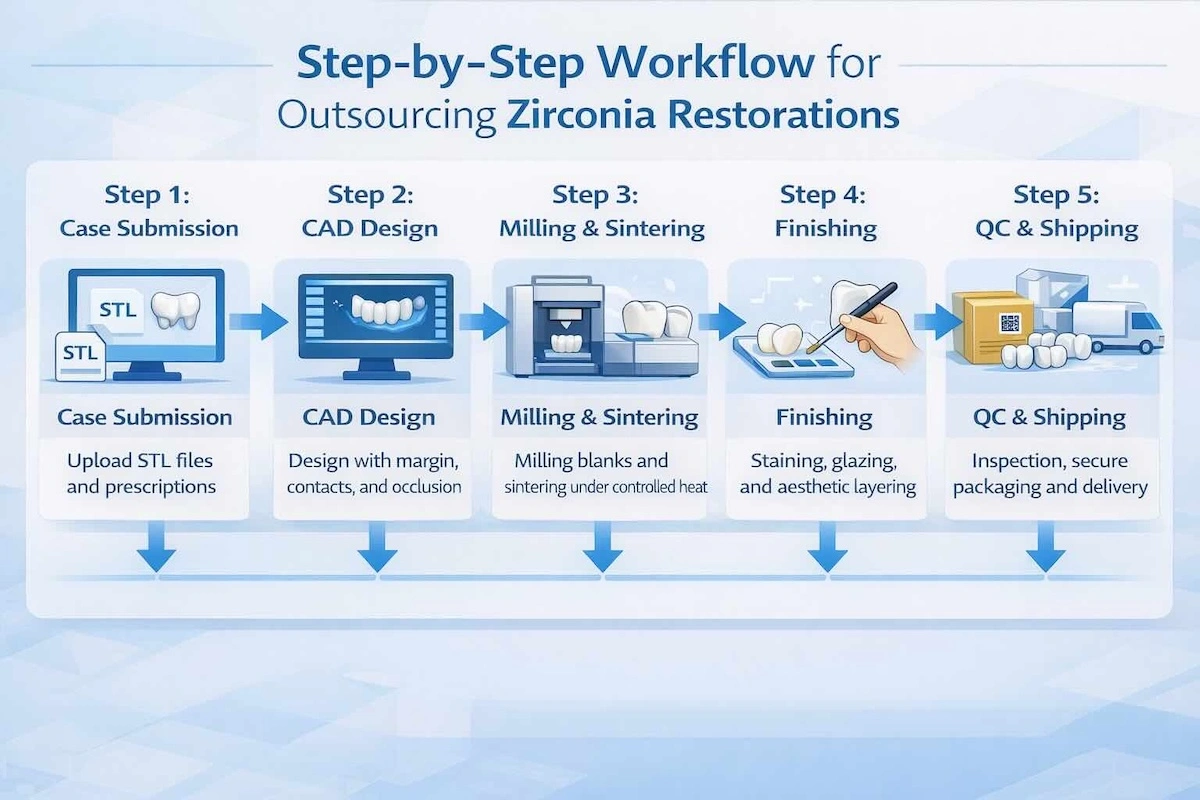
5. Step-by-Step Workflow of Zirconia Outsourcing to China
An established outsourcing process brings structure and predictability and transforms overseas zirconia production into a process that could be replicated and managed rather than a transaction that can hardly be predicted. The quality and standard Chinese dental laboratories generally use a standardized workflow that is in line with CAD/CAM practices as used internationally.
Step 1: Case Submission
It begins with the input of cases that are complete and accurate. The majority of zirconia cases are also presented electronically, with STL files of the prepared teeth, opposing arch, and bite registration in addition to an unambiguous prescribed form of restoration type, zirconia choice, and shade requests. Unambiguous information on cases at this level will considerably decrease revisions at the downstream.
Step 2: CAD Design and Review
Once the case has been received, a technical check is done on the case to ensure that there is a margin, occlusal space, and that the case is feasible. Designing of the restoration is then undertaken with references to dental CAD software, margins, contacts, occlusion, and anatomical form. Approval of design previews can be offered in case of need, such as in complex cases.
