Outsourcing removable dental restorations has been a strategic move, rather than an experiment, to save money. Flexible dentures are the most convenient example of a category of removable prosthetics that can be manufactured in an offshore setting since they have material properties, standardized workflows, and are in high demand.
The guide is aimed at the dental laboratory and clinics interested in getting a clear, organized, and realistic picture of how to outsource the flexible partial dentures to China- what works, what does not, and how to do it safely and effectively.
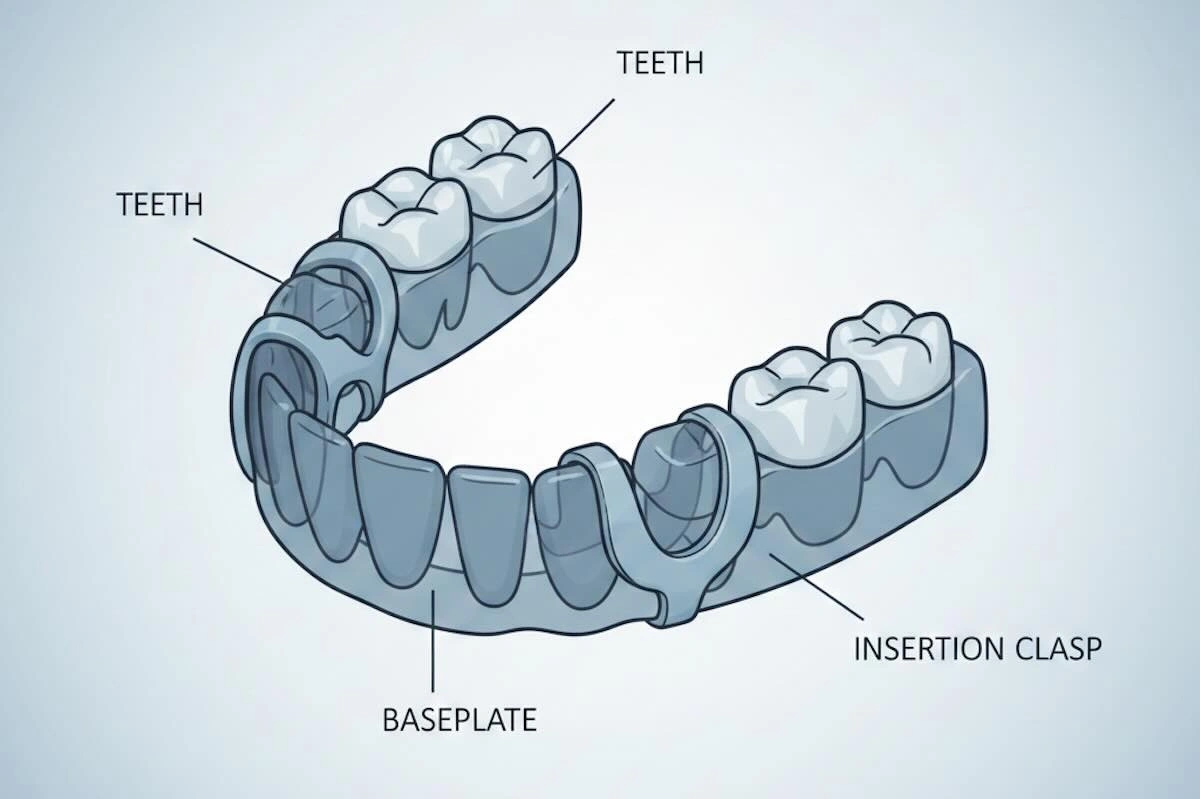
1. What Are Flexible Dentures?
Flexible dentures are removable partial dentures that are designed using thermoplastic resin materials rather than the usual acrylic (PMMA) or metal frameworks. The popular ones are nylon-based resins or polyamide resin, which offer great flexibility, strength against fractures, and better patient comfort.
Flexible dentures do not have any metal clasp as opposed to conventional removable dentures. Retention is done by the use of flexible gingival-colored extensions that hook into natural undercuts. This contributes to their visual discretion and better acceptance by patients who are aware of esthetics.
Clinically, flexible dentures are frequently ordered to treat:
- Allergic patients to metal
- Cases in between, transitional cases
- Incomplete edentulism and natural teeth
- Comfort- and esthetic-oriented patients
Although it is not a universal substitute for cast metal structures, flexible dentures are taking a well-known and increasing niche in contemporary prosthodontics.
