Outsourcing dental restorations is no longer a short-term measure of capacity overload. It is now a long-term operational strategy for many dental laboratories and clinics worldwide. Among all types of restorations, Full Cast crowns and bridges have remained one of the most commonly outsourced options due to their technical stability, predictability, and cost-effectiveness.
The guide is addressed to overseas dental laboratories, DSOs and clinics interested in having a clear, realistic and professional idea of how to outsource Full Cast restorations in China, without speculation or unseen dangers, or unrealistic hopes. This article describes what works, what does not, and how to remain in control of the outsourcing process, as opposed to concentrating on marketing claims.
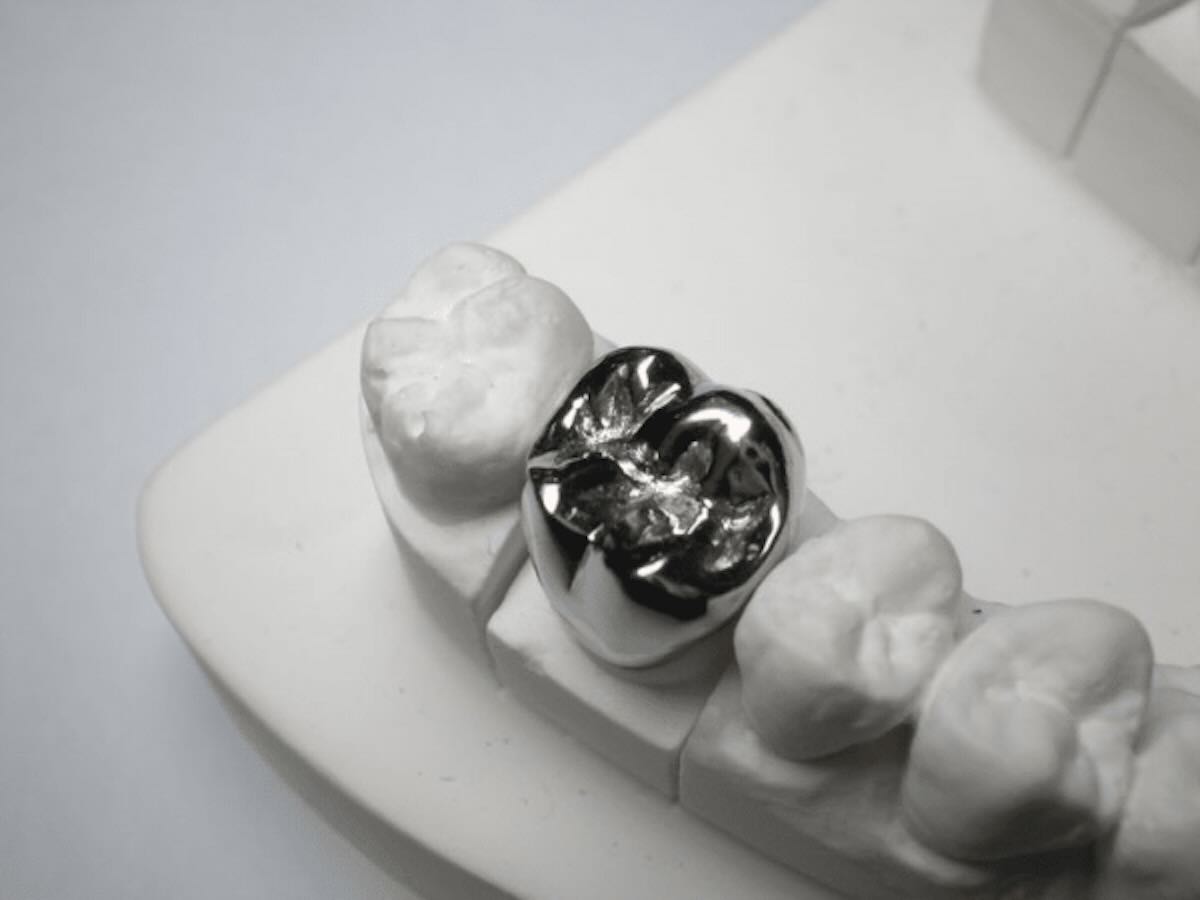
1. What Are Full Cast Crowns and Bridges?
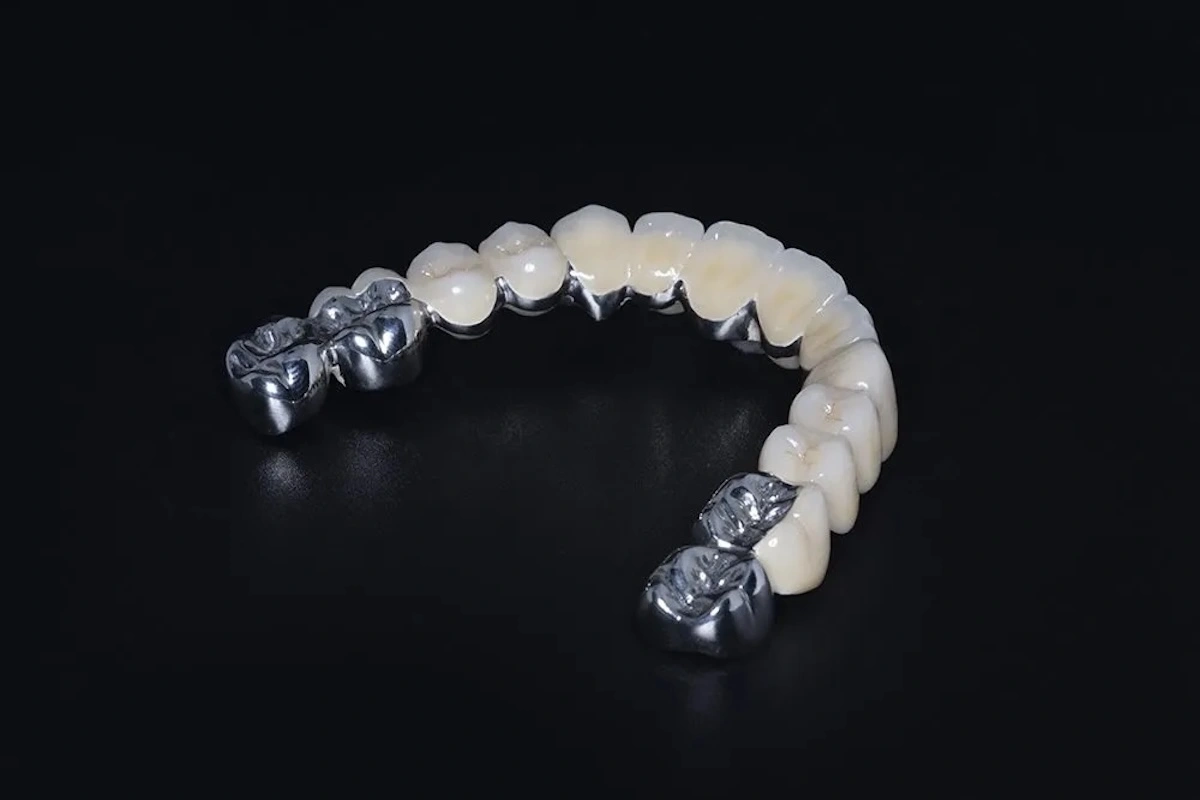
Full Cast Crowns and Bridges Full cast crowns and bridges are 100 per cent metal alloy with no porcelain or ceramic veneer. Full Cast restorations, in contrast to PFM or all-ceramic restorations, are monolithic structures that are constructed with the purpose of strength, durability and functional reliability, but not esthetics.
Clinically, they are most prevalent in the posterior areas, particularly molars, where the forces of chewing are the greatest and esthetic needs are the least. Full Cast restorations do not involve the use of layered materials; therefore, they result in reduced tooth loss, high levels of marginal accuracy, and long-term clinical stability.
As far as functionality is concerned, they have a value in predictability. There is no risk of chipping of ceramics, no shade that would be challenging, and a lot fewer variables when fabricating. It is this natural simplicity that is one of the primary reasons Full Cast restorations remain widely used- and it is such simplicity that makes them easily adapted to outsourced manufacturing models.
2. Why Full Cast Restorations Are Particularly Suitable for Outsourcing
Dental restorations do not lend themselves equally to the outsourcing process. Others demand substantial artistic input, frequent chairside manipulation, or intensive clinician-technician interaction, which makes them more risky and less predictable. Full Cast restorations, in their turn, are inherently consistent with the features of effective outsourcing.
