Temporary restorations are a crucial yet often underestimated aspect of contemporary restorative dentistry. Regardless of the type of implant healing, crown fabrication, or full-arch treatment planning, temporary restorations have a direct impact on patient comfort and aesthetics, as well as on occlusion and clinical outcomes. With the growing globalization of dental procedures and the growing price-conscious nature of these processes, temporary restorations have become a strategic option that many international dental workflows and clinics are considering to outsource, especially to China.
This guide is aimed at offering a comprehensive, practical, and professional guide on how to outsource Chinese temporary restorations. It is authored not only to the readers who are already in the field of the work of the dental professionals, but also to those who are new to outsourcing or those who might be new to the model of dental manufacturing abroad. At the conclusion of this paper, you must have a clear idea of what temporary restorations are, why and how they are outsourced, what the dangers are, and how to choose the appropriate Chinese partner with whom you can work long-term.
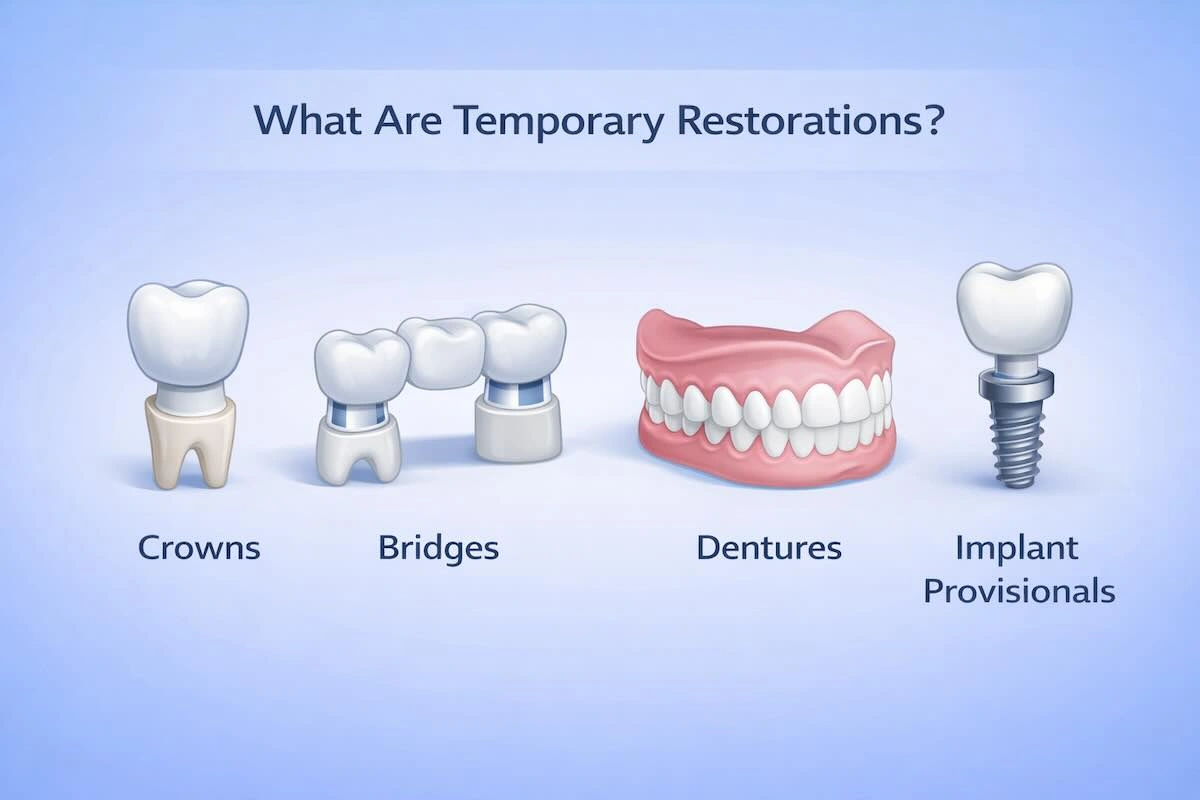
1. What Are Temporary Restorations?
Temporary restorations: These are temporary dental prostheses that are designed to safeguard prepared teeth, implants, or edentulous spaces until permanent restorations are made. Even though they are not designed to be used in the long term, they have a significant functional and clinical role during the process of treatment.
