The need to have solutions that are balanced in terms of durability, esthetics and tooth preservation has never been greater in modern restorative dentistry. With the trend in the philosophy of treatment turning towards more minimally invasive techniques, inlays and onlays have gained an ever-growing popularity as a method of restoration of posterior teeth with moderate structural impairment.
Simultaneously, dental laboratories and clinics across the globe are under increased pressure of operations: rising labour expenses, a lack of technicians, a heavy investment in equipment, and the necessity to improve the turnaround time without worsening the quality. It is against this backdrop that outsourcing inlays and onlays to China is a feasible and scalable approach as opposed to being a cost-cutting measure.
The guide is to be used by international dental laboratories, group practices, and clinic owners who desire to know the real process of outsourcing inlays and onlays, what can and cannot be outsourced, what the risks are, and how to establish a stable and long-term outsourcing system with Chinese dental laboratories.
1. What Are Inlays and Onlays?
It is imperative to first define what outsourcing is and what it is not before addressing the subject of outsourcing, and it is also important to define the product in question, particularly to those readers who might not be in the field of indirect restorations.
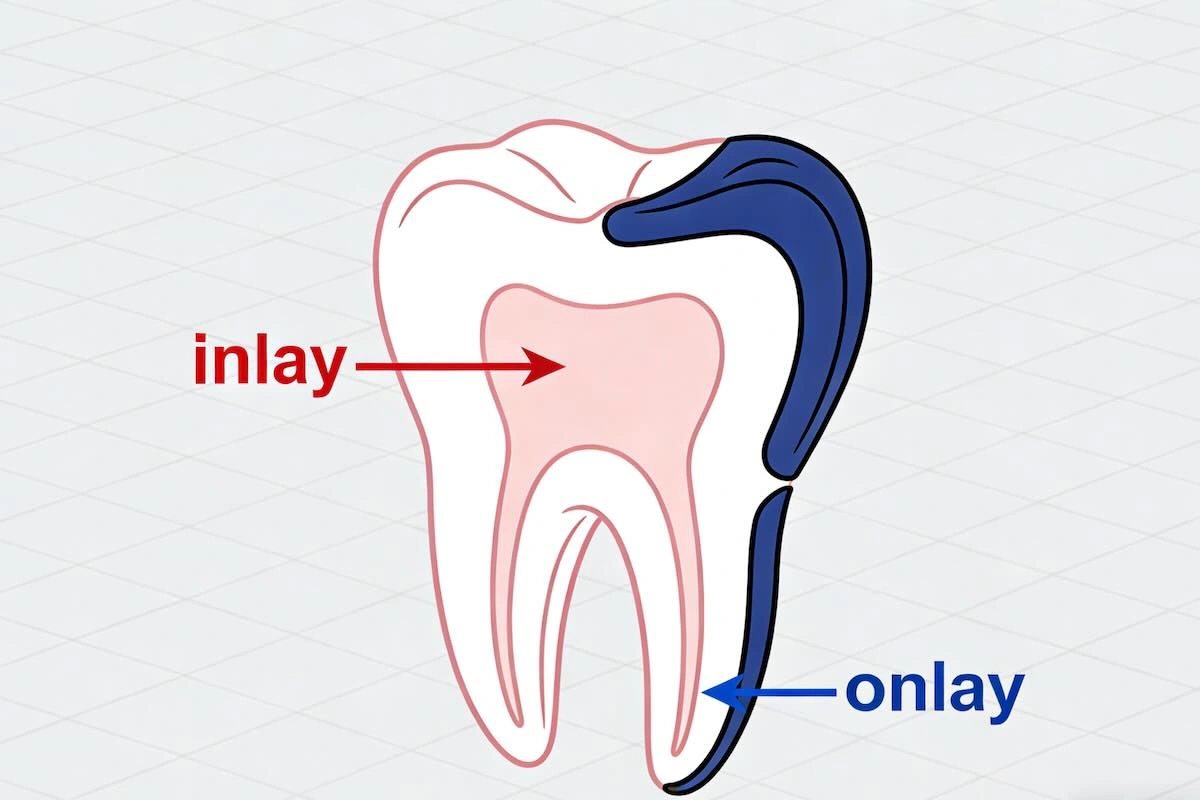
Inlays and onlays are indirect restorations that are designed outside the mouth (usually in a dental laboratory) and bonded to the prepared tooth. They are mainly applied in the back teeth, which are damaged beyond the restorative capabilities of a direct composite filling, but do not warrant a full-coverage crown.