2. Why Are Flexible Dentures Suitable for Outsourcing?
The structural characteristics of flexible dentures make it a good outsourcing option because of its logic of production (repetitive) and material-driven.
First, the manufacturing process is very standardized. After impressions, bite registration, and tooth setup have been verified, the manufacturing process adheres to a foreseeable injection or pressing process. The number of subjective artistic variables is lower in comparison with complex fixed restorations.
Second, demand is usually price-sensitive and high-volume. Most laboratories and clinics need a steady production, and not a tailored production. This is exactly the case with centralized production settings.
Third, flexible denture materials are not technique-sensitive as compared to layered ceramics or esthetic veneers. Offshore labs are capable of keeping their results consistent at scale with the right protocols.
Lastly, outsourcing enables domestic labs to redirect the skilled technicians to higher-margin work and retain service breadth on removable cases.

3. Why Outsource Flexible Dentures to China?
China has emerged as the world leader in the outsourcing of dental services, not only due to the presence of cost factors, but also due to the maturity of systems.
Chinese dental laboratories have taken over 20 years to develop infrastructure in cases across the globe. This includes:
- Case coordinators are English-speaking
- Digital file (STL, Exocad, 3Shape) compatibility
- Familiarity with FDA, CE, and ISO-compliant materials
- Massive disposable departments
In the case of flexible dentures, Chinese laboratories have the advantage of the material sourcing scale and specialization in the process. The possibility of high volumes per day allows maintaining the same injection parameters, color control, and optimization of the fit.
Moreover, shipping chains between China and North America, Europe, and Australia are currently streamlined to deliver dental products, and turnaround times are no longer uncertain but predictable. Outsourcing to China is not an experimental or novel solution but an industrialized solution.

4. What Can and Cannot Be Outsourced?
However, to develop trust, it is necessary to understand the limits of the scope, not only between the outsourcing partners but also between the laboratories, clinicians, and their patients. Clarity in what to outsource and what not to outsource can be considered the direct determinants of the rates of case success, number of remakes, and the stability of long-term cooperation in the case of flexible denture outsourcing. Mature outsourcing is characterized by not purporting to have infinite capability, but by recognizing technical and procedural boundaries.
1) What Can Be Outsourced
- Flexible partial dentures (unilateral or bilateral)
- Tooth arrangement depending on the given bite and shade
- Try-in frameworks
- Relines and repairs (case-dependent)
- Electronic design of scan impressions
To conclude, the cases where outsourcing is applicable have certain similarities: they are well-documented, their anatomy is predictable, and the logic of fabrication is standardized. Such cases play to the offshore benefits of volume efficiency, process consistency, and material expertise, and thus, outsourcing is not only a possibility but a strategic benefit.
2) What Should Not Be Outsourced
- Cases in which there is a need for chairside adjustment logic
- Very volatile occlusal plans without definite instructions
- Emergency same-day cases
- Ineffective impressions or records of poor quality
The history of outsourcing has proven over and over again that the majority of failures are not related to the quality of manufacturing, but to the selection of a case. Outsourcing cases involving high clinical interaction or quick iteration usually kills all the very advantages outsourcing is supposed to offer.
Effective flexible denture outsourcing does not require stretching of technical boundaries and coercing inappropriate cases into offshore processes. Rather, it relies upon rigorous case screening, an outspoken definition of capability, and adherence to process boundaries.