Step 3: Milling and Sintering
Pre-sintered zirconia blanks are milled and approved for designs. The restorations are subsequently sintered under controlled conditions to attain final strength and dimensional accuracy so that there is a consistent fit across batches.
Step 4: Finalizing and Aesthetics Processing
After sintering, restoration is finished by applying surface finishing, staining, glaze, or porcelain overlay as per the needs of the cases. This move eliminates functional precision without compromising natural beauty, without breaching the original prescription.
Step 5: Quality Control and Shipping
The cases undergo internal quality inspection that includes fit, occlusion, surface quality, and uniformity of shade. Qualified restorations are then safely packed and shipped through international logistics, which are tracked and delivered through schedules.
Through a designed, systematic workflow process, zirconia outsourcing can be a predictable offloading of the production process of the client that provides stability, dissemination, and dependable turnaround times.
6. Turnaround Time of Outsourcing Businesses
One of the most important factors in the case of outsourcing zirconia crowns and braces is turnaround time, which determines how cases will be scheduled and their timing to be delivered to the clinics. In Chinese dental laboratories under professional settings, turnaround time is controlled by using a structured plan of production as opposed to improvisation on a case-by-case basis.
In the case of the majority of zirconia restorations, the manufacturing process would be 3-5 working days, which includes CAD design, milling, sintering, finishing, and internal quality control. Due to the high level of zirconia workflow digitization, the timelines are usually predictable and less sensitive to the variation in technicians.
The international shipping normally takes 3-7 days, depending on the destination country, the courier, and the customs clearance. This has led to a general turnaround period of 7-10 working days in normal zirconia cases upon receiving the case to delivery.
In the case of larger-volume customers, the established suppliers often introduce windows of production and batching, which further enhances predictability. As much as rush services might be offered in a few cases, steady planning and sensible lead times are the surest mechanism of ensuring seamless workflow in the event of outsourcing of zirconia to China.
7. Pricing Guide of Outsourcing Zirconia
The second most significant aspect of outsourcing zirconia crowns and braces is usually pricing, which is also one of the most misperceived. Zirconia outsourcing prices are not determined by chance, but rather by rational cost considerations due to the complexity of the case, the choice of the material, and the needs of its processing.
Instead of absolute figures, the international clients need to comprehend the primary pricing forces that underlie zirconia outsourcing in China, the determinants of the price of zirconia are core determinants, which include:
- Restoration type: Multi-unit bridges, full-arch restorations, and single crowns vary greatly in terms of design time, milling strategy, and finishing workload.
- Zirconia material category: There are standard zirconia, multilayer zirconia, and high-translucency zirconia that have various materials and processing costs.
- Aesthetic requirements: The monolithic restorations are the ones that are more cost-effective, and the layered zirconia requires more manual labor and quality control.
- Implant involvement: The zirconia restorations that are supported by implants need more refinement and tougher inspection protocols.
In international terms, zirconia outsourcing to China can generally provide a 30-60 cost reduction over local or in-house manufactured products, mostly because of labor productivity and mass production, not because of material trade-off. The long-term customers of the suppliers also have a stable pricing framework and volume structures, which enable the labs to have a consistent margin in the long term.
The knowledge of the structure of pricing can enable the clients to make reasonable judgments on the quotations and not to make judgments on the basis of the lowest price per unit.