1) High Technical Stability
The fabrication process with digital CAD/CAM-based or traditional casting is repeatable and standardised, with little subjective interpretation. As soon as margins, occlusion, and connector sizes are clearly stated:
- The internal fit is consistently possible
- Occlusal alignment is predictable
- The validity of the connector strength and span can be easily validated in the case of bridges
This consistency enables laboratories to trust their foreign collaborators to deliver precise results without regular in-house control that is essential in scaling down or handling high-volume cases.
2) Low Esthetic Sensitivity
Unlike the layered ceramics or earlier restorations, which demand careful colour matching, surface characterisation, and translucency, Full Cast restorations are mostly utilitarian. This eliminates the chances of being dissatisfied with the visual expectations and minimizes the cross-border aesthetic corrections.
- Changes in colour or shading are almost unimportant
- Small surface polishing can be performed within a short time at the location
- Visual remakes are not very common
Consequently, it allows laboratories to attain low remake rates even when working with other countries.
3) Easy Adjustment and Fine-tuning
Minor adjustments do not object to Full Cast restorations. Post-delivery adjustment is never difficult or dangerous, as the corrective actions are simple and easy to perform: either occlusal refinement, proximal contact adjustment, or a minor marginal polish.
- The amount of chairside adjustments is often minimal
- Minor changes do not affect structural integrity
- Facilitates a solid connection with the lab workflow
4) Predictable Outsourcing Success
Due to their technical stability, low esthetic sensitivity, and simple adjustability, Full Cast restorations have a high success rate in the laboratory as the first type of restoration to be outsourced. They are not necessarily easy, but their manageability makes them the best in the case of cross-border production, and this lowers operational risk as well as guarantees consistent results.

3. Why Outsource Full Cast Restorations to China?
The concept of outsourcing in itself is not a guarantee of success. Location is key, and China has turned out to be the leading dental outsourcing destination on a structural basis and not cost benefits in the short term.
The dental manufacturing sector in China has grown in a history of over 20 years, targeting North America, Europe, Australia, and some of the Asian markets. Chinese dental laboratories have developed mature casting workflows, export-oriented quality-scaleable teams of technicians, and dental manufacturing during this period.
The price is included in the equation, but it is not the entire story. The actual benefit is scale cost stability. The Chinese laboratories are also able to experience the same pricing with an increase in volume, which is becoming a challenge in high-labour-cost areas.
Experience is also important. Chinese laboratories that specialise in exports are familiar with international prescriptions, electronic case delivery, and international communication. Not only do they know how to manufacture restorations, but they also know how to fit into the laboratories of foreign countries.
The thing that most buyers fail to appreciate is not that it is more cost-effective, but that it can produce in bulk, and that they can do so consistently, and this is where China has its upper hand.
4. What Can and Cannot Be Outsourced
Poor expectations are one of the leading causes of outsourcing failure. There is no limit to defining boundaries of capability in the beginning–that is a mark of professionalism. These boundaries are beneficial as they assist the laboratories and clinics to know what to anticipate, reduce risks, and to have a smooth cooperation with the partners in foreign countries.
1) Cases Typically Suitable for Outsourcing
Full Cast restorations, which are often outsourcing-friendly, are:
- Single-unit Full Cast crowns: Perfect in molars and premolars, where practicality is more important than esthetic subtleties.
- Short- to medium-span Full Cast bridges: When clear instructions are given, multi-unit bridges with controlled spans and connectors can be cast and finished offshore with reliability.
- Non-precious metal alloys (Co-Cr, Ni-Cr)l: These alloys are relatively cheap, do not change when cast, and are highly acceptable to the export markets.
- Digital STL-based cases: The STL workflows minimise communication errors and permit pre-production verification.
- Conventional impression cases with clear margins: Professional outsourcing works well with well-constructed physical impressions that have identifiable margins.
2) Additional considerations for suitable cases
- Stable occlusion cases with low anterior esthetic requirements
- Regular posterior restorations in which chairside adjustments are predictable
- Those that do not entail personalised artistic overlaying or sophisticated shading
3) Cases Less Suitable or Requiring Extra Evaluation
Some of the more difficult to outsource or potentially pre-approved restorations are due to technical complexity or the sensitivity of the material:
- High-noble gold alloy restorations
- Demands expert manipulation, accuracy of casting, and finishing skills.