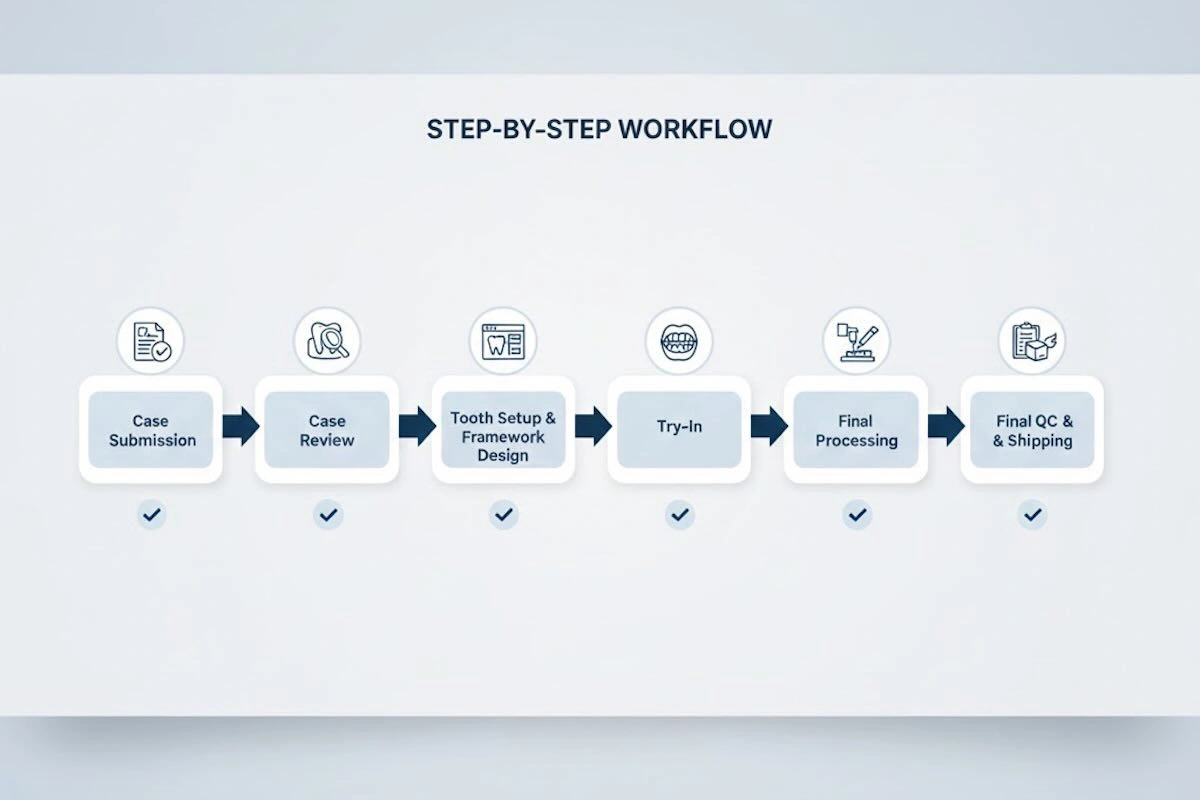
5. Step-by-Step Outsourcing Workflow
The most significant aspect of a successful flexible denture outsourcing is a controlled and well-documented workflow. In contrast to fixed restorations, flexible dentures rely heavily on the undercut management, path planning of insertion, and material behavior, and so, every stage of the outsourcing process has functional implications. A step-by-step production process is not merely a production chain–it is a risk management framework that makes offshore production look like an extension of local production.
Step 1: Case Submission – Defining the Foundation
The workflow of outsourcing starts way before the fabrication, at the stage of submission of cases. Accurate and complete records are required in the case of flexible dentures because the retention system depends on controlled interactions of natural undercuts as opposed to fixed structures.
An entire submission normally consists of:
- Physical impressions or intra-oral scans (STL files) having distinctly defined undercut zones
- Vertical dimension and occlusal relationship registered by bite
- Shade data of the denture base and teeth
- Selection of tooth molds or reference photos
- Written instructions of design, such as aesthetic priorities and retention expectations
At this point, the outsourcing lab is not producing anything yet; it is doing an evaluation of feasibility. The most important preparation step is to ensure that incomplete or ambiguous data is remade downstream because this is the most critical step in the preparation.
Step 2: Case Review – Technical Feasibility and Risk Screening
After the case is received, a structured review of the case is carried out by the Chinese laboratory. This action is often overlooked by new outsourcing clients, but where most of the possible failures are avoided.
Key review points include:
- Analysis of the undercut depth and dispersion to ascertain the suitability of the flexible materials
- Identification of the most desirable course of insertion to provide the balance of retention and patient comfort
- Comparison of tissue support and clasp design options
- Case anatomy and functional demand material suitability analysis
The lab should seek clarification on anything that is identified as wrong, like too many undercuts, ambiguous insertion paths, or inconsistent instructions, and so on. This premature communication is actually an indication of professional maturity, rather than delay.
Step 3: Tooth Setup and Framework Design – Translating Instructions into Structure
Upon approval of cases, the setup of teeth and framework commences. In the case of a flexible denture, this is a very delicate step since it is here that retention, comfort, and esthetics are all to be established.
Depending on the workflow, design may be:
- Simulated by the digitally transferred method, with the simulation of insertion path and clasp flexibility performed by means of CAD software.
- Manually performed, and on a case-by-case judgment of technicians in the event of traditional impressions.
During tooth setup, technicians consider:
- Occlusal harmony with alveolar residuation dentition
- Midline positioning and esthetics
- Distribution of functional loads to prevent stress concentration
An effective installation reduces the need for further correction and makes the flexible material work as desired.