Clinically, temporary restorations save prepared structures’ sensitivity, bacterial exposure, and mechanical damage and preserve tooth position and occlusal relationship. They are also applicable in the guiding soft tissue shaping, assessing esthetics, and testing occlusal schemes, which are to be delivered in the end in implant and full-arch cases.
Popular examples of temporary restorations are temporary crowns and bridges, temporary dentures, implant provisionals, and PMMA full-arch temporaries. The most common materials are PMMA, composite resins, and biocompatible 3D-printed resins, which depend on the workflow and indication.
Simply put, temporary restorations act as placeholders of critical significance. Although temporary, they have a direct impact on the comfort of patients, predictability of their treatment, and final restoration design, which makes accuracy and consistency critical, which, in turn, makes them appropriate to standardized outsourcing.
2. Why Are Temporary Restorations Suitable for Outsourcing?
Not every dental product can be outsourced; however, temporary restorations have some specific attributes that render them quite suitable for offshore manufacturing.
(1) Repeatable, high-volume demand
Temporary crowns, bridges, dentures, and implant provisionals are manufactured on a large scale as routine workflows. This standardization puts a strain on in-house capacity and renders outsourcing a valid method of transforming fixed labor into scalable output.
(2) Standardized technical requirements
Temporary restorations are done with standardized design parameters, materials, and occlusal guidelines as compared to definitive restorations. This enables them to be generated consistently by using digital workflows in controlled processes.
(3) Better distribution of skilled labor
By outsourcing temporaries, local technicians can be involved in more valuable tasks, including final esthetics, complex implant cases, and treatment planning, thereby enhancing overall operational efficiency.
(4) Good fit with electronic processes
Geographic distance is not a very big consideration now that there is intraoral scanning, CAD design, and CAM manufacturing. This is a digital-first character that eliminates numerous traditional obstacles to outsourcing.