8. How to Control the Quality of Zirconia Outsourcing?
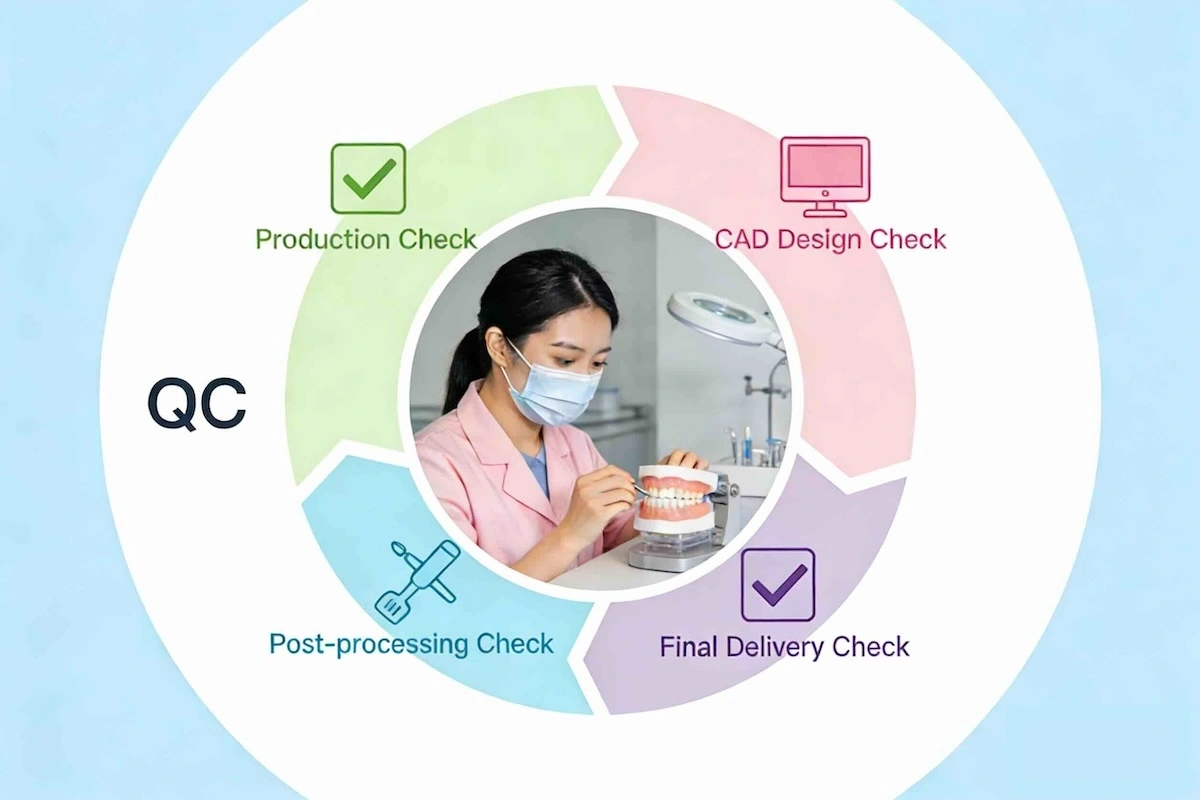
The most decisive element in the zirconia outsourcing is quality control. When dealing with B2B, the quality is not determined by the individual craftsmanship, but by the repeatable systems that identify and rectify the problems before delivery. Chinese dental laboratories with a good reputation do not use a single final check to control the quality of zirconia, but a multi-level system of quality checks.
A professional zirconia QC system is widely used in several main steps:
(1) Design-stage control
Cases are checked concerning clarity of maize, occlusal space, connector size, and material appropriateness before manufacturing commences. Early identification at the CAD phase avoids remakes downstream due to design-related problems.
(2) Production-stage verification
Throughout milling and sintering, the parameters of machine calibration, consistency of batches of materials, and shrinkage compensation are closely observed. This phase provides dimensional accuracy and mechanical reliability in the various cases and production batches.
(3) Post-finishing inspection
Restorations are examined after being stained, glazed, or layered and examined in terms of marginal integrity, proximal contacts, occlusion, surface quality, and shade consistency. Any non-conformance to internal standards instigates correction before shipment.
(4) Last instance correspondence and responsibility
Every restoration would be checked against the original prescription to determine specifications, labelling, and case completeness. This action will make it traceable and also responsible in case there are any problems after delivery.
Remakes and variability are minimized by a considerable percentage by the experienced outsourcing partners by adopting QC as a process, and not a checkpoint. It is this systems-based solution that makes offshore production of zirconia reliable to international clients as an extension of their individual standards in the laboratory.
9. Communication Requirements to Avoid Remakes
Communication gap is another reason why remakes occur in zirconia outsourcing compared to manufacturing defects. Well-organized communication gives the impression that overseas production is in line with clinical and laboratory expectations during the first attempt.