- Complex occlusal rehabilitation cases
Multi-planar occlusal schemes, a large amount of anterior work, or special functional designs might require tighter in-house surveillance.
- Full-mouth reconstructions: Extensive clinician-technician cooperation is required in highly individualised treatment plans.
- Cases with incomplete bite records or unclear preparations: Absence or lack of clarity of data is very likely to promote remakes and production errors.
- Restorations with unusual or experimental designs: Non-standard connectors, mixed materials, or special forms can surpass the normal offshore capacities.
4) Why Clear Boundaries Matter
Establishing clear boundaries:
- Minimises confusion and cross-examination
- Guarantees both the laboratory and the outsourcing partner against avoidable remakes
- Allows the supplier to offer proper pricing, dependable schedules, and quality that is predictable
- Enhances success in long-term outsourcing because it enables the workflows to be standardised and thus work efficiently
Laboratories establish the basis of predictable, low-risk, and scalable Full Cast production by clearly stating what and what cannot be outsourced.
5. Step-by-Step Workflow: How Full Cast Outsourcing Actually Works
The results in Full Cast outsourcing are based not so much on personal competence as on the clarity of the stages of production, control, and documentation. Reliable workflow is not based on the experience of the technicians; it is based on similarities, reproducible steps that minimise uncertainty, remakes and enable consistent quality when dealing with international clients.
Stage 1: Case Submission
Accuracy starts at the submission level with full and standardised information. Regardless of the method used to submit cases (digitally (STL files) or physically (impressions and bite records)), the overseas laboratory should have a clear understanding:
- Margin design and preparation details
- Occlusal intent, contacts, and bite registration
- Restoration type (crown, bridge, pontic configuration)
- Bridge span, connector positions, and any implant involvement
Key inputs that materially affect success include:
- Definition of margin, depth and type of finish line
- Bite record or antagonist information of occlusal verification
- Occlusal and contact preferences (light contact, functional contact, etc.)
- Bridge span, connector dimensions, and functional load considerations
This is the most frequent reason for downstream remakes and production delays because of missing or ambiguous information at this stage. Laboratories with designed forms of submission of cases minimise the process of clarification and have faster and error-free production.
Stage 2: Design Review and Validation
Instead of shifting directly to production, professional suppliers stop at the design phase to prove feasibility. Reviewing this ensures that all technical requirements can be met before casting any metal, avoiding the need to make costly corrections afterwards.
Typical review tasks include:
- Reviewing margin transparency and preparation sufficiency
- Checking the path and space clearance of bridges or multi-unit restorations
- Assessing the occlusal clearance and any possible interferences
- The measurability of the connector dimension in structural integrity during occlusal load
Additional best practice: There are laboratories that offer a digital mock-up or 3D design approval phase to the client. This minimises miscommunication, and the functional and aesthetic expectations are well understood before production is done.
Stage 3: Casting, Finishing, and Pre-shipment Control
After verification, the case is cast, finished, and quality checked. In Full Cast restorations, the following stage has priority:
- Internal fit: Making sure that it fits accurately into the prepared tooth or abutment
- Structural integrity: Connector thickness, wall strength and metal density are sufficient
- Functional accuracy: Proper contacts, occlusal fit, and insertion route
- Surface finishing: Appropriate surface polish without excessive reduction of margins
Embedded QC checks include:
- In-house checks at critical stages of casting
- Bridge connector strength verification
- Pre-packaging functional and marginal fit determination
Multi-stage QC will ensure that defects do not make it to the final shipment, and outsourcing will become a system with better control and reliability as opposed to a high-risk system with a single point of inspection.
Stage 4: Shipping and Post-delivery Feedback (Optional but Recommended)
Professional outsourcing processes, though not always emphasised, have post-shipment inspections and feedback:
- Monitoring deliveries to improve on-time delivery
- Client testing of fit and function
- Noting any small process improvement modifications
This is the last stage that comes as a loop, which allows objectively improving and giving actionable data to use in the case in the future, which is particularly useful in long-term outsourcing partnerships.