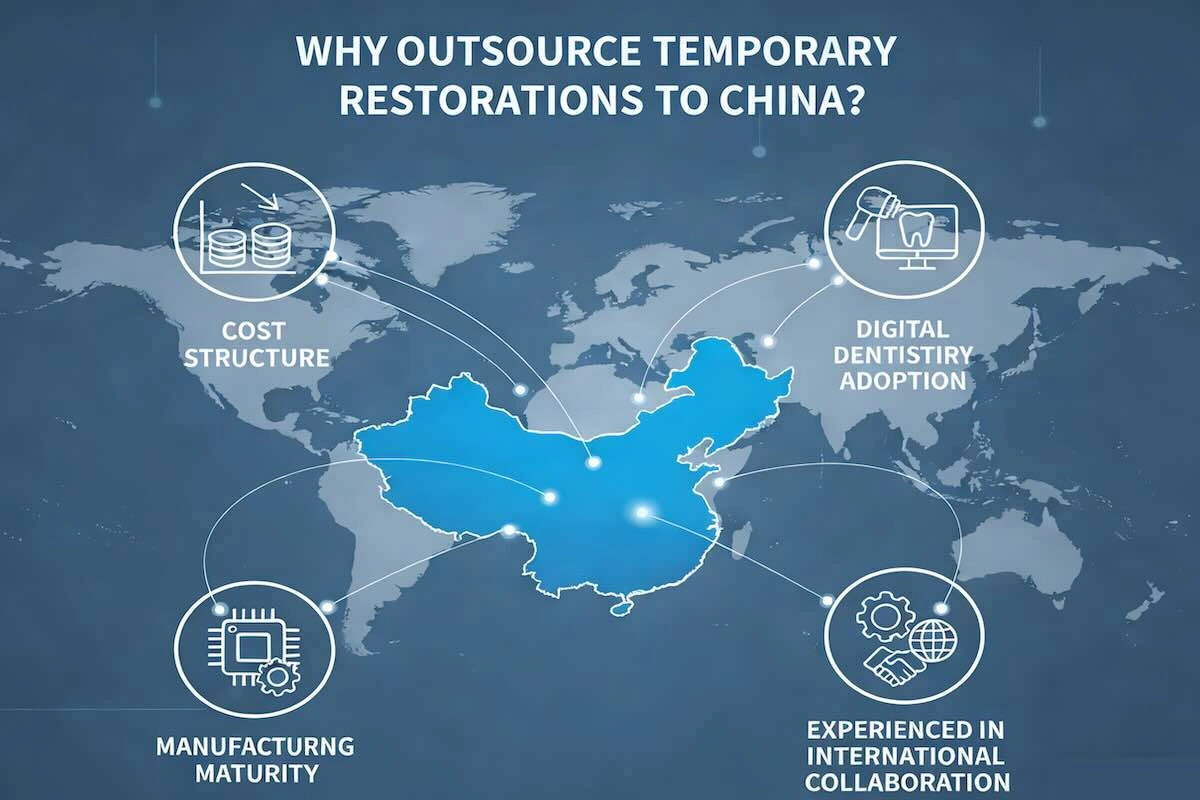
3. Why Outsource Temporary Restorations to China?
China has emerged as one of the major dental manufacturing centres in the world, especially in outsourced temporary restorations.
One of the main forces is cost structure. Competitive prices are offered by Chinese dental labs, which do not compromise on standardized processes or materials, thanks to lower labor costs, mature supply chains, and economies of scale.
Maturity in manufacturing is also important. The dental outsourcing business in China has been built over the decades, and it caters to international markets, offering the best quality systems, CAD/CAM infrastructure, and consistent internal processes in line with the ISO standards.
The Chinese laboratories are also at the forefront of using digital dentistry. The design teams are centralized, the milling and printing are hybridized, and the production schedules are long enough to guarantee a regular turnaround time to the clients overseas.
Lastly, Chinese dental laboratories are accustomed to working with other countries. This is because China is especially suited for outsourcing temporary restorations, whereby speed, consistency, and cost control are paramount, as one is familiar with overseas clinical standards, documentation requirements, and communication practices.
4. What Can Be Outsourced—and What Cannot?
The scope of outsourcing is a key to developing trust and preventing misunderstandings in cross-border dental cooperation. In the case of international clinics and laboratories, a clear scope can be used to overcome unrealistic expectations, avoid unnecessary remakes, and enable overseas partners to work within well-defined technical constraints.
1) What Can Be Outsourced
The majority of Chinese dental laboratories are reliable in outsourcing:
- Temporary braces and crowns (PMMA or resin)
- Partial or complete temporary dentures
- Implant temporary restorations
- All-on-X PMMA full-arch temporaries
- Wax-ups and mock-ups diagnostic
- Prosthetic treatment planning with try-in
These items are normally manufactured by means of electronic documents, standardized materials, and replicable processes. Temporary crowns, bridges, and dentures are designed and fabricated based on established design and manufacturing specifications, and therefore, their installation and operation are predictable. Both implant provisionals and full-arch PMMA temporaries depend on digital planning and CAD/CAM production, both of which are done on a large scale by Chinese labs. Non-final restorations Diagnostic wax-ups, mock-ups, and try-ins are mainly used in planning and verification and thus are especially appropriate in offshore manufacturing, where consistency and efficiency are of higher importance.
2) What Should Not Be Outsourced
The outsourcing is less appropriate in the following scenarios:
- Chairside emergency temporaries that need to be delivered on the same day
- Cases that have poor or missing scan data
- Very experimental or unconventional provisional designs
- The cases of inevitable clinical adjustment
Chairside emergencies involve fabrication at the moment and are not able to suit the international production and shipping schedule. Unfinished or erroneous scan data exposes cases to a higher risk of misfit in situations where the cases are generated remotely. Provisional designs that are highly customized or experimental in nature usually demand close and real-time cooperation, which will be better managed locally. Similarly, cases that are supposed to be heavily changed in the chairside will be less efficient in the case of outsourcing.
Through a well-established understanding of what is and is not covered in the scope of outsourcing, the clients and Chinese dental laboratories will be able to manage their expectations, minimize friction in the operation, and create a more consistent and professional outsourcing relationship.
5. Step-by-Step Workflow for Outsourcing Temporary Restorations
The most important aspect of outsourcing temporary restorations is the presence of a well-defined workflow. It not only dictates efficiency, but also predictability, quality control, and accountability. A professional workflow in outsourcing must minimize uncertainty in all the steps and provide clinics and labs with a feeling of control over the process.
Step 1: Submission of Cases and Data Preparation
The process begins with the orderly submission of cases. The clients submit intraoral scans, bite records, prescription and specific notes about the occlusion, retention, or treatment purpose. At this stage, it is required that the scan data and the written instructions are of high quality because this is what directly affects the design accuracy and minimizes the revisions downstream.
