Dental veneers have become the most commonly prescribed restorations in both cosmetic and restorative dentistry, as the need for esthetic dentistry appears to be increasing worldwide. Meanwhile, the increasing costs of labor, capacity, and turnaround pressure are forcing more dental clinics and laboratories to consider outsourcing.
China has become a major outsourcing destination for dental veneers in the world. Nevertheless, cost is not the factor that should be considered when outsourcing veneers. It needs to have a clear perception of the product, the manufacturing capacities, quality control measures, the communication requirements, and risk management.
This guide is authored to assist the dental clinics, group practices, and dental laboratories in getting a complete grasp of how to outsource the dental veneers in China in a controlled, professional, and predictable manner.
1. What Are Dental Veneers?
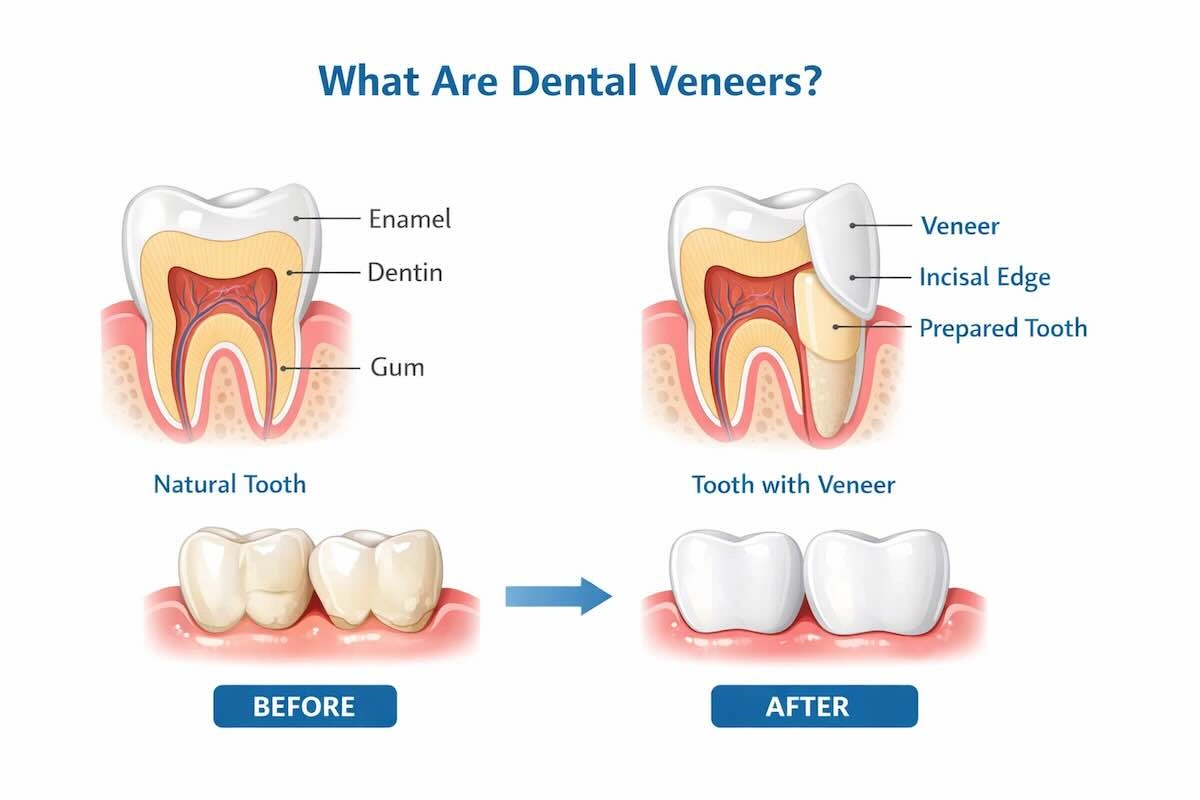
Dental veneers are slim, tailor-made restorations that are meant to cover the front side of teeth. They are more utilized to enhance the aesthetics, but they also offer functional advantages in some clinical cases.
1) Purpose of Dental Veneers
Veneers are commonly prescribed to:
- Right tooth discoloration that cannot be repaired through whitening
- Correct tooth shape, size, or symmetry
- Close small diastemas
- Reform small enamel flaws or wear
- Improve the general aesthetics of the smile
2) Common Types of Dental Veneers
Manufacturing and outsourcing veneers can be divided into the following categories based on the material:
- Porcelain Veneers: High aesthetic value, good translucency, and color stability in the long-term.
- Lithium Disilicate (E.max) Veneers: Strength/esthetics balance, which is common in contemporary cosmetic dentistry.