6. Turnaround Time: Breaking Down the Real Delivery Cycle
Turnaround time is not a value; it is rather the outcome of several synchronised processes. Clients who consider outsourcing based on the claimed speed of production tend to ignore the point of delay.
| Stage | Description | Typical Duration |
| Case review & confirmation | Design validation and clarification | 0.5–1 day |
| Production | Casting, finishing, internal QC | 2–4 working days |
| International shipping | Express logistics & customs | 3–7 working days |
| Total turnaround | Door-to-door average | 7–10 working days |
Practically, the greatest time wastes are incurred in the clarification cycles than in production itself. The above timeline is stable and predictable when the information about the case is full, and the responses are in time.
In the case of laboratories and clinics, predictability is better than speed marginal gains since it can be incorporated in the usual schedule of delivery without interruption.
7. Pricing Guide: What You Are Really Paying For
Full Cast outsourcing pricing is not always understood as something easy; however, seasoned purchasers understand that unit price is not the sole indicator of the total price. Knowing the pricing arrangement will prevent the occurrence of concealed inefficiencies.
Core Cost Drivers in Full Cast Outsourcing:
- Alloy type (non-precious alloys offer the highest stability)
- Unit count (single crowns vs bridges)
- Case complexity and connector design
- Involvement of implants, where needed
- Re-responsibility and policy transparency
Whereas non-precious Full Cast restorations tend to be price-sensitive, the cost-effectiveness of these restorations depends more on the price-reliability over time than on the discounts. Suppliers who change their prices often or have high volumes of remakes tend to add to the total cost of operations, even though they have low nominal prices.
The real worth of outsourcing from a management point of view is the predictability of costs per success case rather than the lowest price quoted. With the consideration of efficiency in communication, handling of remakes, and stability of delivery, pricing is a variable that can be controlled and not a repeat risk.
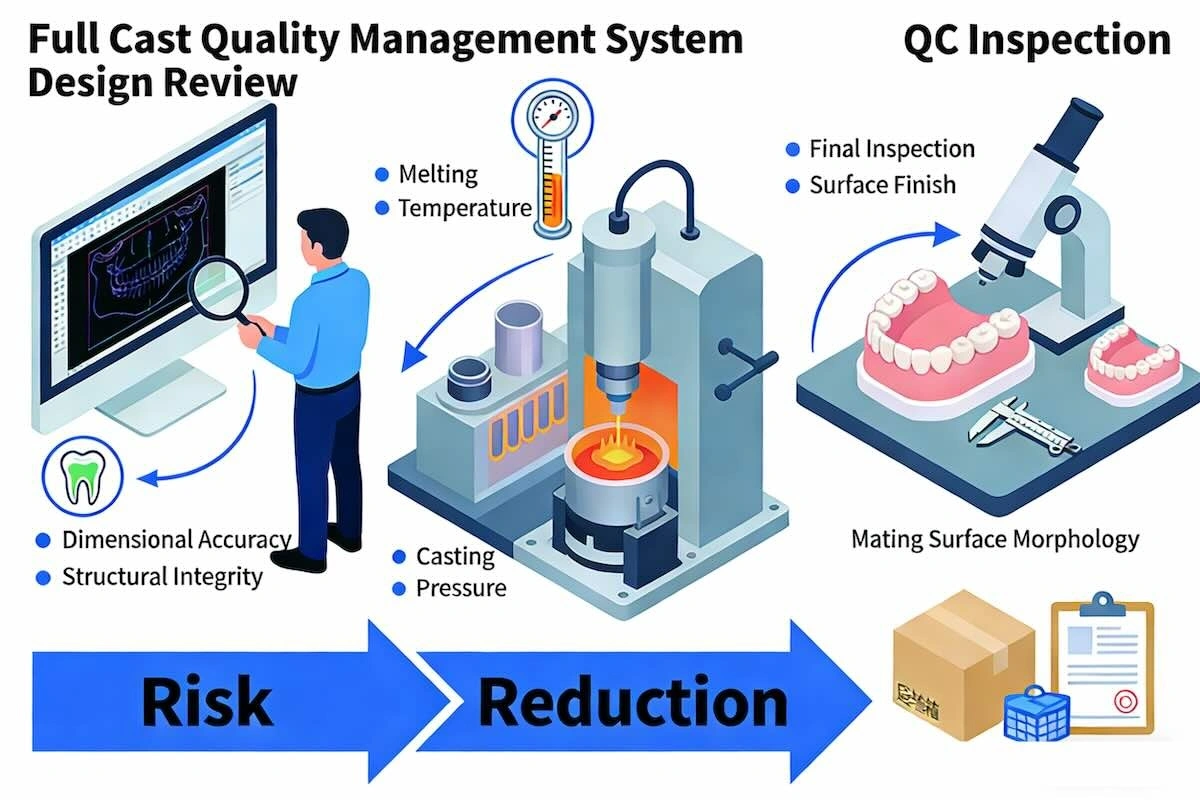
8. Quality Control Systems: How Professional Outsourcing Manages Risk
Quality in B2B dental outsourcing is not something that comes at the end of production. It is a thing that has to be planned in the process. This difference is particularly significant when Full Cast restorations are involved, with the mistakes made at the beginning being hard or impossible to fix later.
