With the ever-optimization of the restorative processes in global dental laboratories and clinics, outsourcing has become not an experiment of cost reduction but a strategy, a practice. Post and Core restorations are among the most developed and widely used categories of restorative elements, which have been outsourced to dental professionals in recent years. Their technical features, mass production of the fabrication, and the predictability of the clinical performance precondition their idealization as partners of international cooperation, especially Russian-Chinese dental laboratories.
This guide is intended to be read by dental lab owners, managers of production, clinicians, and those who make decisions about purchasing, who are interested in having a clear, realistic, and professional idea of Post and Core outsourcing. Instead of presenting shallow selling points, this article clarifies the nature of Post and Core restorations, the reasons why outsourcing would be a good idea, the way outsourcing to China would work, the location of the risks, and the way they can be addressed in a controlled fashion. It is not just about education, but confidence in decisions.
1. What Are Post and Core Restorations?
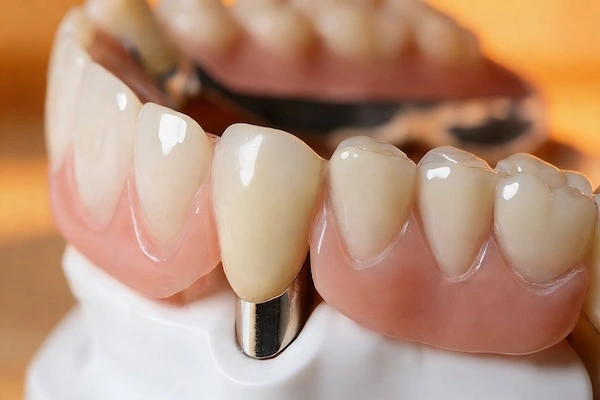
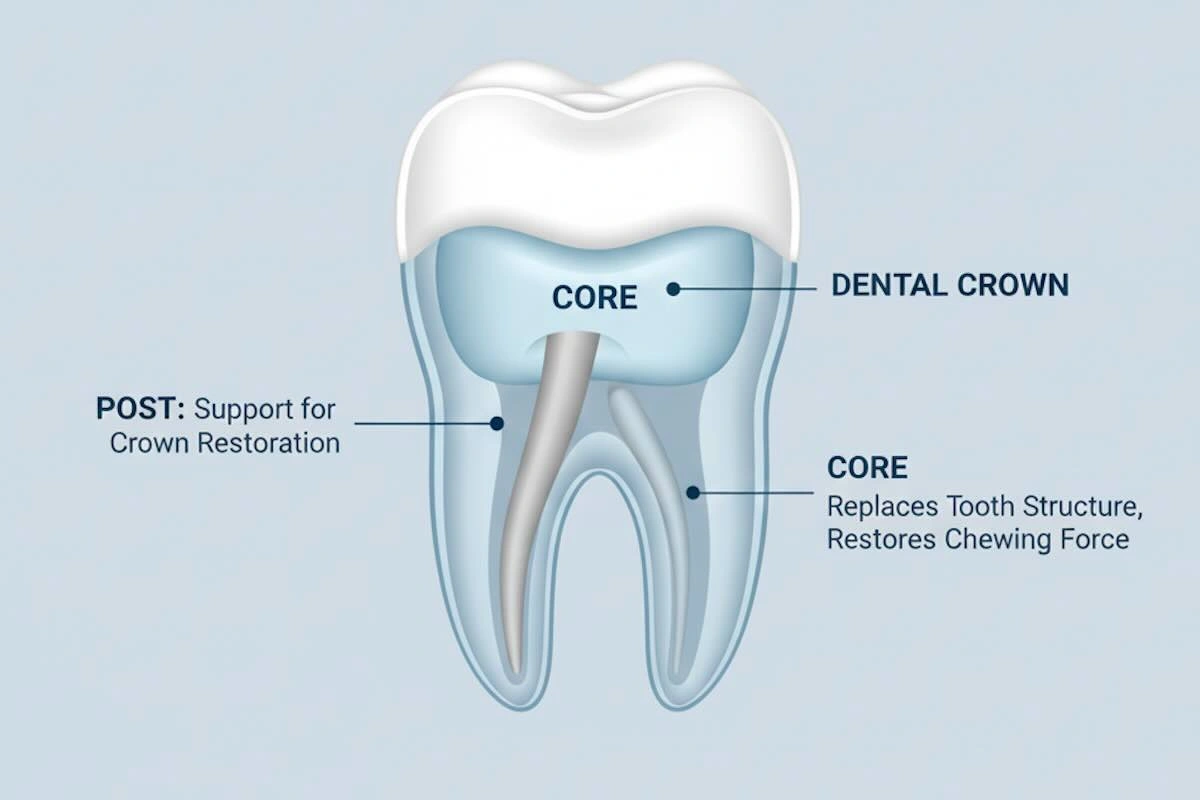
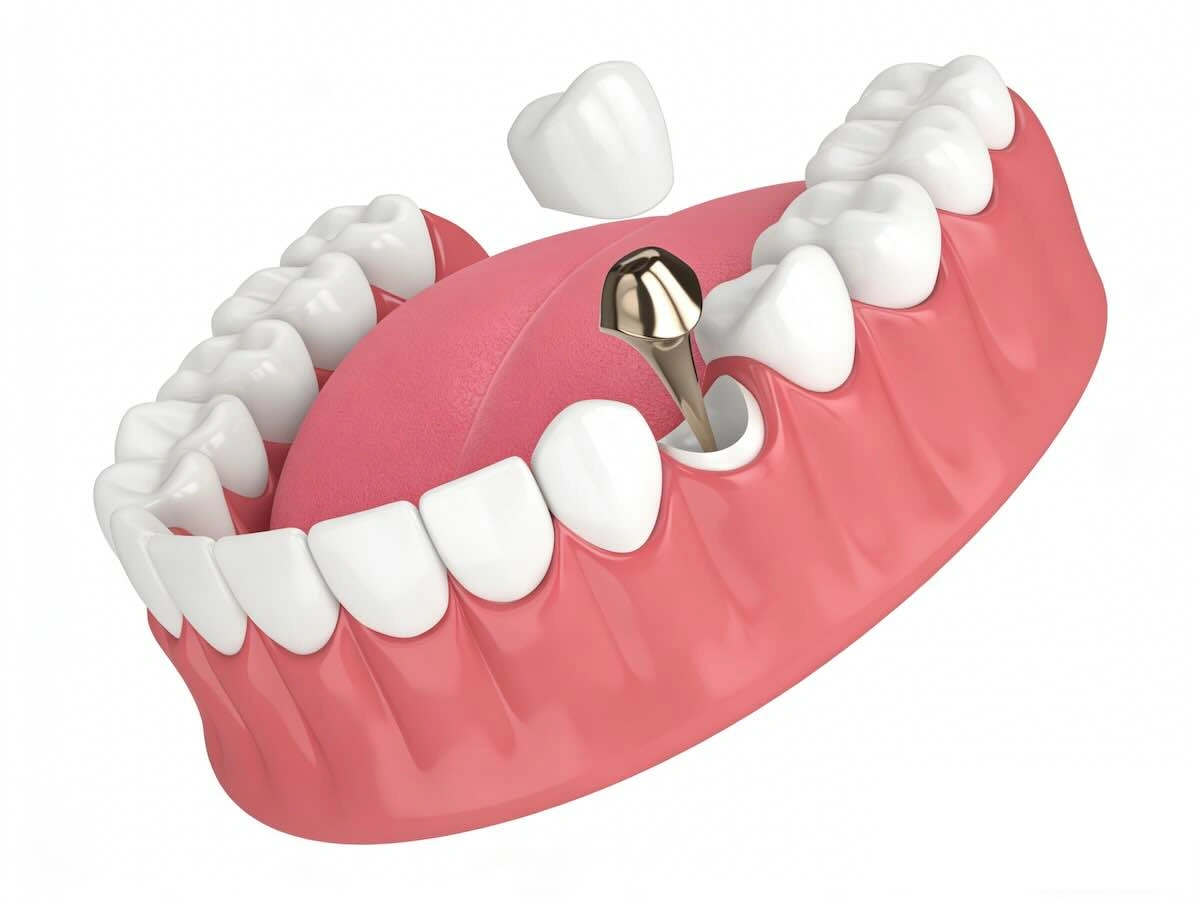
A Post and Core restoration is a restorative therapy that is applied in situations where the natural structure of a tooth has been lost in large amounts, most often after root canal therapy. A Post and Core is developed to rebuild the internal support, unlike crowns or veneers that focus on restoring the appearance of a tooth, which makes the tooth have enough retention and stability in the long term.