- Zirconia Veneers (Ultra-thin or Layered): Increased strength, where it is necessary.
- Composite Veneers (Lab-fabricated): Reduced price, increased speed, shorter lifespan.
Veneers are accurate restorations. Although they are thin, they require precision in margin control, shade matching, contouring, and surface finishing. Such demands render veneers especially sensitive to the skill and workflow discipline of technicians.
2. Why Are Dental Veneers Suitable for Outsourcing?
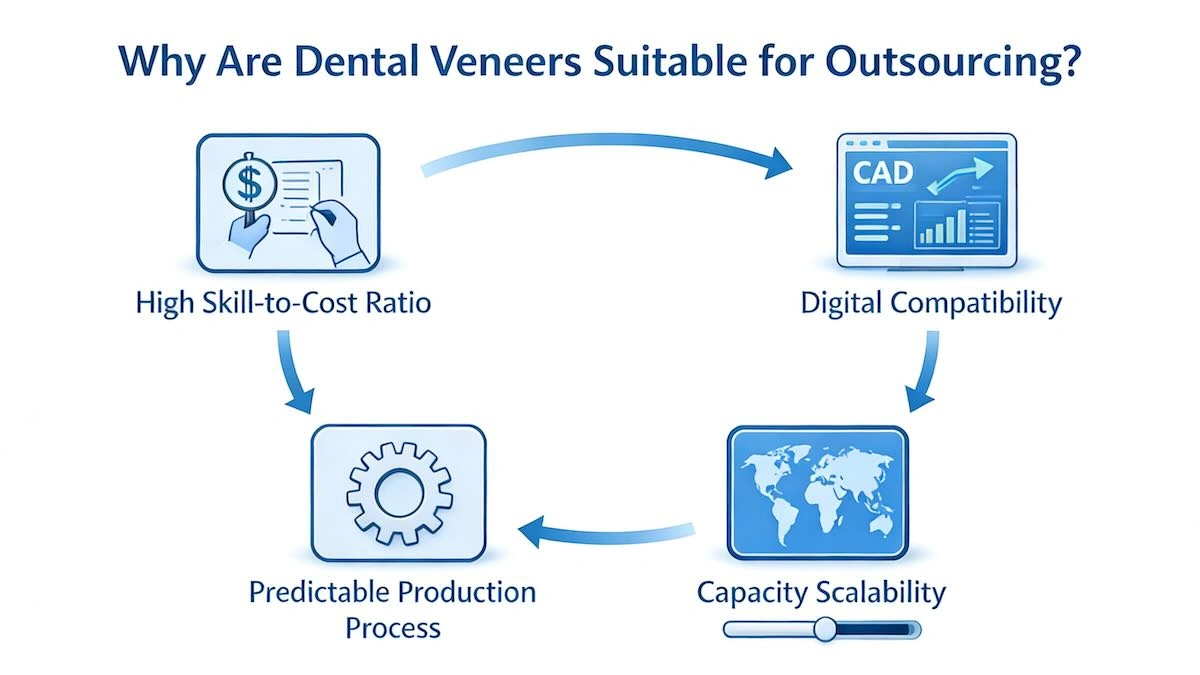
Dental products cannot be outsourced to all. However, dental veneers have a number of structural and workflow features that render them a very viable option when it comes to offshore manufacturing, provided that they are managed appropriately.
(1) High Skill-to-Cost Ratio
The contouring, overlaying, and surface finishing of dental veneers need skilled technicians, but use comparatively little material. This establishes a good balance between skills and cost, where laboratories are able to cut down on production costs without compromising aesthetic results. This benefit is even more evident in large scale in clinics and labs dealing with multi-unit veneer cases.
(2) Digital Compatibility
The contemporary veneer processes are entirely dependent on digital input like intraoral scans, CAD designs, and high-resolution reference photos. These digital files of standard can be sent across countries without any accuracy being lost, and the design intent remains the same, no matter where the production is taking place. Distance does not have much influence on the final results as long as both of the parties adhere to the same digital protocols.
(3) Predictable Production Process
After clinical preparation and design parameters have been verified, veneer fabrication is a highly repeatable process. The selection of the material, milling or pressing, layering, and glazing may all be controlled within tolerances. This predictability will greatly minimize the uncertainty and will make veneers more outsourceable than the restorations that need regular clinical feedback.
(4) Capacity Scalability
Veneers outsourcing helps clinics and labs to handle the changing volumes of cases without the need to increase staffing or equipment on-site. The capacity to produce can be changed quickly depending on the demand, especially during peak cosmetic seasons or when the business is growing fast. It is flexible and promotes operational stability in the long-term.