An outsourcing partner of Full Cast (professional) does not have a single final inspection. Rather, quality control is spread over various steps, each of which is aimed at detecting a certain type of risk.
(1) Design-stage control
A review of the case before production starts is to ensure clarity of the margins, occlusal clearance and structural feasibility. This measure avoids the problems of design-related failures, which are the most expensive to remedy once cast.
(2) In-process control
Internal fit and structural integrity are checked in the process of casting and finishing. In the case of bridges, connector dimensions and strength are verified to make sure that they can last over time due to occlusal load.
(3) Pre-shipment control
Restorations are also subject to a last functional check before dispatch, which pays attention to margins, contacts, and the condition of the surface. This measure will make sure that what is shipped is what has been approved.
Instead of increasing the time, this tiered QC methodology minimises overall turnaround uncertainty through avoiding rework and remakes. This quality control by system is what renders outsourcing scalable and not fragile to international clients.
9. Communication Requirements: Reducing Remakes Through Clarity
In Full Cast work outsourced, the majority of remakes are not due to technical incompetence. They are brought about by assumptions made on both sides of the partnership. Effective communication is not a soft skill; then, it is technical.
The ambiguity poses a risk to the supplier. On the part of the client, communication failure will cause frustration and time wastage. Standardisation is the most effective way of removing this gap in the most successful outsourcing relationships.
Information That Should Always Be Explicit
- Margin location and clarity expectations
- Occlusal scheme (light contact, firm contact, opposing dentition considerations)
- Proximal contact tightness preference
- Bridge span and connector expectations
- Any deviation from the routine laboratory procedure
In addition to the information itself, the timeliness of the response is also important. The time spent on design confirmation usually consumes more time than production. Labs where communication is viewed as an integral component of the work process, rather than an independent one, will always have fewer remakes.
Practically, standardised prescription templates and well-established responsibility rules help to minimise misunderstandings much better in comparison to lengthy email explanations when issues arise.
10. Risks and Mitigation: What Can Go Wrong—and How It Is Controlled
There is never a risk that is not created by outsourcing. Professional purchasers are recognising this initial net present value instead of believing that risk can be avoided. The distinction between the failed and successful outsourcing is in the manner in which the risks are systematically dealt with.
Common Risks in Full Cast Outsourcing and Their Controls
| Risk | Typical Cause | Professional Mitigation |
| Misinterpretation of cases | Incomplete instructions | Standardised prescriptions & design confirmation |
| Inconsistent quality | Technician variability | Process-based QC and stable teams |
| High remake rates | Late-stage error detection | Multi-stage quality control |
| Delivery delays | Communication lag or customs | Defined timelines and logistics planning |
| Cost overruns | Unclear remake policies | Written responsibility agreements |
With such controls in place, outsourcing risk can be measured and handled. Without them, even technically competent suppliers are likely to have difficulties with providing consistent results. This is not zero risk but foreseeable results in the normal operation conditions.
11. How to Choose the Right Full Cast Outsourcing Partner
An outsourcing partner is not a buying decision but an operational decision to make. The wrong partner will hardly fail instantly. Rather, problems emerge over time, such as missed deadlines, inconsistent output, or a growing level of communication tension.
Three factors, which a good Full Cast outsourcing partner has to possess, are process discipline, transparency, and long-term consistency.
What to Evaluate Beyond Price:
- Experience in Full Cast restorations
- Well-defined production and QC processes
- Consistent teams of technicians, as opposed to turnover
- Stable turnaround performance
- Clear and fair responsibility policies
Numerous foreign labs prefer Bestodental not due to the fact that it is the cheapest, but rather because it provides regulated working processes, achievable promises and regular performance. In the long run, these considerations are much more important than cost benefits in the short term.