Structurally, a Post and Core is composed of two functional components that meet various mechanical needs in the same restoration:
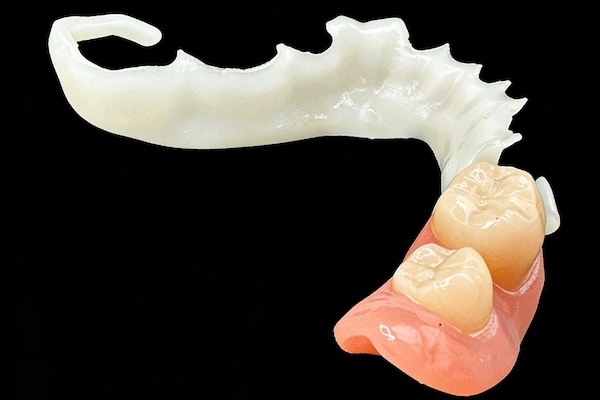
- Post – is placed into the prepared root canal, and it gives internal retention to the restoration by holding it in the root. Its adaptation, length, and diameter have a direct relationship with stress distribution and fracture resistance.
- Core – placed above the post, the core fills in lost coronal tooth structure and restores the correct geometry required to prepare and place the crown.
The roles of these components are different, although they are usually made as a unit. The post fixes the restoration in place in the root, and the core forms and gives a sound base to the final crown.
Post and Core restorations are clinically suggested when the remaining tooth structure is not sufficient to support a crown on its own, and long-term management of loads is of importance. They are not primarily used for aesthetics, but for mechanical integrity, retention, and durability.
2. Metal vs. Zirconia Post and Core: Understanding the Materials
Post and Core restorations are now usually made out of either metal alloys or zirconia. All materials possess unique features, signs, and constraints, which directly affect outsourcing decisions.
The clinical history of Metal Post and Core restorations is long and is still popular, especially in the posterior areas. Cast metal posts: Cast metal posts are usually cobalt-chromium or some dental alloy that is very strong, predictable when under load, and very tough to fracture. Due to the accuracy with which metal can be cast to fit the canal anatomy, it is especially applicable to irregular or flared canals. From a laboratory perspective, metal Post and Core fabrication is very standardized and therefore fits well in an outsourcing environment.