Step 4: Try-In (Optional but Strategically Important)
Although not applicable to every case, try-ins are essential in risk management in complex or aesthetically challenging cases. A try-in will provide a chance to verify clinically prior to irreversible processing.
Try-ins are especially suggested in case:
- Occasional relations are doubtful
- The expectations of esthetics are high
- The anatomy of the patients is asymmetrical or damaged
At the try-in phase, clinicians will be able to evaluate fit, retention, occlusion, and esthetics, which is able to be integrated before final fabrication. This will take time, but it will go a long way to decrease the chances of remakes during the last stage.
Step 5: Final Processing – Material Execution and Finishing
After the design or try-in is accepted, final processing starts. Injection molding or pressing are generally used to make flexible dentures, with temperature and pressure control being very important.
This stage includes:
- Controlled injection and preparation of material
- To maintain dimensional stability, the flask was cooled and deflasked
- Trimming, contouring, and polishing to obtain tissue comfort and esthetic finish
Mature laboratories are concerned with not just fit, but also surface smoothness and flexibility of the clasp, which directly influence the acceptability of the device by patients and durability.
Step 6: Final Quality Control and Shipping – Ensuring Deliverability
The final quality control process is done on the denture before shipping. It is not a visual check as such but a functional check.
QC typically covers:
- Consistency of occlusal contacts
- Path validation, retention, and insertion
- Finish of the surface and edge comfort
- Accuracy and aesthetic display of shade
The case is only packaged and shipped after the QC, and with traceable international logistics.
This process, based on a step-by-step workflow, does not merely give a moment of visibility; it establishes a point of correction, communication, and confirmation. In flexible denture outsourcing, the success is not based on the location of the denture being fabricated but on the manner in which the workflow has been organized and handled.
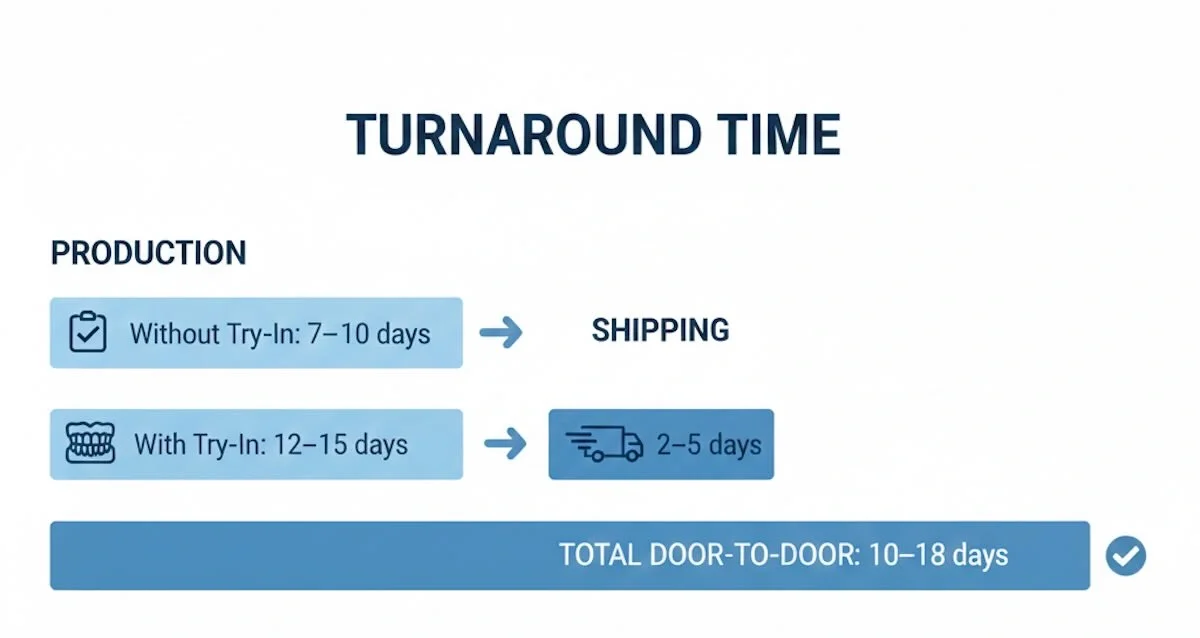
6. Flexible Denture Turnaround Time: What to Expect and What Affects It
One of the most often mentioned issues in the flexible denture outsourcing is the turnaround time, and it is one of the most misconceived as well. Most buyers are just concerned about the number of days offered by a supplier without really understanding what they entail, what they do not entail, and what variables really affect the speed of delivery. In the case of flexible dentures, the turnaround time is not a given promise- it is the output of the regulated production and communication process.