An inlay is installed in the cusps of the tooth, and it replenishes the internal structure. It is not applied to cusp tips and is mostly applied to teeth whose external walls are relatively intact.
Onlay, in turn, covers one or more cusps. It offers further support, and it more evenly allocates occlusive forces; it is suitable for the teeth that have been more structurally compromised.
Clinically, both restorations are designed to retain as much of the natural tooth structure as possible and provide long-term functional stability. Laboratory-wise, they are extremely pre-occupation products, which rely on the correct digital layout, milling precision, and regulated finishing guidelines.
This is what makes inlays and onlays particularly appropriate in outsourcing, namely this combination: clinical value and production standardisation.
2. Why Are Inlays and Onlays Suitable for Outsourcing?
Not every dental restoration is equally well outsourced. Others demand close chairside-lab communication, artistic personalisation, or live occlusal modification. However, inlays and onlays hold a special place in the spectrum of restorations.
To begin with, they are completely compatible with workflows that are digital. The whole production process becomes data-driven as soon as the preparation and bite records are appropriately captured either through intraoral scanning or through digitised impressions. This enables the transfer of cases across borders without any loss of accuracy.
Second, inlays and onlays have high repeatability. The design of posters, the design of margins, and contact standards are based on established conventions. When a laboratory follows set procedures, the result can be predicted on a large-scale level.
Third, such restorations usually need not be subjected to the same level of subjective aesthetic art as in the case of anterior veneers. Although esthetics are still important, fit, contact, occlusion, and marginal integrity that can be measured and controlled are the key parameters that determine success.
This provides an ideal environment to outsourcing partners since there are standardised inputs, scalable production and predictable outputs. To clients, it would imply reduced risk and increased control.
3. Why Outsource Inlays and Onlays to China?
Although in the past China was only linked with the benefits of low labour costs, this definition is no longer the case in the current dental outsourcing industry.
The long-term industrial development and not the short-term cost arbitrage has led to China being a global hub of inlays and onlays outsourcing.
(1) Scalable Industrialised CAD/CAM Infrastructure
Chinese dental laboratories have been investing in CAD/CAM systems for the last twenty years. Massive milling facilities, multi-brand scanner compatibility and central production planning are becoming the norm among established laboratories. The given infrastructure allows managing large amounts of posterior restorations without compromising accuracy or repeatability.
(2) Specialisation of high-level technicians
Many Chinese labs specialise CAD designers to a particular type of restoration, unlike smaller labs where technicians frequently work in a variety of product lines. Special teams that specialise in inlays and onlays gain a thorough understanding of the margin design, occlusal morphology and control of contact. The specialization minimizes variability and lowers learning curves in large volumes of cases.
(3) Experience in International Compliance Standards
The reputable Chinese labs that cater to international clients have a wide understanding of the regulations and compliance requirements. The adoption of materials registered by the FDA, systems that are certified by CE, and workflows that are in line with ISO has become a level instead of a point of difference. This knowledge reduces the compliance risk of foreign partners.
(4) Cost Effectiveness as a Structural Result
The advantage of lower production cost is still there, and better it should be regarded as an incidental aspect of scale, specialisation, and process efficiency, than as the main cause of outsourcing. The real worth is that China can provide quality that is predictable and has industrialised processes.
To conclude, inlays and onlays will no longer be a compromise to outsource to China due to its cost. It is a business decision that is based on process maturity, specialisation, and scalable manufacturing capacity.
4. What Can Be Outsourced—and What Cannot?
Among the most general outsourcing errors is the belief that nothing can and/or cannot be outsourced. The professional outsourcing strategy starts with the boundaries, which are clearly defined, especially when it involves precision restorations like inlays and onlays.
The following table will describe what kind of cases would normally be outsourced to China, and which would be better suited to stay in the local jurisdiction because of the increased complexity of clinical or communication requirements.
| Category | Suitable for Outsourcing | Not Recommended for Outsourcing |
| Case Type | Standard posterior inlays and onlays | Complex bite reconstruction cases |
| Data Quality | Complete STL files with clear margins and stable bite records | Incomplete scans or unclear preparation margins |
| Occlusal Conditions | Stable occlusion with predictable functional patterns | Severe occlusal instability or parafunctional habits |
| Restoration Design | Monolithic zirconia or lithium disilicate | Highly customised, experimental, or non-standard designs |
| Communication Needs | Cases with standardised design protocols | Cases requiring frequent real-time design adjustments |
| Volume Characteristics | Repetitive, volume-driven workflows | One-off cases requiring intensive customisation |
A clear-cut selection of cases where outsourcing is possible and those that demand close clinical partnership will allow dental laboratories to decrease the rates of remakes considerably and achieve a higher efficiency in the overall outsourcing. Outsourcing is not about completely taking all of the production overseas, but rather picking the right cases to apply the appropriate model of production.