A more recent development is the Zirconia Post and Core restorations, with esthetic requirements and material biocompatibility being the main forces behind its creation. The tooth-like appearance of zirconia eradicates the possibility of dark shadowing underneath all-ceramic crowns, which is especially significant in the dental restorations of the anterior. Also, the corrosive property and positive reaction of zirconia on tissues have become an appealing alternative to most clinicians. Zirconia is, however, not as forgiving when it comes to canal adaptation, and it needs accurate digital design and milling.
It is very important to understand such material differences, since the success of outsourcing is not about defaulting to the latest or the most cost-effective material to use, but rather about choosing the appropriate one to make the appropriate indication.
3. Why Post and Core Restorations Are Well-Suited for Outsourcing?
Dental restorations cannot be outsourced to all. However, post and core restorations have a number of intrinsic features that render them especially suitable for external production.
To begin with, the Post and Core fabrication is a very standardized technical process. As soon as the clinical parameters are properly defined, including the canal depth, taper, and material selection, the process of production is guided by a foreseeable workflow. In contrast to the highly aesthetic restorations where subjective interpretation of shade is necessary or artistic layering that must be applied, the Post and Core restorations use precision, repeatability, and engineering accuracy.
Second, Post and Core restoration fabrication does not involve any real-time chairside communication. All the crucial clinical decisions are taken in advance of the commencement of production, and the laboratory is left to operate independently without interfering with the clinical schedules. This division of clinical treatment and technical fabrication is one of the essential preconditions of successful outsourcing.
Lastly, operationally, the Post and Core restorations are usually non-differentiating products that dental labs need. They are crucial to repair processes, but do not generally determine the brand or competitive edge of a lab. The outsourcing of such cases enables in-house technicians to concentrate on work with higher value, like the implant restorations, full-arch cases, or the more complicated esthetic ceramics.
4. Why China Has Become the Primary Destination for Post and Core Outsourcing?
Lower pricing is no longer the only reason that drives outsourcing of Post and Core fabrication to China. The Chinese have established a very sophisticated dental production ecosystem over the last twenty years, which promotes large scale production on export-based production for export. This structural maturity, and not any given advantage, is the reason why China has become the main outsourcing destination of global dental labs and clinics.
(1) Integrated Dental Manufacturing Ecosystem
The dental industry in China is closely coordinated in a supply chain, with CAD design, material sourcing, CAM production, finishing, and quality inspection. In the case of Post and Core, this integration minimizes differences in design intent and final output, particularly in handling non-standard preparations or complicated canal anatomies. The outcome is increased consistency when dealing with large volumes of cases.
(2) Scaled Adoption of Digital Dentistry
Major Chinese dental laboratories have completely embraced digital processes that are founded on STL submission, CAD-based post-and-core design, and standardized CAM procedures. This enables foreign partners to consult, make corrections, and accept cases without a lot of friction. Digital workflows are applied at a large scale, where accuracy is not compromised even in a large volume outsourcing case.
(3) Export-Focused Experience with International Standards
Most of the Chinese dental laboratories are well established with a history of serving the North American, European, and Australian markets. Specific international teams understand the format of prescription, the expectation of communication, and the quality standards of the overseas market. This minimises the number of clarifications and minimises the risk of remake in Post and Core outsourcing.
(4) Cost Efficiency Supporting Process Stability
Although cost efficiency is also applicable, it is actually operational stability that is valuable. The reduced production cost enables capable Chinese laboratories to invest in multi-stage quality control, backup, and standard process management. This, when done well, will lead to scalable and sustainable outsourcing and not mere reduction of costs.
5. Defining the Scope: What Can and Cannot Be Outsourced?
Not every Post and Core case is the best suited to be outsourced, and this difference is the key to quality and predictability. Practically, the success of outsourcing depends not as much on the simplicity or complexity of a case, but rather upon its own clarity, standardization, and predictability in the clinical context. Setting these limits at the start will enable dental laboratories and clinics to prevent unjustified remakes and mismatched expectations.
The following table identifies the type of Post and Core cases that can be typically outsourced- and more to the point, it will explain why some cases are not in the optimal fit.
| Case Type | Outsourcing Suitability | Reason |
| Cast metal Post and Core | Suitable | Mature fabrication process, high tolerance for canal variation |
| CAD/CAM zirconia Post and Core | Suitable | Digital design allows precise control when input data is complete |
| Single-unit, well-defined cases | Suitable | Predictable geometry and limited variables |
| STL-based digital submissions | Highly suitable | Reduces interpretation errors and improves consistency |
| Same-day or emergency cases | Not suitable | International logistics cannot support an immediate turnaround |
| Cases with incomplete clinical data | Not suitable | Missing canal depth or margins increases remake risk |
| Highly experimental designs | Not suitable | Lack of standardization undermines process control |
| Chairside-adjustment–dependent cases | Not suitable | Requires real-time clinical feedback |
How to Use These Boundaries in Practice:
These boundaries do not mean that outsourcing is restricted, but are manifestations of the control of the professional process. In the event of the cases being chosen on the basis of clarity and predictability, the outsourced dental lab is a trusted extension of the dental lab instead of a source of uncertainty. On the other hand, trying to outsource situations that are based on real-time decision-making or incomplete information renders the risk of trying to unnecessarily undermining the benefits of international cooperation.