3. Why Outsource Dental Veneers to China?
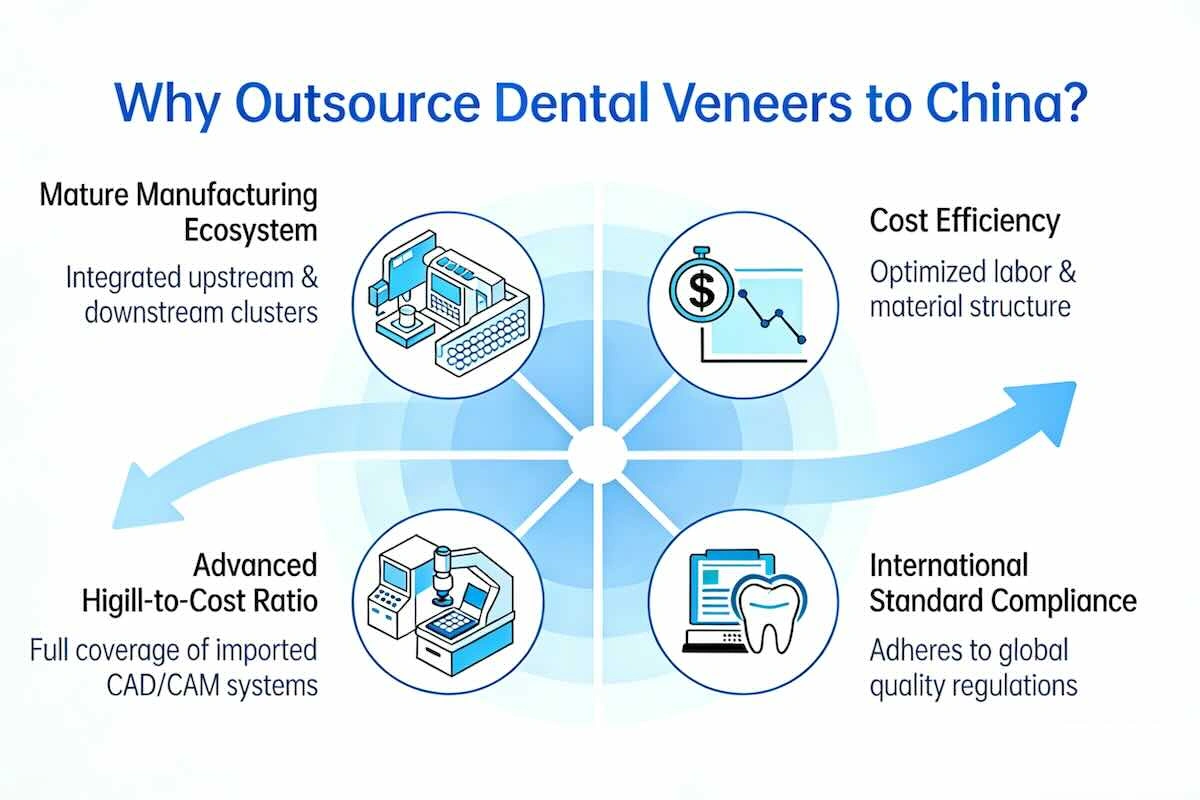
China has been transformed into one of the most established dental outsourcing destinations in the world, not coincidentally, but through the decades-old structural benefits. Long-term industrial specialization, mass training of technicians, and extensive penetration of world dental markets are the factors behind its leadership in outsourcing dental veneers, not just cost competition in the short term.
(1) Mature Dental Manufacturing Ecosystem
China has thousands of specialized dental laboratories, most of which:
- Concentrate on international outsourcing
- Work under standard work processes
- Have the long-term experience of the US, EU, UK, and Australian markets
This state of concentration of export-oriented dental labs forms a mature ecosystem whereby processes, communication models, as well as quality expectations are already pre-established with overseas clients. In the case of international clinics and laboratories, it decreases the time of onboarding and minimizes the risk that is usually tied to cross-border collaboration.
(2) Cost Efficiency Without Process Simplification
The low labor expenses in China enable the production of veneers at low costs without compromising on the materials and processes used, as long as the lab is well managed. Instead of streamlining processes, Chinese labs with more experience have retained all fabrication stages, design, milling or pressing, layering, and glazing, and are streamlining labor distribution. This is possible to allow competitive pricing without affecting aesthetic or functional standards.