5. Step-by-Step Workflow for Outsourcing Inlays and Onlays
To the majority of dental laboratories and clinics, outsourcing is worth more than its apparent value in unit cost, and more in the certainty of the process. A well-established workflow minimises the level of ambiguity, avoidable mistakes, and enables both parties to perform within foreseeable parameters.
Professional inlay and onlay outsourcing workflow is not a linear action or a one-time action, but a controlled flow of steps, each having its goals and control points.
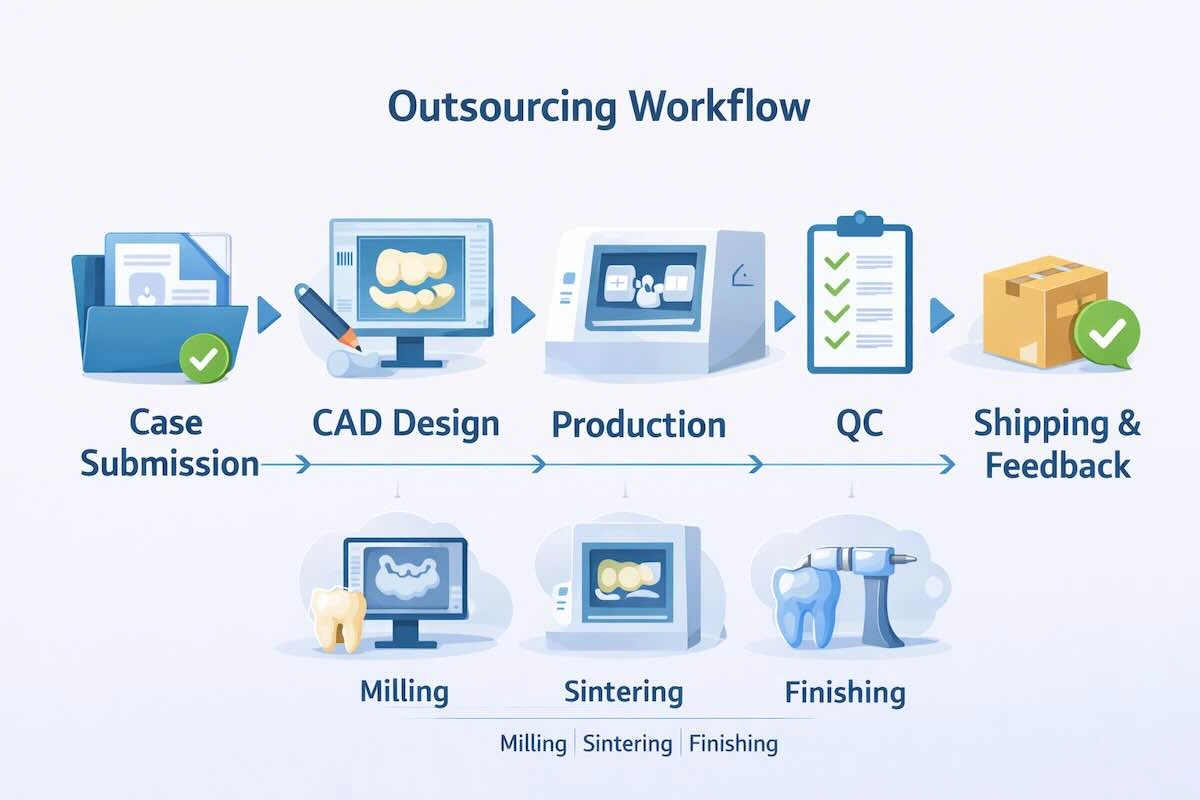
1) Stage 1: Submission of Case and Data Validation
The process starts with the case submission. In this step, the client gives full digital inputs which usually consist of STL files, bite records, shade information and a written prescription.
It is not just a mere file transfer phase. Outsourcing laboratories with a good reputation do first data verification, scan completeness, margin clarity, occlusals and case viability. Problems found here are resolved before design commences, and later downstream corrections are not possible.