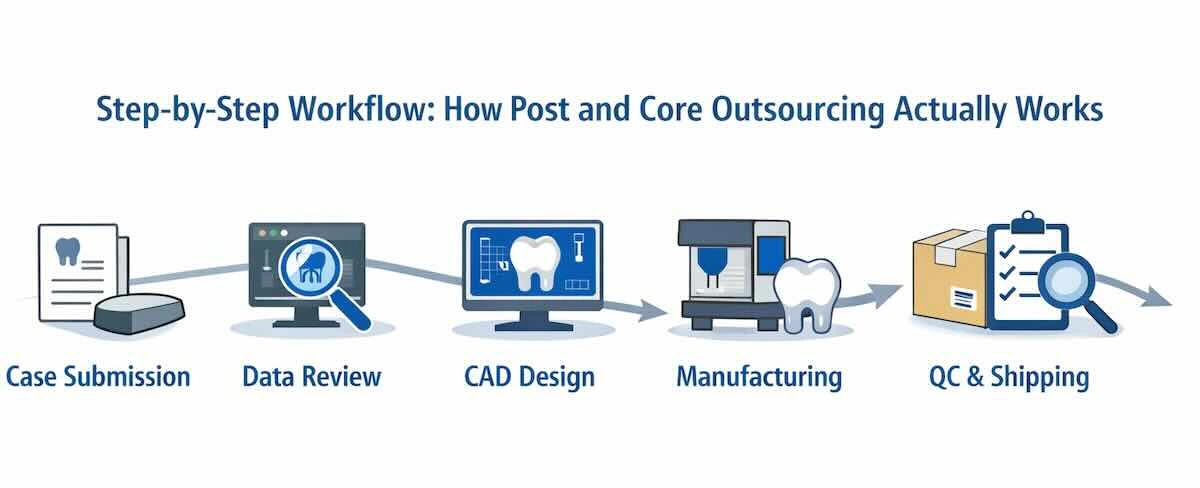
6. Step-by-Step Workflow: How Post and Core Outsourcing Actually Works?
The foundation of a good outsourcing relationship is a clear and consistent working process. Although the specifics of operations might differ across laboratories, professional Post and Core outsourcing tends to be standardized to achieve consistency, traceability, and clinical predictability.
Step 1: Case Submission
The process starts with the submission of the case by the clinic or partner laboratory. The cases can be presented in the form of physical impressions or digital scans with a specific prescription. Material selection, canal depth, post length, and any other considerations regarding the restoration that may affect the final design should be clearly stated in the prescription.
Step 2: Review of the Data and Feasibility Check
Data review on the lab side after receipt is done to ensure completeness and clinical practicability. This process aids in determining the missing information, ambiguous instructions, or anatomical constraints before the design work, which minimizes the need for remodeling or redesigns in the downstream.
Step 3: CAD Design and Alignment Planning
The Post and Core are designed by qualified CAD technicians using dental-specific CAD software. The design aims at precise adaptation of the canals, correct angulation of the posts, and alignment to the intended final crown. Design preview is provided to the client to be reviewed or confirmed before manufacturing in most of the professional workflows.
Step 4: Production and Material-Certain Processing
The production is material protocol-based. Metal Post and Core restorations are cast and finished, whereas zirconia restorations are milled, sintered, and refined. The process consistency is presented by documenting and tracking every production stage.
Step 5: Packaging, Quality Control, and Shipping
The completed restoration is inspected before being shipped to ensure that it fits, finishes, and is in compliance with the prescription. The approved cases are then well packaged and ready to be shipped internationally. This organized process gives the customers predictability and control of operations, even in the case that production is done in another country.