(3) Advanced Equipment Penetration
Top-tier Chinese labs are equipped with:
- 3Shape, Exocad CAD systems
- High-precision milling machines
- Pressed ceramic systems
- Layering and staining departments
The technologies are not restricted to several flagship facilities alone but are popular among the export-oriented laboratories. This has opened the opportunity to have the same digital and material workflow in veneer production in China that the major Western laboratories are using, thus making the process consistent across borders.
(4) Strong Adaptation to International Standards
The Chinese outsourcing labs that are reputable are conversant with:
- FDA-compliant materials
- ISO quality systems
- Western aesthetic expectations
- English-based case communication
These labs have been serving international clients over the years, and this has helped them to adapt not only technically, but also operationally. Prescription interpretation, case feedback, and remake handling communication and quality benchmarks are becoming aware of the global dental outsourcing standards.
4. What Can Be Outsourced—and What Cannot?
Organizational boundaries of outsourcing are critical to success in the long run. In dental veneer outsourcing, technical feasibility is less of an issue and more of a predictable, remotely executable task flow. Assessment of the cases using practical decision criteria can assist clinics and laboratories to avoid unwarranted risk and stable turnaround times.
Instead of categorizing the cases based on the type of products alone, the suitability of outsourcing is more adequately determined through the review of a number of fundamental clinical and technical criteria. The table below shows the effect of these factors on the suitability of a veneer case for offshore production.
| Evaluation Factor | Favorable for Outsourcing | Unfavorable for Outsourcing | Why It Matters |
| Treatment urgency | Flexible timeline | Same-day or emergency cases | Offshore production requires defined manufacturing and shipping cycles. |
| Margin clarity | Clearly visible, well-prepared margins | Ambiguous or subgingival margins | Clear margins are essential for an accurate fit without chairside correction. |
| Occlusal stability | Stable, well-recorded bite | Inconsistent or uncertain bite | Occlusal errors are difficult to resolve remotely. |
| Esthetic definition | Clear shade, photos, mock-ups | Experimental designs without references | Esthetic predictability depends on visual and technical guidance. |
| Case repeatability | Repeat or standardized prescriptions | One-off, highly subjective cases | Repeatability reduces interpretation risk and remakes. |
| Chairside dependency | Minimal adjustment expected | Heavy reliance on real-time adjustment | Offshore workflows depend on defined remake protocols. |
Cases that fit the above favorable conditions are usually adequately suited to outsourcing since they enable the laboratories to work under controlled and repeatable parameters. In-house fabrication or local laboratories can be more beneficial in clinical control when there are several negative factors that are involved.
Through these decision criteria, clinics and laboratories will be able to assess cases of veneer more objectively and decide whether it is feasible to outsource before committing to production.
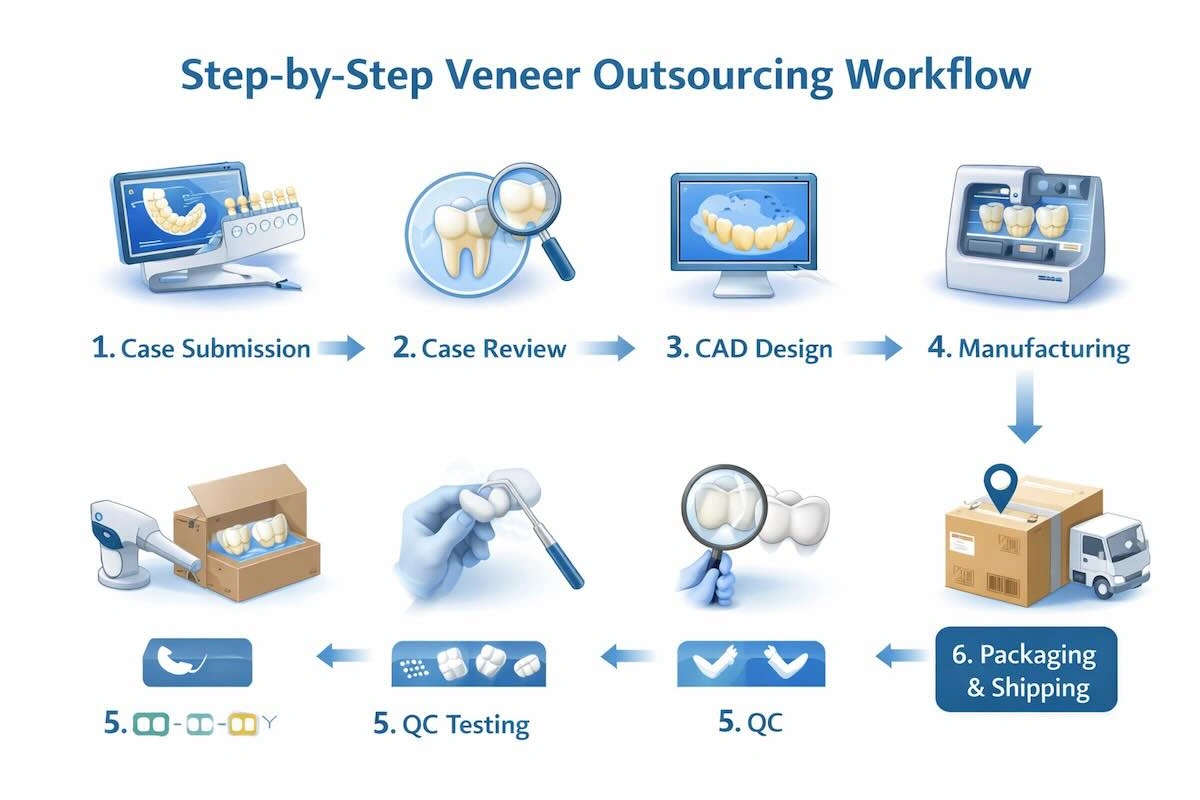
5. Step-by-Step Veneer Outsourcing Workflow
The most critical success factor in successful veneer outsourcing is a structured workflow. In reality, the failure of outsourcing is not largely due to material or equipment constraints, but a lack of clarity in process control. A clear process of work offers predictability, accountability, and consistency across borders.
Step 1: Case Submission