A typical outsourcing situation would have a production timeline of flexible dentures in China that would typically be in the following ranges:
- No try-in cases: around 7-10 working days of laboratory production
- Try-in cases: about 12-15 working days working on the cases, including the fabrication and clinical tests
- International freight: normally 2-5 calendar days by express courier
Turnaround time may be increased or decreased by a number of factors, but the most determining factor is the clarity of the case submitted. Laboratories run without any trouble when complete impressions or clean digital scans are provided, there is an accurate bite registration, and the instructions to the design are clear. Conversely, the absence of data or unclear information about occlusal tends to lead to delays as clarification is sought.
The other significant variable is the use of a try-in. Even though try-ins increase the duration of the production cycle, they often save time on the total delivery time through avoiding remakes, especially in the case of flexible dentures, where there is increased esthetic or occlusal sensitivity.
Seasoned vendors are also conscious of uniformity and not the merciless pace claims. Stable and predictable turnaround performance is not determined by the occasional fast cases, but rather by the skills of providing consistent and predictable results with large volumes of cases without affecting its fit, retention, or material integrity. Realistic timelines in flexible denture outsourcing are an expression of professional control of processes and not inefficiency.
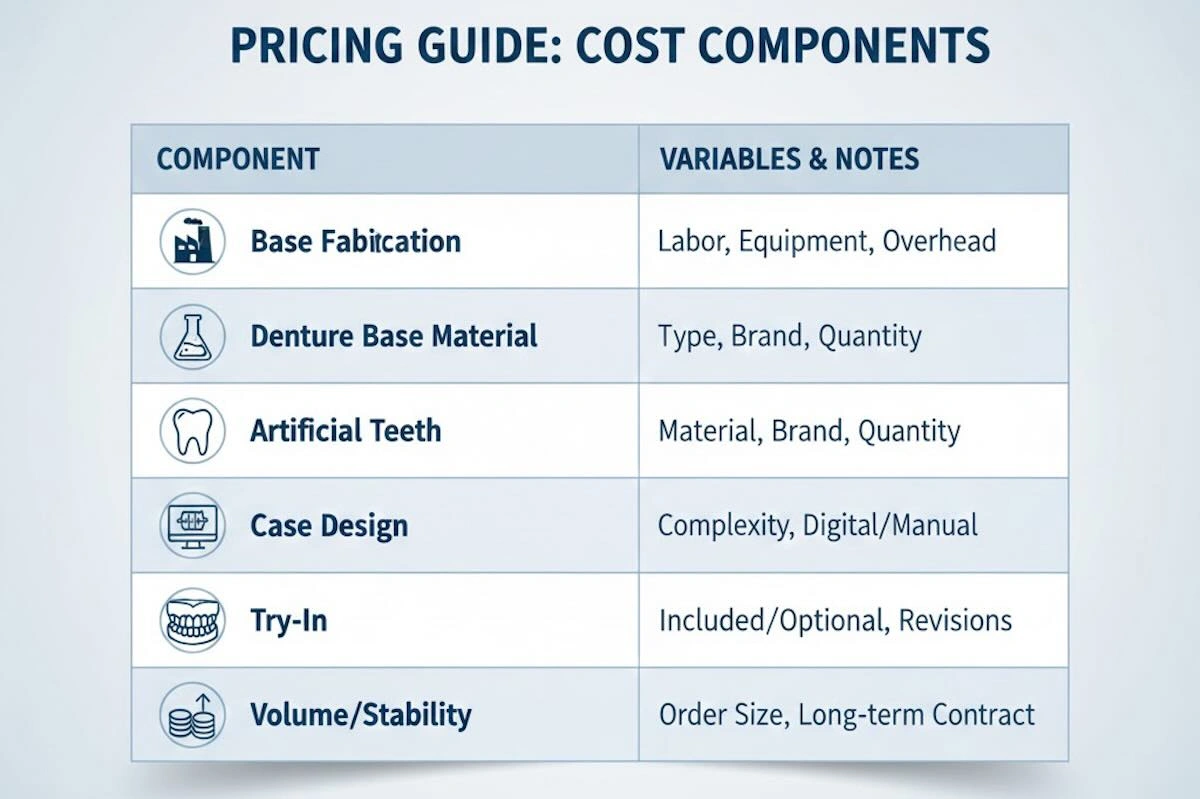
7. Pricing Guide: Understanding Cost Structure
Pricing is a significant point to outsourcing clients; however, effective assessment demands that the cost of a flexible denture should be structured correctly, and not the unit prices on their own. In professional outsourcing, pricing is a factor that represents the combination of material selection, complexity of the case, and process demands.