Pivotal goal: Before design, make sure that all inputs are in accordance with the production requirements.
2) Stage 2: CAD Designed and Internal Review
After the case has been successfully tested in terms of data validation, it is then sent to the CAD design stage. Developed protocols of identifying the margins, occlusal morphology, and control of contacts are standardised protocols that are followed by specialised designers for inlays and onlays.
To design new clients or sophisticated clients, most labs provide design previews or internal design reviews before production. This optional gate-checking keeps the expectations in line at the beginning and minimises the risk of adjustment, especially at the early stage of cooperation.
Pivotal goal: Transform clinical intent into a digital design that can be manufactured and predicted.
3) Stage 3: Production, Finishing and Quality Control
Once the design is approved, the case is approved for the production stage. Depending on the material, whether zirconia or lithium disilicate, milling, sintering or crystallization as well as finishing, are performed based on material-specific protocols.
Multi-level quality control helps in supporting this stage, which is concerned with dimensional accuracy, marginal integrity, interproximal contact, and occlusal relationships. The quality checks are incorporated in the production process, and not just a last-minute check.
Pivotal goal: Check functional correctness and consistency before shipment.
4) Stage 4: Delivery, Feedback and Process Optimisation
Finished restorations are properly packed and transported through the international logistics systems. Nevertheless, the working process is not completed once the delivery is made.
The partners of the professional outsourcing services are also keen on gathering post-delivery feedback on fit, contact, occlusion, and adjustment needs. This data is fed back into design and production processes, creating a closed-loop system of improvement that increases consistency in the long run.
Rational principle: Never stop improving results with systematic feedback.
In its entirety, this workflow will result in the outsourcing process being reorganised into a controlled production process. Inlays and onlays outsourcing can be predictable, scalable, and sustainable when all the stages are defined and controlled.
6. Turnaround Time: What International Clients Should Realistically Expect
The first metric that is commonly mentioned when outsourcing is turnaround time; however, it is also one of the most misconceived. Most overseas dental laboratories will first base their attention on the number of days, but will not fully comprehend the point of time wastage in an outsourcing process.
Offshore outsourcing has several stages, both controllable and uncontrollable, unlike local production. An evaluation that is realistic needs the division of turnaround time into parts as opposed to viewing it as a single number.
The calendar of a mature China-based outsourcing model will usually follow the following pattern:
| Stage | Typical Duration | Notes |
| Case intake & file verification | Same day | Delays often occur here due to incomplete data |
| CAD design | 24 hours | Dedicated CAD teams significantly reduce variance |
| Production & internal QC | 2–3 working days | Material-dependent |
| International shipping | 3–5 working days | Courier and destination dependent |
Between submission and delivery, 6-9 working days would be realistic and sustainable to the vast majority of international clients.
It is significant to mention that speedy turnaround is not necessarily good. Timelines that are aggressively tightened may also pose remake risk, especially in occlusion-sensitive restorations such as inlays and onlays. Professional outsourcing is more concerned with consistency than spikes in speed, so that the performance of delivery is not going to fluctuate month after month.