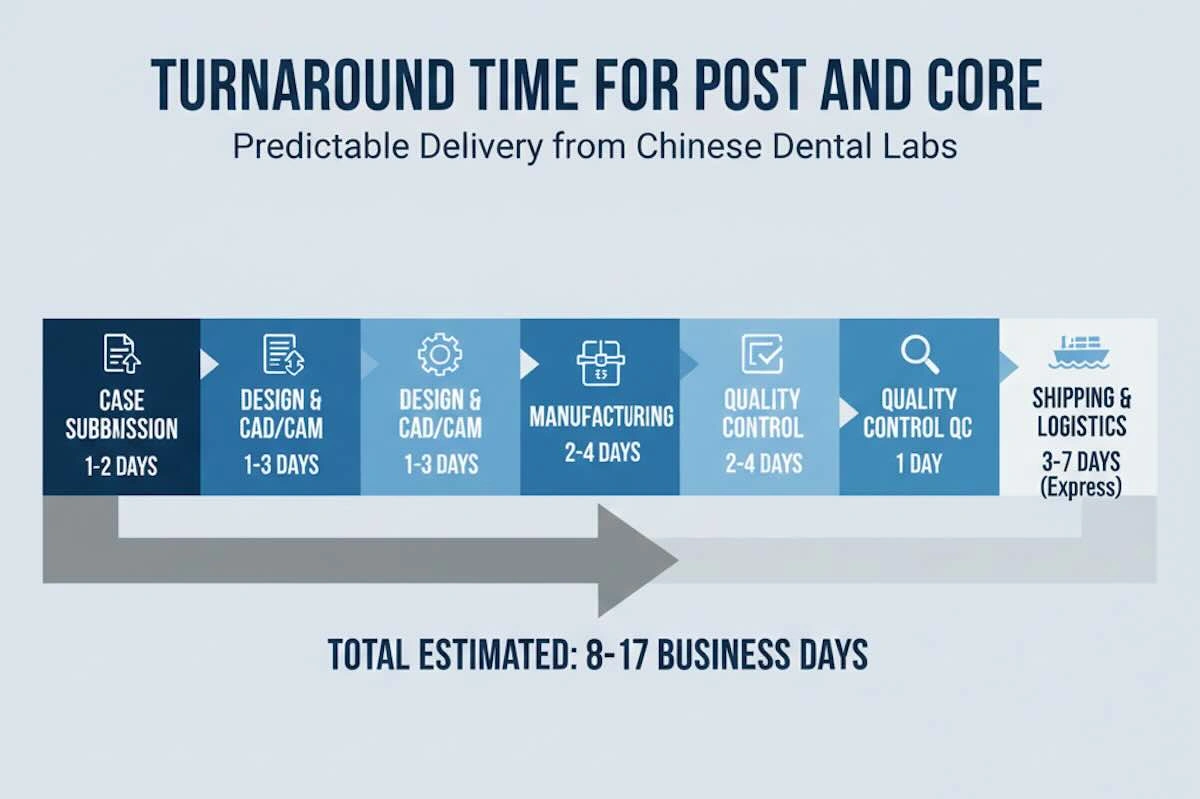
7. Turnaround Time: What International Clients Should Really Expect?
The first operational issue that can be brought to the table by foreign dental laboratories and clinics deciding whether to outsource Post and Core restorations is turnaround time. Speed is a factor, but mature purchasers know that predictability and consistency are much more valuable than headline turnaround promises. Both production and logistics should be treated as a single process, and therefore, a realistic discussion of the delivery timelines should exist.
The manufacturing process of the Post and Core restorations in the professional dental laboratories in China is very streamlined. After case data is verified and accepted, it is common practice in metal Post and Core cases to take between two and three working days to cast, finish, and perform internal quality control. Zirconia Post and Core restorations could be a little slower because of milling and sintering steps, although in the vast majority of instances, they remain within a three- to four-day production range. These schedules presuppose full and precise clinical information; any missing or vague information is bound to cause delays.
International shipping is another complication. The express logistic options that are usually utilized by laboratories that are export-oriented (DHL, FedEx, or UPS) take three to six days, based on the destination country and the level of customs clearance. In cases where production and shipping go hand in hand, a total turnaround time of five to ten working days would be expected by most clients, and this is very suitable in the planning of restorative treatment.
Notably, the suppliers with a good reputation are concerned with providing consistent ranges of turnaround and not unrealistic minimums. This stability enables clinics and labs to book appointments with confidence, minimize rescheduling, and keep patients trusting them, which is a highly underestimated but essential operational advantage.
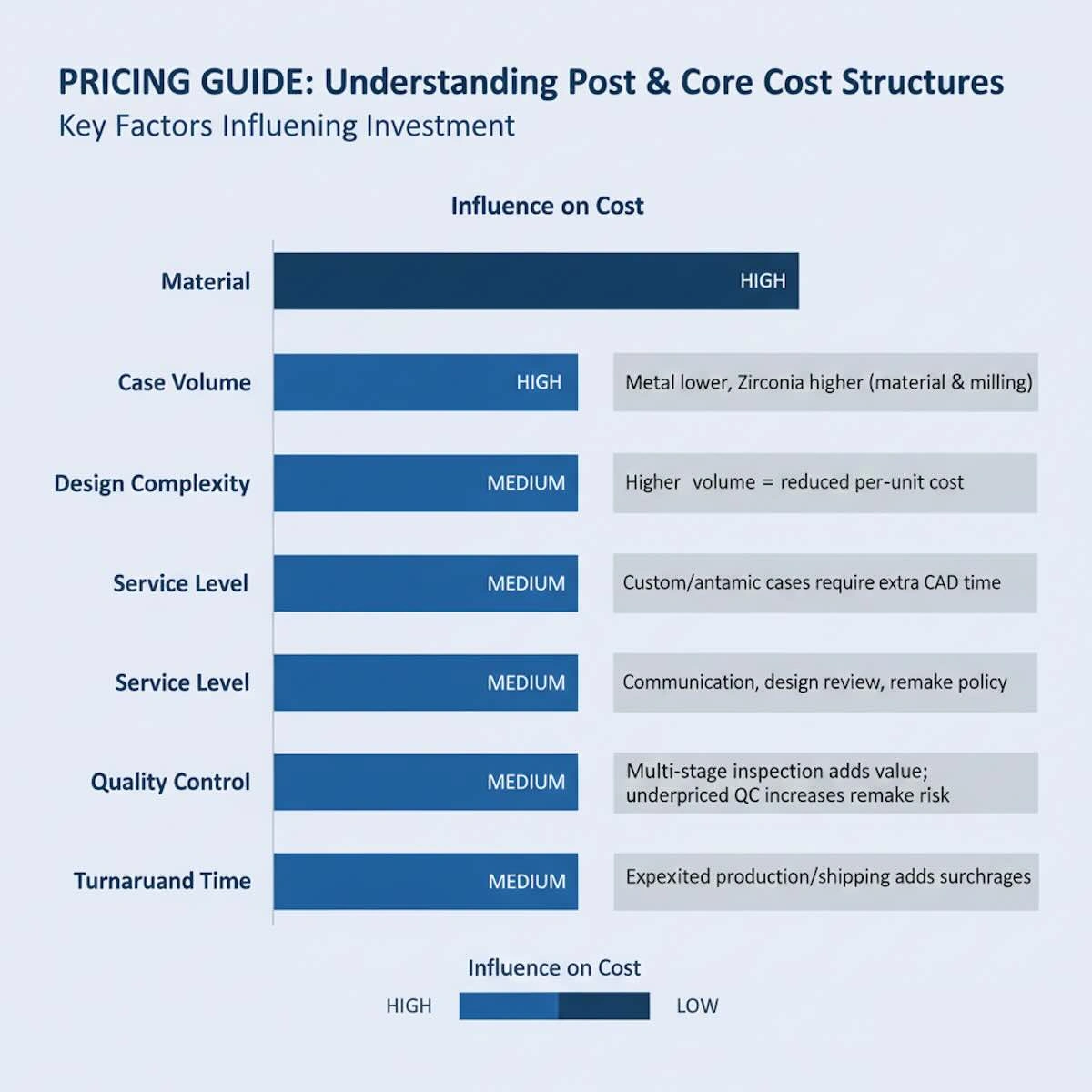
8. Pricing Guide: Understanding Cost Structures Without Oversimplification
The second most discussed subject on the Post and Core outsourcing is the pricing, which is also the most misconceived. Most buyers are only concerned with the unit price comparison, but they do not look at the overall cost framework, which eventually defines whether outsourcing is a source of real value.