Flexible Denture Outsourcing Cost Structure Overview
| Cost Element | What It Covers | Influence on Final Price |
| Base Fabrication | Core labor, standard flexible material, processing | High |
| Denture Base Material | Brand, origin, flexibility grade | Medium–High |
| Artificial Teeth | Tooth brand, shade system, esthetic level | Medium |
| Case Design | Unilateral vs. bilateral partial | Medium |
| Try-In (Optional) | Additional fabrication and verification step | Medium |
| Volume Stability | Monthly case consistency | Price-stabilizing |
This table helps to show that flexible denture pricing is not fixed but variable-driven.
Chinese outsourcing is not cheap, come what may. Alternatively, the benefits of pricing are a result of specialization of labor, central material sourcing, and volumes and repeatable workflow, which reduces the per-unit costs without compromising quality or control over the process.
Base fabric costs and optional services like try-ins or higher materials must be distinctly separated by a professional pricing model, and adjustment or remake policies must be pre-defined. This transparency minimizes conflict, enhances the accuracy of budgeting, and promotes long-term relations of outsourcing.
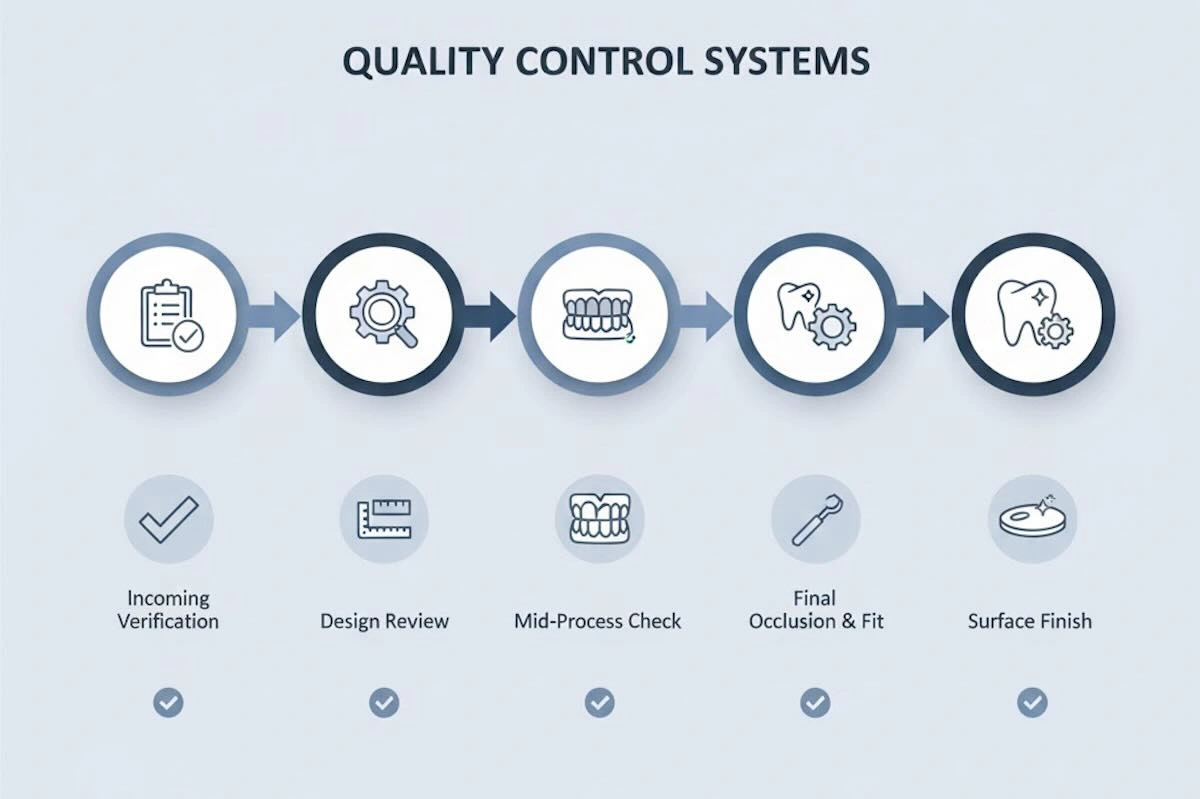
8. Quality Control Systems for Flexible Dentures: Ensuring Fit, Retention, and Consistency
B2B dental outsourcing is based on quality control with respect to the flexible dentures, where the material behavior, undercut engagement, and surface finish are directly correlated with clinical performance. In comparison to rigid restorations, flexible dentures do not allow much deviation in processing and finishing, and a structured QC system will be needed to ensure the same results.