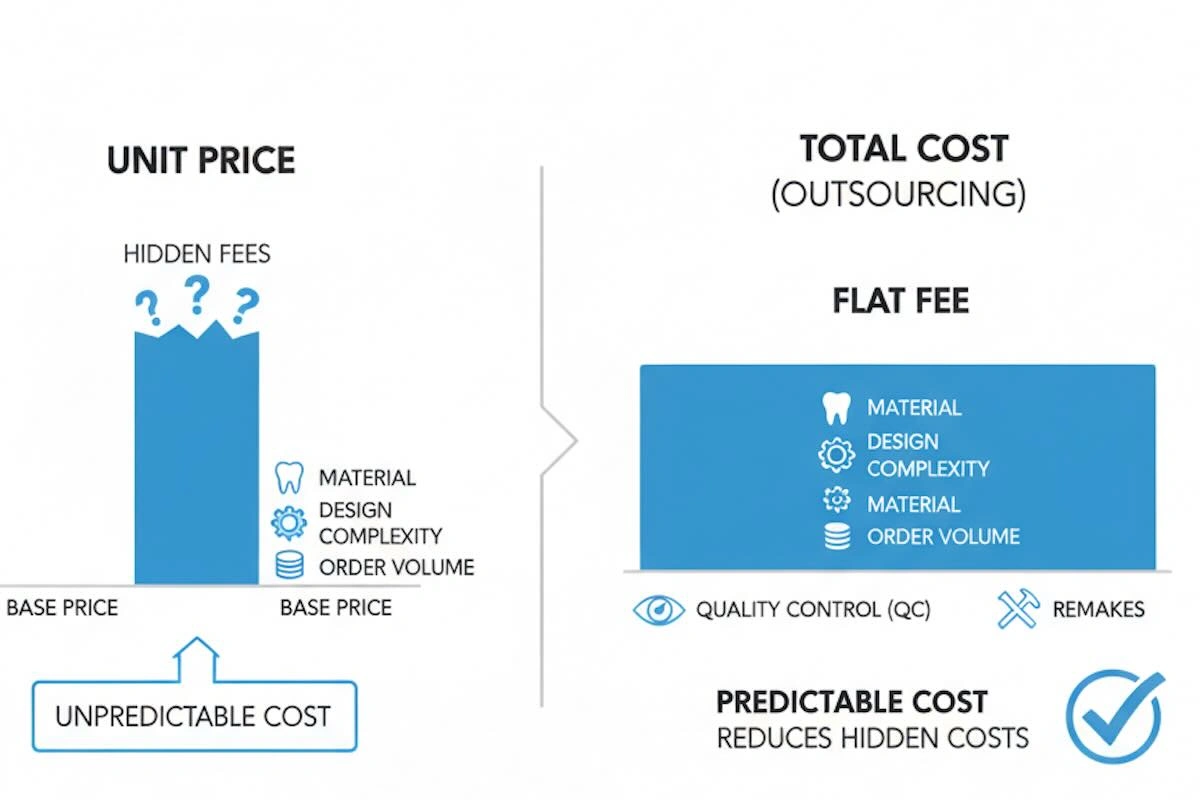
7. Pricing Guide: Understanding Cost Structure Beyond Unit Price
To lots of dental laboratories, the price becomes an issue not due to the high cost of outsourcing, but due to the lack of comprehension of the actual cost structure. Unit price is simple to compare, but it is a minor fraction of the overall outsourcing price.
A professional pricing analysis is based on the overall cost per case done, including both visible and operational variables that determine efficiency and risk.
Several structural forces influence the cost of outsourcing inlays and onlays:
(1) Material strategy
The difference between zirconia, lithium disilicate and hybrid ceramics is not only in terms of the cost of the material, but also in milling time, finishing labor and the remakes of the occlusal/preparation.
(2) Design approach
Monolithic restorations tend to offer a greater level of cost stability, whereas the layered designs add more technician dependency as well as inter-batch variability.
(3) Case quality and complexity
Poor definition of margins, incompatible preparation or marginal instability usually results in further design revisions, longer turnaround, and a higher probability of remake.
(4) Order volume consistency
Predictable pricing models, priority scheduling, and more efficient allocation of capacity can be achieved through consistent monthly volume, which lowers the cost fluctuation per case.
(5) Responsibility and quality control
Clearly defined QC criteria and well-established remake policies have a direct impact on the cost exposure in the long term and the predictability of operations.
Although the labs located in China are commonly linked with lower prices, the true benefit of these types of labs is the predictability of their costs at scale. Consistent pricing models enable laboratories and clinics to predict margins effectively, scale the order volume without operational pressures, and reduce indirect expenses due to remakes, delays, and internal rework.
Finally, successful outsourcing changes pricing choices to a proactive one compared to cost-control, and outsourcing becomes not a temporary cost-reduction strategy but a long-term operational model.