Step 2: Online Design and Case Review
According to the presented data, the Chinese lab designed a CAD of the temporary restoration. In the case of implant provisionals and full-arch temporaries, a thorough design check is usually done internally, and screenshots or previews can be given to confirm. This stage acts as a control point to fit the expectations before the commencement of production.
Step 3: Approval of design and manufacturing authorization
Only when design approval or confirmation is made, production is done. Depending on the type of restoration, it could be manufactured either with PMMA milling, resin 3D printing, or with hybrid processes including manual finishing. Unambiguous approval of this phase will help avoid unnecessary remakes and create the limits of responsibility.
Step 4: Production and Internal Quality Control
The temporary restorations are then checked internally after they are manufactured. These are usually margin checking, occlusal checking, surface checking, and visual defect checking. In the case of implants, the connection accuracy and seating stability are also considered in order to provide functional reliability.
Step 5: Packaging, Shipping, and Feedback Loop
On successful quality control, the restorations are neatly packaged in protective materials, clearly labeled, and sent. Professional outsourcing partners frequently promote post delivery feedback, which they use to correct future designs and enhance long term consistency instead of perceiving each case as a one-off transaction.
This workflow stepwise process converts outsourcing as a cost-based decision to a regulated production mechanism that is crucial in sustainable B2B relationships in dental outsourcing.

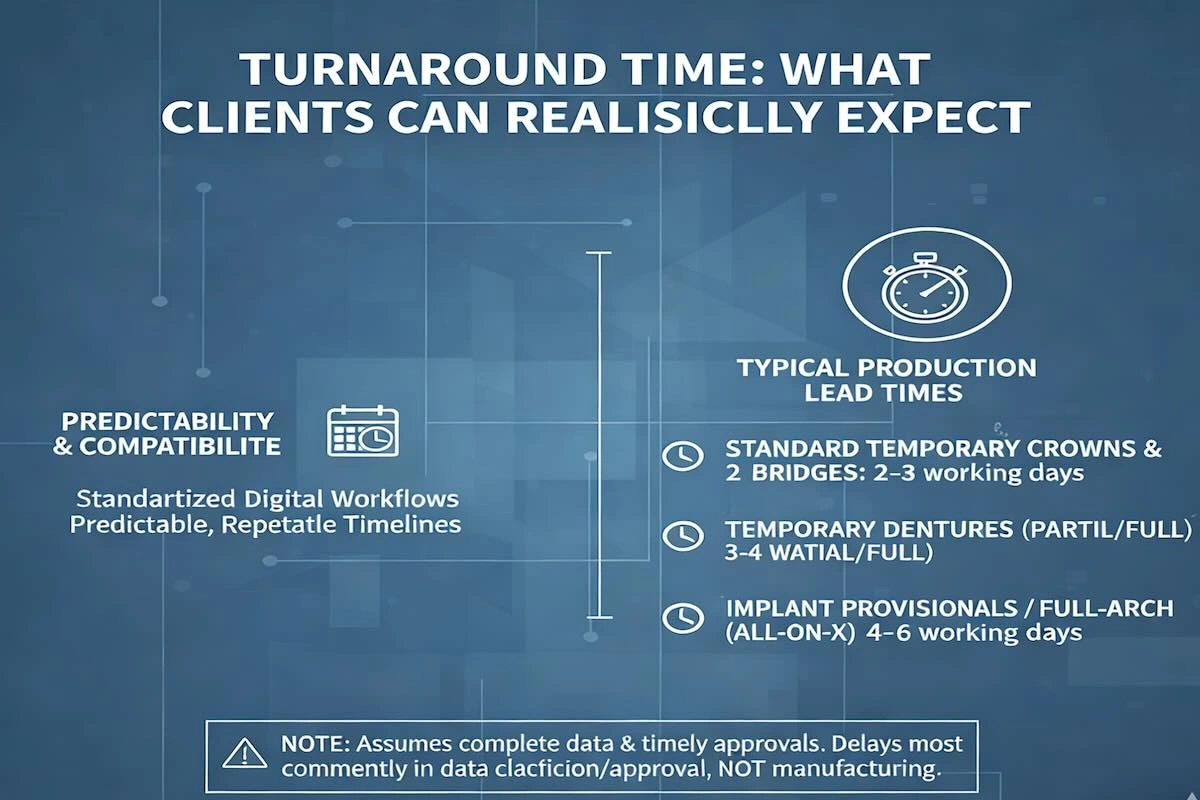
6. Turnaround Time: What Clients Can Realistically Expect
The most important and common question that most clinics and dental laboratories ask themselves when thinking of outsourcing overseas is turnaround time. Practically speaking, clients not only care about the speed of a case but also want to know whether the schedule can be repeated, predicted, and fit within their clinical schedules.