Most Chinese dental laboratories that are reputable have multi-stage quality control systems that are tailored to removable and flexible prosthetics and usually encompass the following quality control points:
(1) Incoming Case Verification
Case data is considered on receipt to ensure that there is integrity of the impression, completeness of the scan, accuracy of the bite registration, and clarity of the prescription. Obvious risks, like a lack of knowledge of where to be inserted or a lack of knowledge of undercut information, are identified before production.
(2) Inspection (Design and Set-Up) at Mid Process
Technicians ensure that there is an occlusal alignment, retention area position, and esthetic position in the process of tooth setup and framework design. This is crucial to the sensitive flexible dentures because the errors in design cannot be corrected completely once the injection processing is done.
(3) Final Occlusal and Fit Check
The dentures made are tested on the consistency of the occlusal contacts, carefulness of insertion path, and stability balance to ensure that the dentures do not press on the abutment teeth or soft tissues too hard.
(4) Surface Finish Inspection/Visual
The quality of the smoothness and polish of the edges, clasps, and tissue contacts is checked. Surface finishing helps to minimize irritation and enhance patient comfort, particularly with flexible materials.
Documentation, case photography, and internal QC checklists are some of the stages that support these stages and establish traceability and accountability. This QC framework would turn flexible denture outsourcing into a perceived risk and a repeatable, controllable production system when applied continuously.
9. Communication Requirements for Flexible Denture Outsourcing: Reducing Remakes at the Source
When quality control is the governing factor on what occurs within the laboratory, the communication is what controls what occurs before production starts. In flexible denture outsourcing, the remakes are not mostly as a result of manufacturing defects, but rather are a result of incomplete, inconsistent, or unclear clinical instructions. Because flexible dentures are based on the strict logic of undercut engagement and insertion, the errors of communication are frequently magnified instead of being absorbed.
The following communication needs will be necessary to reduce remakes and problems with the adjustment:
- Well-defined Insertion Path Directives: Controlled undercut engagement is used in flexible dentures. Clear instructions on the intended direction of insertion assist technicians to come up with retention spaces that are stable and comfortable.
- Specified Esthetic Preferences: Guidelines are to be used to explain whether it is esthetics, retention, or comfort that should be the main consideration, particularly in anterior or high-visibility cases.
- Confirmed Occlusal Scheme: The opposing dentition conditions, the occlusal relationships, and the functional expectations should be clearly mentioned to avoid setup assumptions.
- Formed Prescriptions: Structured forms minimize risks in interpretation and make sure that all important data is always given.
- Quick Response to Lab Requests: A quick clarification will avoid a production stall and minimize the chances of a technician making unilateral decisions.
Communication in FDO is not an administrative assignment, but a technical necessity, which has a direct connection to clinical outcomes.

10. Risks and Mitigation Strategies in Flexible Denture Outsourcing
Despite the systems of quality control and the explicit procedures of communication, some risks can be determined with flexible denture outsourcing. Professional outsourcing does not overlook these risks; it addresses these risks with well-planned mitigation measures. The table below indicates the most common types of risks and their respective control measures.
Flexible Denture Outsourcing Risk & Mitigation Matrix
| Risk Category | Typical Root Cause | Mitigation Strategy |
| Fit Discrepancies | Incomplete impressions, unclear insertion path, and undercut misinterpretation | Pre-production case review, clear insertion path instructions, and pilot cases |
| Occlusal Inaccuracies | Inaccurate or missing bite registration, unclear occlusal scheme | Mandatory bite verification, try-in for complex cases |
| Esthetic Mismatch | Vague shade or tooth setup instructions | Defined esthetic priorities, tooth setup confirmation, or try-in |
| Retention Issues | Over- or under-engagement of undercuts | Experienced in flexible denture design, mid-process design inspection |
| Shipping Delays | Logistics disruptions, incomplete documentation | Buffer scheduling, reliable courier partnerships |
| Remake Disputes | Undefined responsibility boundaries | Clear remake and adjustment policies agreed in advance |
This risk matrix shows that the majority of outsourcing risks are process-based as opposed to manufacturing-based. With quality control (Section 8) and communication discipline (Section 9) well put in place, the risks that will remain will be able to be predicted and controlled as opposed to being reactive.