The Chinese dental laboratories are in a position to give competitive prices due to structural benefits such as reduced labor costs, central production, and economies of scale. In the case of Post and Core restorations, this can be reduced to 30-60% of the price of production in North America or Europe. Nevertheless, such savings are significant when they are accompanied by regularity of quality and dependability of service.
| Factor | Influence on Cost | Notes / Considerations |
| Material | High | Metal generally lower cost; zirconia reflects higher material and milling expenses |
| Case Volume | Medium | Higher volume can reduce per-unit cost due to economies of scale |
| Design Complexity | Medium | Custom or anatomically challenging cases require additional CAD time |
| Service Level | Medium | Includes communication support, design review, and remake policy |
| Quality Control | High | Multi-stage inspection adds value; underpriced QC can increase remake risk |
| Turnaround Time | Medium | Expedited shipping or production often incurs surcharges |
Simply put, sustainable outsourcing alliances are not established based on the lowest price, but rather on reasonable, consistent pricing that enables quality production and protracted partnership. Knowing the variables above will enable dental clinics and labs to make sound decisions based on cost saving, operational stability, and clinical outcomes.
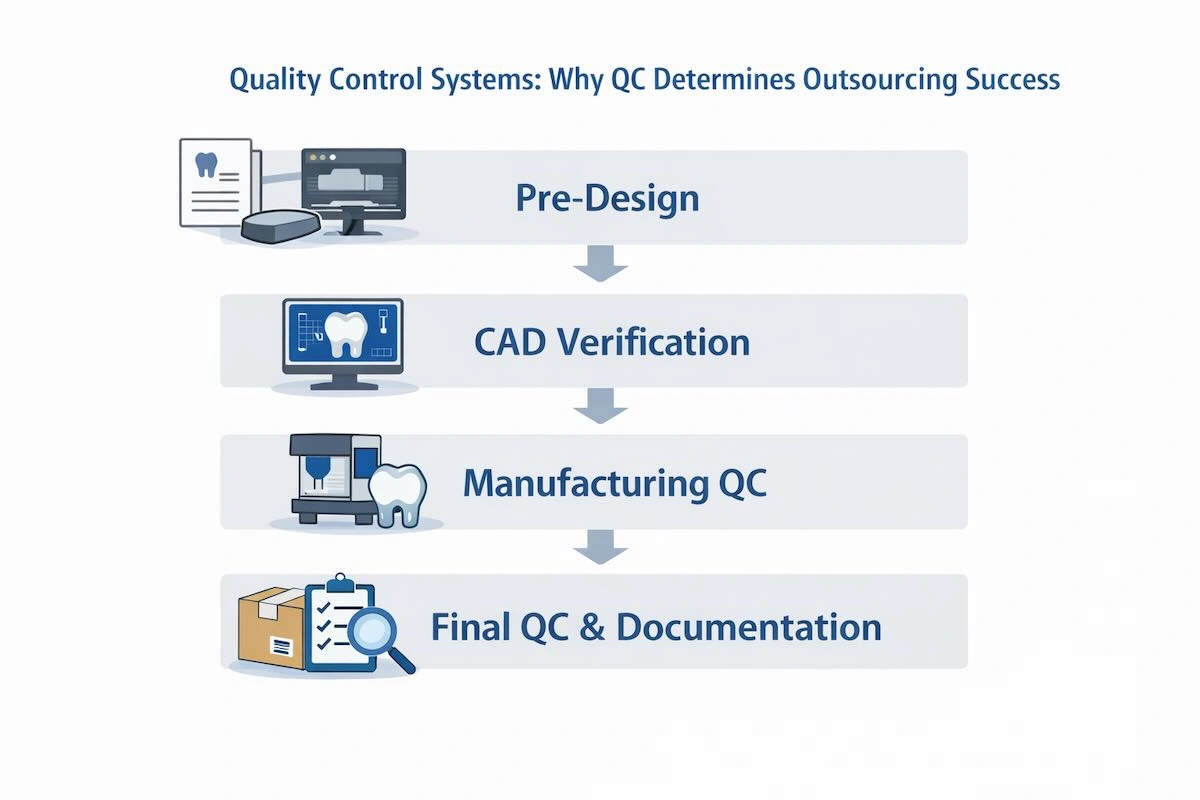
9. Quality Control Systems: Why QC Determines Outsourcing Success?
Quality control is not a value-added feature in the case of B2B dental outsourcing- it is the basis of the whole relationship. Although technically standardized, Post and Core restorations require a high level of dimensional accuracy and consistency. A slight deviation can undermine the crown fit or the long-term clinical outcomes. The answer to this is the multi-layer QC system by the professional Chinese dental laboratories, designed for the whole production cycle.