In the case of temporary restorations that are outsourced to China, production schedules tend to be consistent, owing to the fact that these are products that have a standardized workflow in digital form. In normal operations, the normal lead times of production are:
- Normal provisional crowns and braces: 2–3 working days
- Partial or full temporary dentures: 3–4 working days
- Implant provisionals or full-arch temporaries (All-on-X): 4–6 working days
These schedules are specifically lab production schedules and presuppose full scan data, clear prescriptions, and timely design confirmation. Delays are most often not in the manufacturing, but are found during data clarification or approval phases.
Shipping time is another variable that is relatively fixed. Through international express couriers, delivery normally takes 3-7 days, which will depend on the destination country, customs clearance, and local logistics efficiency. Shipping cannot be completely avoided, but once the routing is determined, it is very predictable.
In business terms, the opportunity offered by outsourcing does not lie in the fact that outsourcing is quicker than local production, but in the fact that it is more scalable and simpler to plan. Combined production and shipping schedules can be incorporated into the treatment planning with a high rate of reliability when the submission of cases in batches and the standardization of workflows are involved.
7. Pricing Guide: Understanding Cost Structures Without Oversimplification
One of the most talked about–and least understood–of outsourcing temporary restorations is pricing. Most buyers are concerned with the unit price comparison, and not paying much attention to the overall cost structure that will eventually reveal whether outsourcing is able to generate actual business value.
Practically, the price of the outsourced temporary restorations is determined by more than one variable instead of being fixed at one price. The following table summarizes the key cost drivers and their common effect on prices:
| Cost Factor | Impact on Price | Practical Explanation |
| Material type | Low to Medium | Standard PMMA temporaries are generally the most cost-effective, while reinforced resin or implant-supported provisionals involve higher material and processing costs. |
| Case complexity | Medium | Simple single-unit temporaries require minimal design time, whereas multi-unit or occlusally sensitive cases increase CAD effort and QC workload. |
| Restoration type | Medium to High | Full-arch temporaries and implant provisionals require additional design validation and manufacturing steps compared to standard crowns or bridges. |
| Order volume | High (cost-reducing) | Consistent batch submissions allow labs to optimize production scheduling, resulting in lower per-unit pricing. |
| Remake rate | Indirect but critical | Lower remake rates reduce hidden costs related to rework, delays, and clinical disruption. |
In the majority of professional Chinese dental laboratories, clear, level pricing schemes are used, where the unit price falls as the volume levels off. Nonetheless, sophisticated customers consider price contextually. A moderately increased unit price combined with stable delivery, low remake rates, and effective communication can easily lead to a lower total cost of ownership compared to the lowest cost available choice.
In the business dimension, pricing analysis is not only cost-effective but also involves predictability, scalability, and efficiency.