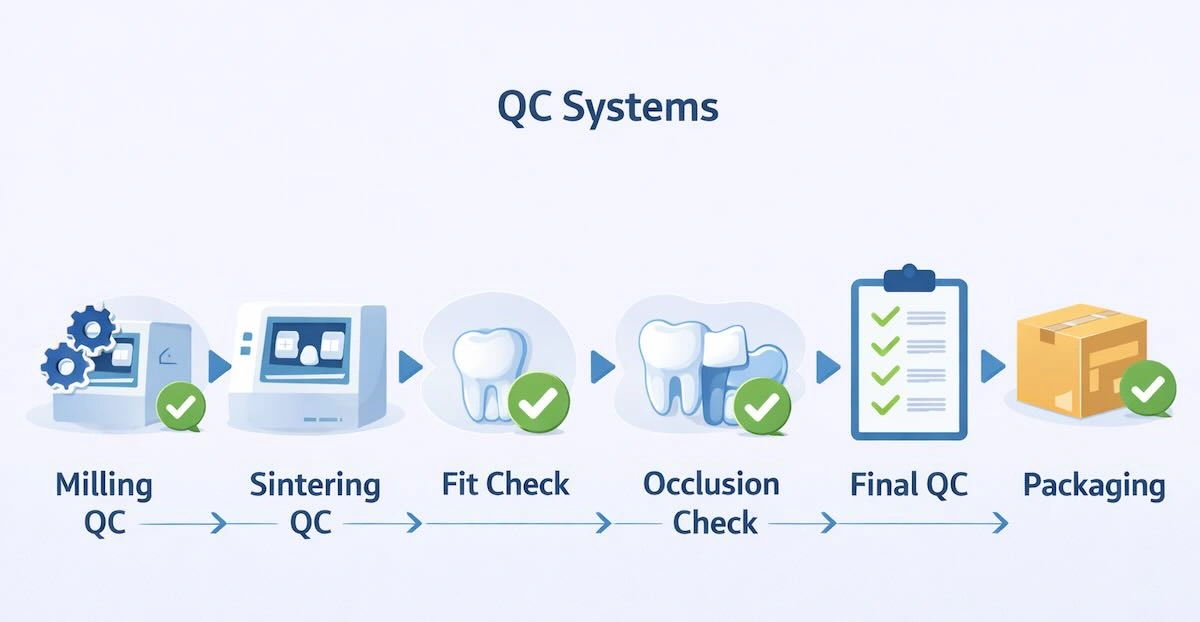
8. Quality Control Systems: The Core of B2B Dental Outsourcing
In B2B dental outsourcing, quality is not identified by individual excellent cases, but through multiple results of hundreds or thousands of units. Such consistency is attained by organised systems of quality control as opposed to technician intuition.
The Chinese dental labs that are reputable have multi-layer QC structures that extend the production cycle. A typical QC system includes:
- Design Quality Control: The margins, insertion paths, the occlusal anatomy and the contact points are checked before the commencement of production. This measure averts the downstream errors which cannot be repaired when milling.
- Production Quality Control: In milling and post-processing, restorations are monitored in terms of dimensional accuracy, material integrity and structural defects.
- Final Quality Control: Finished restorations are simulated in fit, contact, verified in occlusal and visually inspected under magnification.
- Pre-Shipment Verification: Labelling, case matching and packaging are validated to eradicate mistakes in logistics.
Clients that consider outsourcing partners must not inquire whether or not there is QC, but how it is documented, measured and executed. The clear articulation of QC checkpoints is also usually a more effective measure of quality than the marketing assertions.
9. Communication Requirements to Avoid Remakes
In dental outsourcing projects across the world, the remake rates are much more correlated with the quality of communication than the technical capability.
The majority of remakes are not due to the inability of a lab, but rather, the expectations were not spelt out initially. It is particularly applicable to inlays and onlays, where minor differences in the tightness of contacts or the height of the occlusal ridge may make the difference between clinical success and failure.
To reduce remakes, communication must revolve around the information that is critical in decision-making, such as:
- Transparency of margin and extent of preparation
- Clearance anticipations of occlusals
- Interproximal contact preference (light, normal, tight)
- Functional bite considerations
- Instruction on shade and translucency (where necessary)
Successful outsourcing relationships are based more on a standardised prescription format than on ad hoc explanations over time. These templates minimise ambiguity, fasten case intake, and have a great impact on consistency in large volumes.