Professional flexible denture outsourcing is not about risk avoidance, but rather about developing a reproducible control system that can reliably produce consistent results on scale.
11. How to Choose the Right Supplier for Flexible Dentures
Choosing an appropriate supplier defines over fifty percent of the outcomes in outsourcing since the quality of production, the reliability of workflow, and the work communication practice are all influenced by the laboratory partner. The right supplier will make outsourcing more than a logistical convenience; it will be a reliable and quality extension of your practice.
These are some of the criteria that are especially important when considering potential partners.
- Flexible dentures specifically make it possible to be familiar with the undercut management, path of insertion, and material
- A stable QC system ensures multi-stage inspection and traceability
- Open communication eliminates remakes and enables quick explanation of design or bite problems
- Volume capacity will ensure that small and large case batches will be accommodated immediately
- Lastly, long-term partner mentality means that the supplier is focused on collaboration, optimization of processes, and responsibility, not just of one transaction
Suppliers such as Bestodental are different in that they do not just fabricate. They combine formalized QC, standardized digital processes, and proactive communications to reduce risk. The approach of managing and collaborating flexibly in denture outsourcing by Bestodental makes sure that foreign partners can count on quality, predictable schedules, and scalable output, all of which are essential in achieving long-term success.
12. Who Should and Should Not Outsource Flexible Dentures?
It is also worth knowing what forms of laboratories and clinics will be best served by the flexible denture outsourcing before deciding to outsource. There are cases when outsourcing may not be the right choice.
(1) Suitable for Outsourcing:
- Labs that have a large removable volume and that must maximize workflow and minimize work on the in-house side
- Clinics that want to be cost-effective and at the same time maintain a steady quality of services
- Predictable case flow practices that can plan production lead times
(2) Not Suitable for Outsourcing:
- Urgent-based clinics that need immediate or extremely fast turnaround
- Prosthetics with very experimental designs requiring iteration in the chairside
- The situations when urgent changes are required, or the process is unpredictable
Outsourcing is a tactical device and not an omnipresent solution. Its efficiency lies in the matching of types of cases, production schedules, and clinical needs with offshore capacities. It provides efficiency, scalability, and consistency of quality when well applied, but mismatched expectations can result in delays, remakes, or compromised results.
13. Flexible Denture Outsourcing FAQs
There are common questions that dental professionals ask themselves in the case of flexible denture outsourcing. This knowledge helps to clarify expectations and make decisions.
Q1: Do flexible dentures last long to be used generally?
A: They are fracture-resistant and flexible when designed and processed with high quality, and offer long-term service when compared with traditional acrylic partials. The choice of materials and proper undercut control are some major factors.
Q2: Can there be any consistency in Chinese labs in matching tooth shades?
A: Yes. Top laboratories use standardized shade systems and digital or photographic standards, which guarantee high accuracy of color. Clinician instructions are also clear and enhance predictability.
Q3: How are remakes handled?
A: Trustworthy suppliers have a clear remake and adjustment policy, which defines the responsibilities, schedule, and acceptable deviations. This will avoid conflicts and ensure continuity in workflow.
Q4: Does it have a complete digital workflow?
A: STL-based submissions can be accepted by most modern labs, and CAD-assisted design can be done, eliminating manual interpretation errors and accelerating production without compromising quality.
Q5: Is it possible to deal with complex aesthetic or bilateral cases through outsourcing?
A: Yes, but it should be planned. Difficult cases are frequently treated using try-ins, comprehensive occlusal instructions, and mid-course QC to guarantee that the difficult cases will yield similar results with minimal chairside adjustments.
14. Conclusion
The question of whether it is possible to outsource flexible dentures to China is no longer a matter of feasibility, but a matter of finding the right partner, organized processes, and professional communication. When used wisely in terms of case selection, quality control at many phases, and straightforward guidelines, the laboratories and clinics will be able to attain cost-effectiveness, quality consistency, and scalability of production, turning flexible denture creation into a predictable operational benefit.
Bestodental provides a combined solution to practices that would like to have a partner that is knowledgeable of international standards, implements structured QC, and participates in the work of overseas teams. Through integration of technical mastery, trusted workflows, and long-term relationship philosophy, Bestodental can afford clients to outsource biflexible dentures with confidence without compromising clinical quality and patient satisfaction.