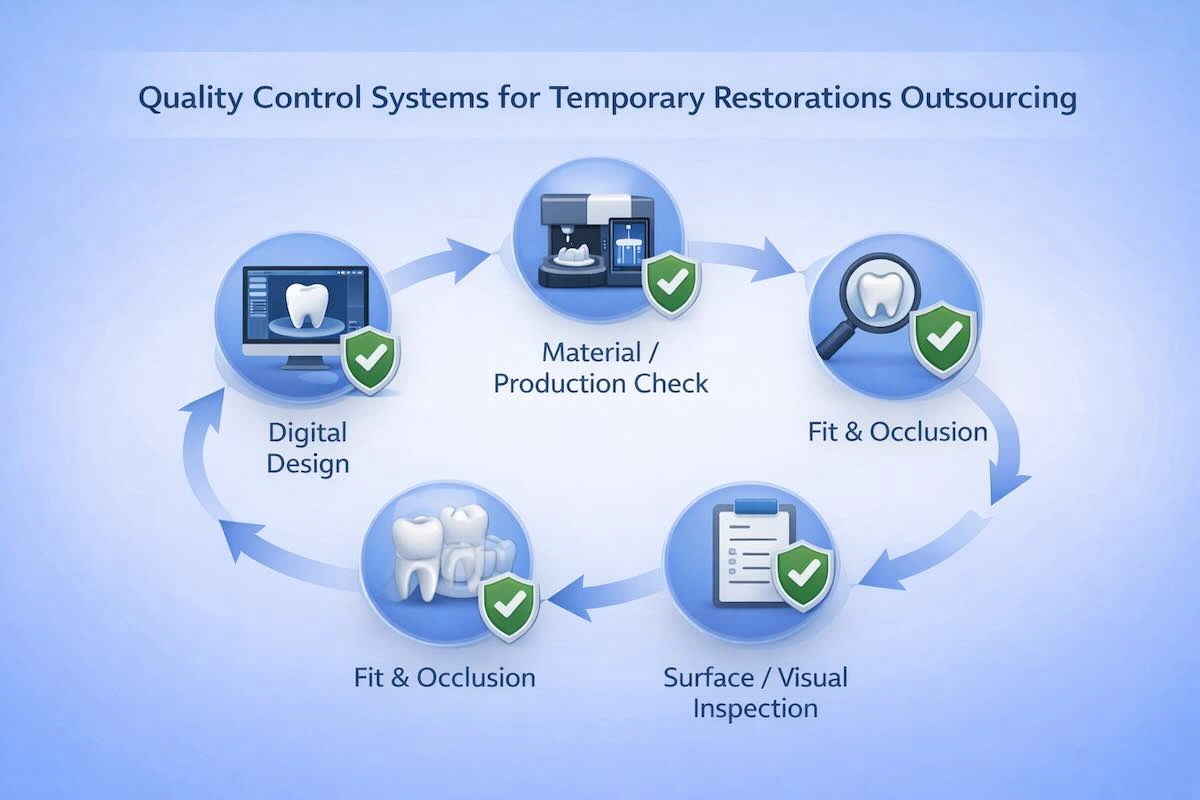
8. Quality Control Systems: What Actually Protects Your Cases
The secret of good dental outsourcing, especially temporary restorations, is quality control, as they should operate effectively despite their provisional nature.
Multi-layer QC systems are used in professional Chinese dental laboratories that aim at identifying errors at the initial stages and achieving consistency in high volumes. A strong QC system is usually characterized by the following:
- Digital Design Validation: CAD designs are checked to make sure that margins, occlusion, and restoration contours are according to the prescription requirements before being produced.
- Material and Manufacturing Checks: Technicians check the integrity of the materials, structural thickness, and production parameters during milling or printing to ensure that it does not deform or have internal defects.
- Post-Production Fit and Occlusion Inspection: The finished restorations are examined for marginal integrity, occlusal accuracy, and stability of seating. Connection and interface verification is also done on the implant provisionals.
- Surface and Visual Quality Review: Smoothness of surfaces, finishing of edges, and apparent defects are examined to check the restorations against functional and handling requirements.
- Independent QC Responsibility: Most of the established labs do not mix the QC tasks with the production technicians, and this minimizes bias and enhances objectivity.
- Documentation and Traceability: Some labs include photographic documentation or digital checkpoints, where cases can be re-examined retrospectively in case of problems.
These QC systems do not aim at eradicating all errors but bring about variability in a systematic manner. In the long term, the regular QC is directly converted to fewer remakes, more predictable workflows, and more effective long-term relationships.
9. Communication Requirements to Avoid Remakes and Delays
The best way of minimizing remakes in outsourced temporary restorations is through clear communication, which is manageable.
At the client-side, structured input is needed. Full prescriptions, proper bite records, and instructions on the use, retention, and intended use of the occlusion assist in getting rid of assumptions in the design stage. In the case of implant temporaries, specifications regarding implant systems and connections should be well defined in order to prevent positional or seating mistakes.
On the laboratory side, professional partners are engaged in actively reviewing the incoming data, finding ambiguities early, and clarifying them before production. Design approvals or previews are design validation checkpoints to make sure that the design aligns prior to the manufacturing process.