The following are typical communication gaps in the zirconia outsourcing- and how they could be resolved:
(1) Imprecise margin or preparation guidelines
If margin preferences have not been well defined, they are assumed at the design level. Explicitly setting margin instructions or checking auto-detection preferences will reduce remakes due to the fit.
(2) Diffuse occlusal and contact requirements
Such words as light contact or normal occlusion may be taken in different ways. Orders should be more consistent when the functional preferences are specified or the past cases are referred to.
(3) Lack of aesthetic allusions
Aesthetic intent may not necessarily be entirely expressed by shade codes. Subjective interpretation is decreased with the addition of intraoral photographs, reference pictures, or notes on characterization and translucency to the prescription.
(4) Incomplete prescriptions
Absence of information usually results in time wastage or redoing. The use of standardized order forms and compulsory fields makes sure that all the vital information is passed across before a production is made.
(5) Lack of feedback loops
There is no systematic feedback on the cases delivered, and thus, problems are repeated. Frequent reporting and periodic communication assist outsourcing partners in improving the cases to come.
Dental laboratories can make a huge step towards reducing and stabilizing the outsourcing process by turning informal instructions into a repeatable standard.

10. Risks and Mitigation
Like any cross-border manufacturing partnership, zirconia outsourcing is characterized by some risks. Nonetheless, developed dental labs have no intention of removing the risk completely- they are interested in detecting, treating, and containing the risk using premeditated mitigation measures.
| Common Risk | Potential Impact | Mitigation Strategy |
| Miscommunication of case requirements | Fit or aesthetic discrepancies | Standardized prescriptions, reference images, and confirmed design protocols |
| Inconsistent quality across cases | Increased remakes and client dissatisfaction | Multi-stage QC systems and batch consistency controls |
| Turnaround time fluctuations | Disrupted delivery schedules | Fixed production windows and realistic lead-time planning |
| Shipping or customs delays | Extended delivery cycles | Reliable logistics partners and buffer time in scheduling |
| Supplier dependency | Operational risk if issues arise | Trial orders, phased volume increase, and performance reviews |
Once risk is dealt with in a systematic, proactive fashion, zirconia outsourcing would mark a controlled increase of production capacity instead of a weak point. These are not aimed at perfection, but to forecast and take responsibility in the long run.
11. How to Choose the Right Zirconia Outsourcing Partner from China?
The selection of any zirconia outsourcing supplier is not necessary to get the lowest price, but to find an outsourcing partner that can provide consistency in the long term, responsibility, and alignment in operations. The systematic assessment strategy can help the decision-makers not to make superficial comparisons.
In terms of rating possible Chinese suppliers of zirconia, it is important to take into account the following dimensions and their consequences:
(1) Outsourcing experience and profile of clients
Labs that have longer-term clients abroad are more likely to have a more consistent stream of work, more defined responsibilities, and a feel of what to expect in the overseas market. Age is more important than size.
(2) Zirconia production capability
The advantage of the supplier of zirconia having a specific zirconia department as opposed to a generic lab is that it typically shows increased control of materials, consistency of the processes, and consistency of cases.
(3) Workflow transparency
The skills to describe design review, QC procedures, remake management, and turnaround management reflect the process maturity. Transparency usually portrays inner discipline.
(4) Communication structure
A clearly established system with dedicated case coordinators and a clear escalation channel also makes life less frictional and more responsive, particularly when problems are raised.
(5) Remake and responsibility policies
Straight policies on remakes, root cause, and remedial measures are all indicative of a partnership mentality as opposed to transactional selling.
The suppliers like Bestodental that focus on systematic operations, roles, and prolonged collaboration can be characterized as the kind of outsourcing partner that global dental laboratories are to focus on in establishing long term sustainable zirconia production capacity.

12. Who Should Outsource, and Who Should Not?
Zirconia outsourcing does not fit all dental labs or dental clinics. It is less geographically-dependent and rather workflow organization, case volume, and operational attitude-dependent. The key question to answer is whether outsourcing aligns with your business model. Before investing, that is the question you must answer.