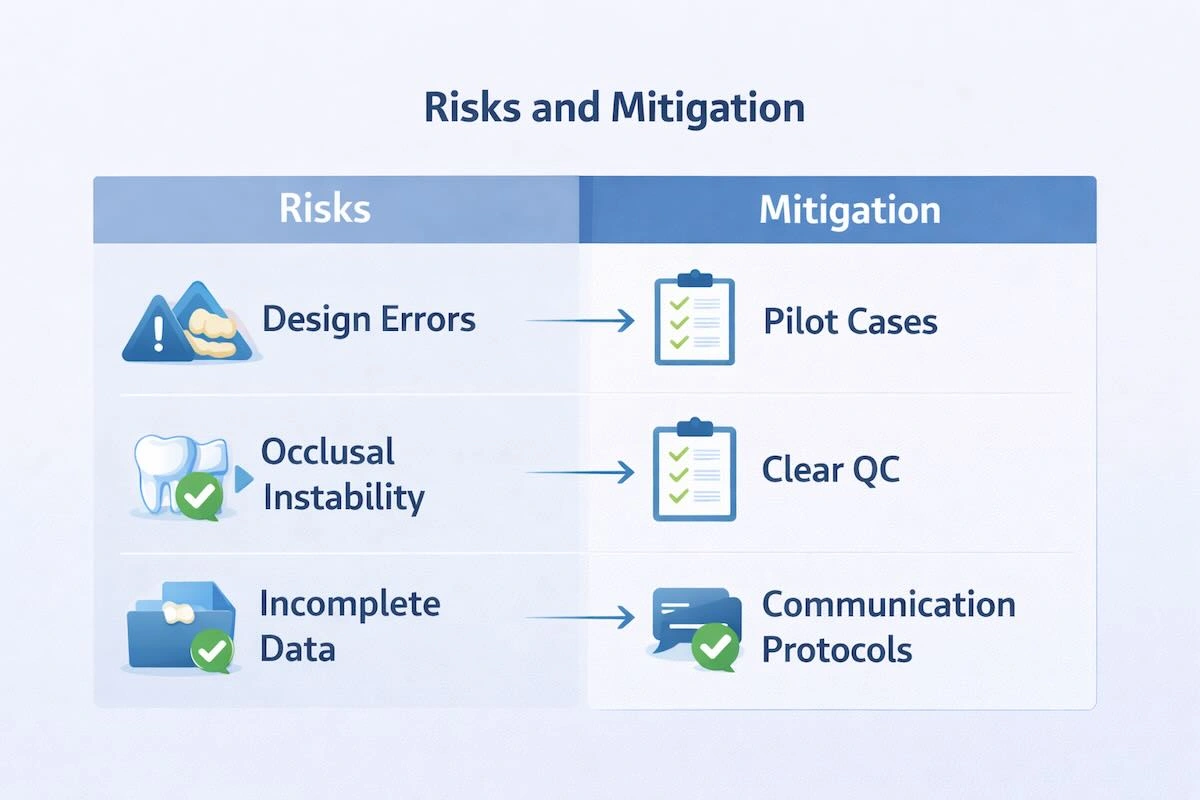
10. Risks and Mitigation: A Professional View of Outsourcing Reality
All models of outsourcing are risky. The major distinction between professional and amateur outsourcing is in the way the risks are expected and handled.
The pitfalls in inlay and onlay outsourcing are the misinterpretation of margins, occlusal gaps, and transportation delays. The root cause of each of these risks, as well as the mitigation strategies, can be identified.
As an example, the problem with margins is usually caused by the lack of clarity of scans or inadequate preparation depth. Mitigation is initiated at the selection of cases and file verification instead of production.
Standardised bite protocols and stable CAD team assignments are the most effective way of controlling occlusal discrepancies. Risks in logistics, in turn, are reduced by planning shipping schedules predictably and contingency plans instead of putting their trust in express delivery.
Professional outsourcing does not do away with risk- it transforms uncertainty into variables that can be managed.
11. How to Choose the Right Outsourcing Partner for Inlays and Onlays?
It is not that hard to choose a country, but it is much more delicate to pick a trustworthy partner. Marketing claims or general lab credentials are the main concerns of international clients, whereas success is in operational competence and performance stability.
The following dimensions are of importance when considering Chinese dental labs:
- Experience in posterior indirect restorations: Seek those labs that deal with high quantities of inlays and onlays specifically, and not general restorative work.
- Workflow and QC system transparency: Documented and clear specifications on how cases are submitted, CAD design, production and quality checks are the keys to minimising errors and remakes.
- Stability of CAD and production teams: Long-term, committed teams guarantee consistency in designs, reduce learning curves, and have predictable turnaround.
- Responsiveness and clarity in communication: Professional communication saves time and effort by eliminating back-and-forth corrections and preventing delays that are expensive to the company.
- Track record with international clients: Labs that are accustomed to operating across borders are well aware of such aspects as compliance, logistics, and client expectations, which dramatically reduce operational risk.