The correct supplier is like a kind of continuation of your lab- he works within prescribed parameters and does not have to improvise on a case-by-case basis.
12. Who Should Outsource—and Who Should Not
Full Cast outsourcing works best in cases where laboratory or clinic operations are congruent with standardisation, predictable volume and well-defined communication guidelines. To put this into action, we can divide it into practical categories:
1) Laboratories or Clinics That Should Outsource
- High-volume posterior restorations: Full Cast crowns and bridges in molar areas are repetitive and technically stable, thus they can be an ideal restoration to outsource without high involvement in-house.
- Cost-controlled treatment plans: The outsourcing will enable predictable unit costs and assist the laboratories in operating within budgets without having to employ permanent staff.
- Unified workflow functions: The established case documentation, clear impression procedures, and electronic workflows reduce the number of errors and maximise efficiency.
- Scalable production needs: Through outsourcing, laboratories can increase capacity when the demand is high, but they do not have to invest in new casting equipment or manpower.
2) Laboratories or Clinics That Should Not Outsource
- Highly individualised rehabilitations: Full-mouth restorations, elaborate occlusals, or esthetically demanding cases in the anterior can be more closely monitored in-house.
- Ad hoc or inconsistent communication: Operations with no standard prescription templates or structured feedback channels are likely to be delayed and remade when dealing with external partners.
- Limited internal documentation or digital readiness: The practices that are more based on informal notes or a lack of uniformity in the quality of impressions impose unnecessary risk in sending the cases to other countries.
3) Key Principle for Success
The success of outsourcing occurs when systems match systems. This is not aimed at substituting internal capabilities but rather to expand them reliably. With well-defined boundaries, responsibilities, and feedback, Full Cast outsourcing can become a predictable, consistent part of the workflow and not a risky experiment in the laboratory.
13. Full Cast Outsourcing FAQs
Questions normally go beyond cost and geography in the case of Full Cast outsourcing in the case of laboratories. The following frequently asked questions will help decision-makers to evaluate the feasibility of the long-term cooperation and onboarding the supplier more clearly by considering the practical issues that may arise in supplier evaluation.
(1) Is Full Cast outsourcing safe in China?
Yes- when dealing with laboratories that have demonstrated a track record of export experience, have developed quality control mechanisms and are conversant with international standards of dentistry. The capability of suppliers and process discipline are much more important than location.
(2) Is it reliable to outsource digital cases?
Absolutely. The use of STL-based workflows is the norm. The majority of professional suppliers assist with the process of digital impression intake, margin verification, and design verification before they go to print.
(3) What is the norm of dealing with remakes or adaptations?
Remake responsibility, applicable scenarios, as well as turnaround timelines are defined in advance by reputable partners. Clearly defined policies on remakes are a major sign of a developed outsourcing operation.
(4) What is the guarantee of occlusion in Full Cast outsourcing?
Professional suppliers are standardised in their parameters of occlusal design and based on calibrated CAD libraries and milling guidelines. Further elimination of the risk of adjustment is achieved through clear bite records and case instructions.
(5) How long does Full Cast cases take to turn around?
Work flows are usually smooth, and this ensures that production timelines remain stable. Outsourcing may be combined with consolidated shipping, which would provide predictable lead times that can be used in regular restorative planning.
(6) Is it possible that outsourcing suppliers can make the quality long-term and consistent?
Yes–so long as the partnership is constructed on predefined specifications, repetition of workflow and continuous performance review. System alignment brings with it long-term consistency rather than one-time transactions.
14. Conclusion
Outsourcing Full Cast crowns and bridges to China is not a trial-above-the-line business decision anymore–it is a business strategy. It provides predictable quality, scalable capacity and sustainable cost control when enabled by well-defined boundaries of cases, structured workflow and disciplined supplier management.
It is not the location of the production that matters most, but the efficiency with which there is governance of the production. Labs which control the data of cases, communication standards and quality benchmarks record positive results all the time.
To minimise operational risk and allow laboratories to grow without losing reliability and clinical trust, collaborating with an established provider of Full Cast outsourcing services, like Bestodental, is a strategy that can greatly decrease the risk of operations and still ensure growth.