1) Who fits Zirconia Outsourcing Well?
Zirconia outsourcing works well in:
- Stable or increasing volumes of cases in dental laboratories, in which scalability and cost management are paramount.
- Labs that experience shortages of technicians or an increase in labor prices, particularly in regular zirconia production.
- Standardized workflow, prescription, and repeat cases in clinics or laboratories.
- Companies that require margins that can be predicted, as opposed to case-by-case improvisation.
In the case of these users, outsourcing is a kind of capacity extension, and it enables the teams of the organisation to concentrate on more valuable or more complex work.
2) Who May Not Be a Good Fit?
Outsourcing is not as appropriate in:
- Small volume (ultra-low) clinics or laboratories where coordination and setup take precedence over cost advantages.
- Workflows that need to be delivered within a day or the next day on an emergency basis.
- Cases of extreme individualization of aesthetics that are strongly dependent on artistry in the chairside or by the technician.
- Any operations that lack standard communication with the expectations that change on a case-by-case basis.
In this case, outsourcing may bring friction instead of efficiency.
In the end, zirconia outsourcing does not concern zirconia substituting local production, but rather the strategic allocation of resources. It is an effective means of consistency, scalability, and long-term growth when it is in harmony with the appropriate operational model.
13. Outsourcing Zirconia FAQs
The outsourcing of zirconia crowns and braces may also create numerous practical issues in regard to dental laboratories and clinics. Although the frameworks and supplier policies create a strong base, the general issues that may come up are case management, quality management, and operational risk. The FAQs presented below will cover the most frequently asked questions by international clients and will gradually go into more detail.
Q1: What should I do to ensure that the outsourced zirconia fits perfectly?
Proper submission of the cases is important. Bite registrations, clear margin instructions, and digital STL files reduce the problems with fit. Good laboratories offer a design preview and in-house QC during milling, which minimizes the chances of making adjustments after delivery.
Q2: What are the things I should not overlook before accepting a design?
Check the clarity of margins, the space of occlusion, and the size of connector of bridges. Affirm aesthetic requirements such as translucency and layering where necessary. Costly remakes can be avoided by early review.
Q3: What can I do to ensure that there is a uniform shade in a variety of cases?
Give sample photos and shade systems. A laboratory of good standing records batch shading and provides reproducibility options similar to prior cases.
Q4: What is the dependence of turnaround time on order complexity?
Single crowns are quicker with a time range of 7-10 working days 7-10 working days, including shipping. Multilayer restoration or bridges are more time-consuming. Massive bulk clients can set up regular production timings to smooth out the delivery schedules.
Q5: What do I do to communicate effectively to prevent the repeat of the mistakes?
There are standardized prescriptions, reference pictures, and account managers that help in keeping things clear. It should be documented that feedback and design approvals are made to set a precedent within cases that have been replicated.
Q6: What are the typical dangers of outsourcing zirconia, and how do they end up being reduced?
Some of the risks are miscommunication, inconsistent QC, and delayed shipment. These measures to mitigate are trial orders, organized QC systems, and dependable logistics. Outsourcing can be made predictable and controllable as a simple extension of your lab in a systematic way.
Q7: What do I do to determine whether a supplier is the right long-term partner?
Find established experience with working abroad, commitment to the zirconia process, open quality control, and obvious remake policy. Assess how responsive they are to communication and integrates into your operational standards.
Q8: Does outsourcing expand with the increase in cases without reducing the quality?
Yes, in case the supplier has organized production planning, multi-stage QC, and digital workflows. Scaling can be applied to those labs that have regular case input and have standardized communication practices.
14. Conclusion
Outsourcing the zirconia crowns and braces to China is no longer an experimental solution, but it is a mature, proven, and strategic solution that dental laboratories and clinics around the world can utilize. Outsourcing can be a solution for cost-effectiveness, quality, and scalable expansion with the correct partner, a well-laid-out workflow, and professional communication. It is not about choosing the lowest supplier, but a long-term manufacturer who has systems, experience, and responsibility. When it is outsourced properly, zirconia is no compromise; it is a competitive advantage.