Examples of such labs are Bestodental. They also position themselves as process-oriented outsourcing partners in addition to providing competitive pricing. Bestodental concentrates on the stability of the workflow, a constant delivery timetable, and strict quality control. They assign their teams based on product category so that there is specific expertise on inlays and onlays, and continuous improvement is achieved by having integrated feedback loops and client communication channels. Bestodental offers an example of how professional outsourcing ought to work, combining efficiency, reliability, and quality at a large scale, to international labs and clinics that are not only interested in finding a vendor, but also in having a long-term partner.
12. Who Should Outsource—and Who Should Not?
Outsourcing is not a universal notion, and the identification of its limitations is a sign of professionalism.
The outsourcing approach best serves dental laboratories and dental clinics with digital workflows, a steady number of cases, and a focus on scale and profitability. These organisations enjoy a constant production capacity without a corresponding rise in overheads.
On the other hand, outsourcing is not as appropriate to the practices that are highly dependent on same-day restorations, deal with highly individualised art cases, or do not have stable digital input information. Local production can be more controllable in such environments, even though it can be more expensive.
This distinction can be understood to avoid false hopes and enhance satisfaction with outsourcing decisions in the long term.

13. Outsourcing Inlays and Onlays FAQs
There are several factors to consider in outsourcing inlays and onlays, including regulatory issues and workflow integration. The list of questions that are often asked will discuss the most common issues and assist the dental laboratories and clinics in making effective outsourcing deals with Chinese laboratories.
Q1: Do the outsourced inlays and onlays meet international regulations?
Yes. Accredited Chinese labs have management systems that are based on ISO and utilize FDA registered and CE-certified materials. The compliance is ensured throughout production, from the CAD/CAM design to the final restoration finishing. To guarantee compliance with the regulatory requirements, the clients may demand documentation of the material certificates, batch records, and workflow audits.
Q2: Is it possible to design standards for my lab or clinic?
Absolutely. Client-specific design protocols are applied in most professional labs following an initial phase of alignment. This covers the types of margins, the types of occlusal schemes, preferred styles of layering, as well as any proprietary design preferences. These standards, once in place, are used in all outsourced cases to minimise variability and mitigate risk.
Q3: What about remakes? Who pays?
Remake policies play a vital roles to reduce conflicts. Usually, labs differentiate between production-specific (e.g., milling faults, sintering, etc.) and input-specific (e.g., incomplete scans, unclear prescriptions, etc.) problems. The errors of production are typically reproduced at the cost of the lab, and the errors that relate to the input should be corrected by the client. Proper records of duties prior to initiating cooperation are necessary to have smooth operations.
Q4: What is the management of cross-time zone communication?
Close communication is guaranteed by special English-speaking coordinators, the organisation of reports and overlapping working hours. Case tracking portals or shared cloud platforms are also offered by many labs so that clients can keep track of design progress, QC checks, and shipment schedules in real time.
Q5: What is the time to stabilise the quality of outsourcing?
The majority of labs attain reliable, quality results once they have a pilot period of 10-30 cases (based on complexity and volume). In this stage, design procedures are enhanced, familiarity among technicians is augmented, and feedback connections are put into place. Once stabilised, cases will generally not need much adjustment, which means a predictable turnaround and lower remake rates.
Q6:What is the scope of the cases that can be outsourced?
Yes. Outsourcing is not usually appropriate in cases where the reconstruction of the bite is complicated, there is severe instability of the occlusal, or where the clinical data is incomplete. Labs advise to always begin with simple posterior restorations to build trust and familiarity with the process, and then proceed to more complicated cases.
Q7: What is the impact of outsourcing on the workflow and turnaround time in the clinics?
Outsourcing has the power to simplify the lab operations and release the resources within the establishment when it is adequately incorporated. Planned workflows and consistent design criteria enable the clinics to schedule cases. Under normal circumstances, the process of the case submission to delivery takes between 7 and 14 days for the regular inlays and onlays, depending on the volume and the material.
14. Conclusion
Saving money is not the only benefit of outsourcing inlays and onlays to China, but predictable workflows, onlays and inlays expertise, and quality are other benefits. Using appropriate cases, coordinating design procedures, and setting clear quality control and communication criteria, dental laboratories and clinics are able to reduce the number of remakes and optimise the processes without any problems with the quality of clinical care.
An example of the process-oriented approach that is used by Labs like Bestodental is the integration of specific teams, clear steps, and consistent delivery to guarantee predictability at scale. Professional outsourcing is a cost-effective and risk-free solution for labs and clinics that are interested in having a reliable partner to increase the restorative capacity effectively.