(1) Pre-Design QC: Ensuring Data Completeness
- New case submissions are checked in terms of completeness and clarity
- Prescriptions are reviewed regarding material selection, canal depth, post length, and restoration planning notes
- The digital scans or impressions are checked to resolve, orient, and make them usable
- Missings or ambiguous information is identified early, which minimizes downstream errors and remakes
(2) Design Phase QC: CAD Verification
- The CAD files are compared with the prescription requirements and anatomical constraints
- The validation of post and core alignment, canal adaptation, and ferrule design is performed
- Design previews can be provided to clients to ensure they are good before production is started
- The occurrence of any inconsistencies or possible design conflicts is identified and addressed in advance
(3) Manufacturing QC: Material-Specific Checks
- Metal restorations: dimensional control, surface finish control, and internal fit control
- Zirconia restorations: sintering compensation, milling accuracy, and post-processing accuracy
- All cases are monitored at the production phases to achieve repeatable quality
- The non-conforming cases are reworked or repainted in the light of recorded procedures
(4) Final QC and Documentation
- Last check is done to ensure that every Post and Core has been put into place to meet set acceptance standards
- There are cases where traces of QC records are recorded to hold accountability and analysis
- Problems are discussed systematically, and corrective measures are put in place to enhance processes
- This process-based QC method will make outsourcing more than a mere transactional process into a trusted extension of the lab operations of the client
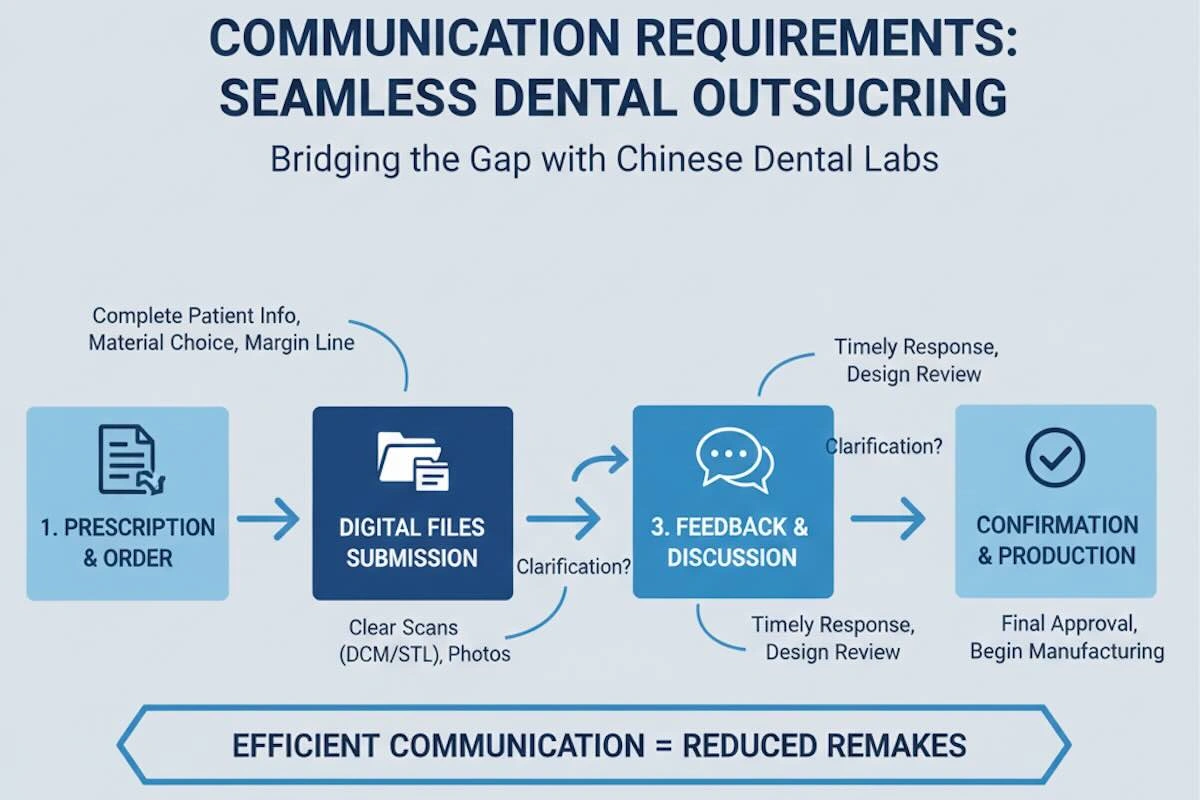
10. Communication Requirements: Reducing Remakes Through Process Alignment
The issue of communication is also mentioned as one of the challenges of outsourcing to foreign countries; however, in practice, the majority of the issues can be explained by ineffective processes rather than the language barrier. There is a special sensitivity of post and core restorations to the quality of communication since they are based on specific technical parameters.
It is necessary to have clear prescriptions. The information about the post length, the depth of canal preparation, the choice of materials, and the sequence of restoration should be clearly mentioned. In case these elements are not defined but assumed, the chances of a mismatch are considerably high. Proper outsourcing relations are thus based on standardized prescription templates and agreed terminologies.
In addition to initial instructions, feedback is very significant. Providing feedback on the fit, adjustment notes, and clinical observations enables the lab to improve designs as time goes by. Such a constant back-and-forth communication process lowers remake rates dramatically and builds a better understanding.
Finally, good communication is not about sending more messages, but setting up common expectations and an organised flow of information. Once this alignment is realized, the outsourcing is smoother, quicker, and more predictable.
11. Risks and Mitigation: A Realistic View of Outsourcing Challenges
None of the outsourcing models is risk-free, and professional buyers are aware that acceptance of risks is a sign of maturity and not a sign of weakness. The most frequent problems in Post and Core outsourcing are design mismatch, occlusal imbalance, incomplete data delivery, and logistical delays.