On the process level, effective outsourcing considers communication as a formal workflow but not informal messaging. Defined submission criteria, contacts, and documented processes of approvals assist in establishing the limits of responsibility. With structured and proactive communication, remakes are reduced, schedules become more predictable, and teamwork becomes more effective.
10. Risks and Mitigation Strategies
There is also inherent risk in outsourcing temporary restorations, yet they can be managed in a systematic way by designing processes and taking the initiative to manage them. Knowledge of these risks and mitigation measures will enable clinics to outsource with ease.
| Risk | Cause | Mitigation Strategy |
| Data misinterpretation | Incomplete or unclear scans, bite records, or prescriptions | Use standardized submission templates, provide reference images, and confirm design previews before production |
| Occlusal discrepancies | Inaccurate bite registration or design errors | Pilot cases for new patients or complex occlusion, digital design verification, and post-production QC checks |
| Delayed feedback | Slow communication between the clinic and the lab | Assign designated communication contacts, set clear timelines for approvals, and use structured messaging platforms |
| Material or production defects | Inconsistent manufacturing parameters or manual finishing errors | Multi-stage QC, documented verification, and traceable batch records |
Professional outsourcing does not imply the removal of the risk, but rather, it involves the control of the risk in a predictable manner. Structured data submission, pilot cases, QC protocols, and effective communication channels will reduce remakes, delays, and clinical disruption in clinics.

11. How to Choose the Right Supplier?
Choosing a good Chinese dental lab is very important, and it is more than just a matter of finding the lowest price. Take into consideration the following criteria:
- Practice with foreign clients: Labs that have been exposed to international clinical standards and documentation are more reliable when it comes to providing uniform output.
- Digital design: Sophisticated CAD/CAM, 3D printing, and design verification enhance precision and minimize remakes.
- Quality control systems: Multi-stage QC, such as design review, production checks, and final inspection, can be used to guarantee functional and aesthetic consistency.
- Communication responsiveness: The laboratories that actively seek clarification, offer a preview of designs, and appoint English-speaking coordinators minimize the risk of miscommunication.
- Transparency and process visibility: Labs will have to be open to begin with trial cases, provide progress updates, and promise a foreseeable turnaround time.
The long-term outsourcing partners, such as Bestodental, present themselves as suppliers of stable workflows, scalable production, and predictable quality of temporary restorations, and not short-term contractors.
12. Who Should Outsource—and Who Should Not?
The temporary restorations can be outsourced specifically to clinics and laboratories that:
- Process large amounts of provisional cases, which takes off the load on in-house resources.
- Pursue cost management without quality and exploit offshore competitive prices.
- Run digital workflows, which facilitate smooth remote teamwork.
- Target to increase operations without increasing fixed labor expenses.
Nonetheless, outsourcing might not be an option when the clinic needs immediate solutions using the chairside, since the international production/shipping schedule does not allow for delivering solutions on the same day. The latter is also inapplicable to clinics that do not want to streamline workflows or ensure consistent delivery of precise digital information, as inconsistencies in submissions, missing scans, and ambiguous prescriptions are the main factors that complicate the process of misfits, remakes, and delays.
With a keen analysis of the compatibility of their operational requirements and type of cases with outsourcing services, the clinics and laboratories can make professional and informed decisions that maximize their efficiency, quality, and maximize the full use of the benefits of offshore temporary restoration production.
13. Outsourcing Temporary Restorations FAQs
The following are the frequently asked questions that dentists usually pose when they decide to outsource temporary restorations to a Chinese lab.
Q1: Is it possible to have clinical accuracy with outsourced temporaries?
Yes. Using high-quality intraoral scans, accurate bite records, and systematic review of design, the fit and occlusion of temporary dentures outsourced to an external vendor are comparable to those produced locally.
Q2: Do small volume orders work?
The majority of professional Chinese labs take low-volume trial cases as well as high-volume production, and it is simple to test the process before scaling.
Q3: How are remakes handled?
Laboratories of good reputation have well-defined remake policies that ensure responsibility, which assures accountability and minimal disturbance of workflow.
Q4: Is it a barrier of language/communication?
No. Established laboratories offer formal communication channels, English-speaking contact persons, and design previews, which do not help to remove misunderstandings.
Q5: How promptly can corrections or feedback be included?
Labs can effectively use digital-first workflows and pre-defined approval channels to make corrections, which usually take 1-2 working days to complete based on the complexity of the cases.
Q6: Do implant or full-arch temporaries represent a higher risk to outsource?
Slightly, due to complexity. Pilot cases, accurate scan data, and special QC checkpoints are all part of mitigation. With proper preparation, experienced laboratories are able to deal with such cases reliably.
These are practical questions that are relevant to actual business issues, and therefore, the clinics will have a working guideline on how to determine whether outsourcing is safe, practical, and predictable.
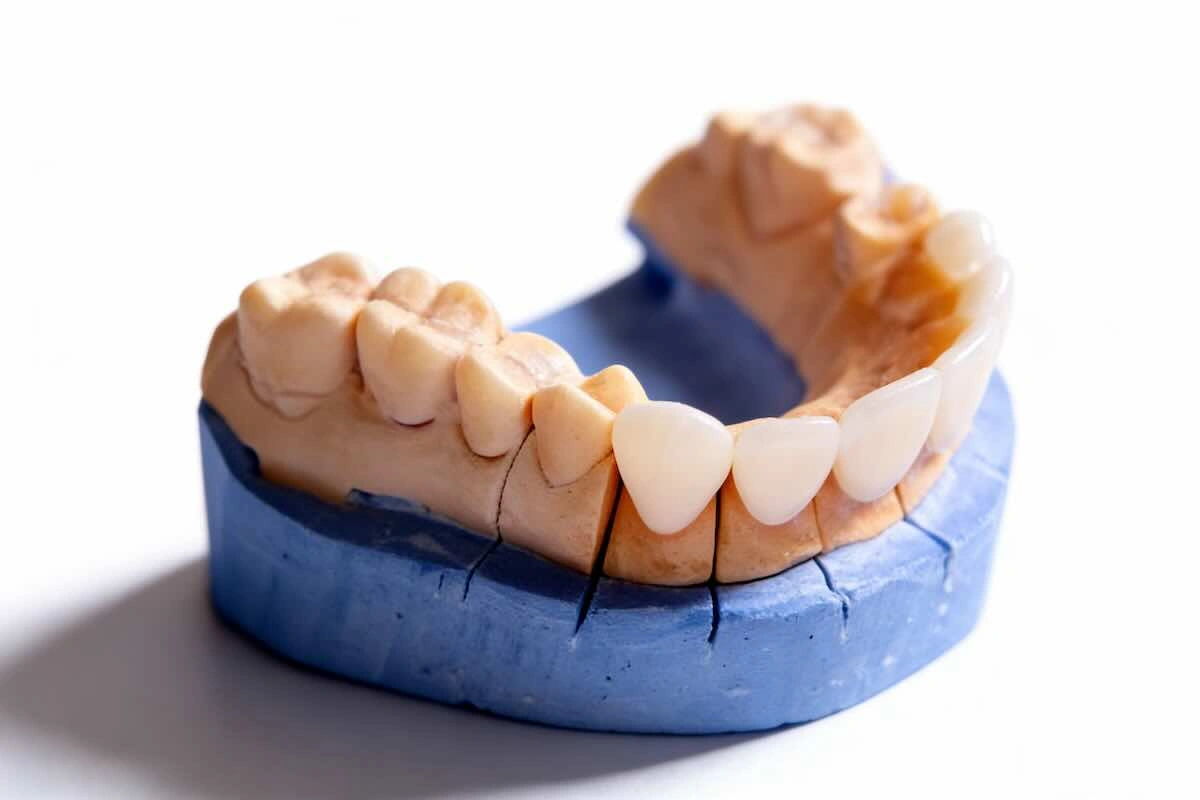
14. Conclusion
Temporary restorations can offer cost-effectiveness, predictable turnaround, and scalable capacity to clinics and labs with high volumes or operating digital workflows by outsourcing such work to Chinese dental laboratories with more experience. With systematic working processes, delivering full case information, and cooperating with partners using a strong QC model and open communication, outsourcing can be considered a valid continuation of internal business, and not a threat.
It is essential to select an appropriate partner. Incumbents such as Bestodental offer high quality and efficiency, as well as full-service packages such as pilot cases and process instructions. To have a leaner production of temporary restorations and a high level of clinical work, laboratories and clinics should contact Bestodental and get started on the path to a smoother operation and fewer remakes.