When risk management is done in a structured manner, it guarantees predictable results. A brief description of some of the common risks and mitigation measures employed by established Chinese dental labs is provided below:
| Risk | Mitigation Strategy | Key Considerations |
| Design discrepancies | Pilot cases & design verification | Start with a small number of cases to validate CAD alignment and crown fit before scaling volume |
| Occlusal misalignment | Clear occlusal planning & digital check | Confirm bite registration and final crown integration during the design phase |
| Incomplete or unclear case data | Standardized submission protocols | Detailed prescriptions, high-resolution scans, and digital STL files reduce misinterpretation |
| Logistical delays | Phased onboarding & reliable shipping | Track shipments, allow buffer for customs, and confirm transit times before committing to large volumes |
| Disputes over remakes | Transparent remake policies | Suppliers define responsibility boundaries upfront and document handling procedures |
12. How to Choose the Right Chinese Dental Lab for Post and Core Outsourcing?
The most important decision when outsourcing is arguably the choice of supplier. Most of the Chinese dental labs provide the Post and Core service, but their potential and professionalism are quite different. Major areas of evaluation are:
- Technical Experience: Assess the competence of the lab with metal and zirconia Post and Core restorations. Seek the signs of the uniformity of the findings in various types of cases.
- Digital Design Capabilities: Ensure that the lab is able to handle the STL files, CAD check, and CAM manufacturing. Online workflow literacy maintains increased accuracy and fewer remakes.
- Quality Control Structure: Determine whether the lab has multi-layer QC, such as design checks, material checks, and final inspection. Documentation practices are also significant.
- Communication Responsiveness: It should be clarified and coordinated in time, particularly to international clients. Support teams are made dedicated to improving collaboration.
- Familiarity with International Standards: The labs that cover North America, Europe, or Australia should be familiar with the local prescription formats, regulatory requirements, and reporting standards.
- Reputation and Process Reliability: As an example, Bestodental represents a professional strategy: export-oriented working processes, CAD/CAM accuracy, QC systematization, and traceability of materials. It focuses on long-term dependability and value of partnership, as opposed to low price competition.
13. Who Should Outsource—and Who Should Not?
It best suits those organizations whose workflow is stable and strategically oriented to outsource Post and Core restorations. Dental labs with moderate to high volumes of cases, clinics with the need to predict costs, and group practices that want to standardize the restorative processes are especially good candidates for outsourcing.
In contrast, the processes based on massively relying on same-day restorations or the frequent variation of the treatment protocol might not be compatible with the outsourcing model. Equally, non-standard or highly experimental restorative practices can be brought under closer in-house control.
Knowledge of these differences will assist decision-makers in not having conflicting expectations, and it will also make sure that outsourcing is deployed where it can bring real value.
14. Post and Core Outsourcing FAQs
The concept of outsourcing Post and Core restorations usually brings practical issues to the minds of dental clinics and laboratories. It is crucial to understand the subtleties of material performance, compatibility of workflow, and clinical contingencies to reduce risk and guarantee the predictability of the results. The common questions are answered in the following FAQs that provide professional knowledge and background.
Q1: Is the zirconia Post and core safe in the long term?
A properly indicated and designed Zirconia Post and Core restorations are very reliable. They offer great strength, fracture resistance, and esthetic properties, particularly in the front teeth where looks are the most important. They are biocompatible and resistant to corrosion, which makes them suitable for permanent restorations. Nevertheless, the success of clinical treatment is related to the close assessment of the canal structure, the form of ferrule, and the thickness of crowns because the wrong balance of stress can affect long-term results.
Q2: Is it possible to outsource both digital and traditional cases?
The workflows are supported by most of the professional Chinese labs. Digital submissions such as STL scans and CAD designs are more reproducible, provide more design intent information, and require fewer adjustment cycles. The conventional impressions are still feasible but need to be carefully verified to eliminate the possibility of inaccuracy in scanning or model casting. Lots of labs have hybrid workflows to serve the interests of clients and the realities of clinical practice.
Q3: What is the situation in an instance that is not clinically fitting?
Famous labs have well-defined remake and adjustment policies. The minor fit problems are rectified systematically, and each case is recorded to obtain feedback. This will make the design or production errors be examined and corrected so that they do not occur again. With time, these feedback systems enhance the accuracy and reliability of the lab, which increases confidence in long-term outsourcing relationships.
Q4: What is the best place to start outsourcing a lab?
An incremental strategy is highly advisable. This can be done by starting with a limited number of pilot cases to ensure that the client and the lab are certain that communication is clear, the designs are compatible, and that the turnaround is reliable. After processes have been confirmed, one can gradually increase volume. This plan minimizes expensive remakes and contributes to creating a predictable and repeatable workflow that is the basis of a sustainable outsourcing relationship.
15. Conclusion
A combination of technical skills, computer-digital accuracy, and scalable production is hard to find elsewhere, which is why outsourcing Post and Core restorations to professional Chinese dental laboratories is an opportunity to be taken advantage of. Having the knowledge of the workflow, quality control standards, cost structures, and risk reduction strategies described in this guide, dental clinics and laboratories are able to make smart choices and attain predictable and high-quality results.
When international clients need to be consistent, trace the material, and be aware of the process, collaborating with a long-term lab like Bestodental would be a long-lasting solution. Having a metal and zirconia Post and Core restoration workflow, Bestodental can be considered an excellent example of the professionalism and long-term performance that should characterize the successful outsourcing relationships.