Proper and full submission of the cases by the clinic or laboratory marks the start of the outsourcing process. At this point, the input information on the quality of the final veneer is directly dependent on the quality of the input information.
The clinic or lab provides:
- Intraoral scans or physical impressions
- Preparation margin clarity
- Shade information
- Occlusal records
- Photos (frontal, lateral, smile, retracted)
The offshore laboratory can comprehend both the functional and aesthetic expectations comprehensively through high-resolution scans, clearly defined margins, and extensive photographic reference. Any missing or erratic inputs in this stage tend to result in downstream rewrites/remakes, although the actual manufacturing might be technically flawless.
Step 2: Case Review & Feasibility Check
After receiving the case, an internal feasibility review by the Chinese laboratory is then done, followed by production. This is not merely a formality but a filtering mechanism of critical risk.
The lab evaluates:
- Margin clarity
- Thickness feasibility
- Occlusion risk
- Esthetic expectations
In case something may go wrong, e.g., the reduction is not adequate, the thickness demanded is unrealistic, or the esthetic objectives are not clearly defined, the potential problems are flagged and reported to the client before the start of production. The initial intervention at this level avoids unnecessary delays and guards the clinical outcomes and turnaround time.
Step 3: CAD Design
Upon approval of a case, the veneer goes through a digital design process. The CAD design converts clinical intent into accurate manufacturing data and forms the technical basis of all further steps.
Design parameters include:
- Veneer thickness
- Emergence profile
- Contact points
- Incisal edge design
In simple cases, design is based on set parameters. In complicated cases of esthetics or smile designs, design confirmation can be ordered to verify alignment before fabrication. This step will help to avoid subjective interpretation and minimize the chances of aesthetic mismatches.
Step 4: Manufacturing
The production process is based on the material and aesthetic needs chosen. Technical consistency and technician expertise is equally important at this stage.
Depending on the material:
- Milling or pressing
- Layering or staining
- Polishing and glazing
Well-structured outsourcing labs have standardized fabrication procedures and permit limited input of technicians to add esthetic layers and surface characterization. The requirements of stable and repeatable quality of veneer include the maintenance of full production steps instead of streamlining the processes.
Step 5: Quality Inspection
Veneers are subjected to an internal quality check before shipment in order to determine compliance with predefined technical and esthetic standards. This is especially necessary in the offshore production where chairside correction is not readily available.
Internal QC verifies:
- Margins
- Fit
- Shade consistency
- Surface quality
Multi-level inspection is to indicate the problems at an early stage and provide only clinically acceptable restorations for delivery. Credible labs have QC as a compulsory gateway and not an optional checkpoint.
Step 6: Packaging & Shipping
After approval, the cases are well packed to be transported internationally. Adequate labeling, record keeping, and packaging should be done to ensure that they are not damaged or mixed during transit.
Documents are shipped through international courier with the labeling of cases. Easy identification and tracking of shipments of cases assist clinics and laboratories in making bookings with confidence and to ensure consistent treatment regimes.
6. Turnaround Time: What to Expect and What Actually Matters
The turnaround time is among the most popular issues of the international clients who think of dental veneer outsourcing. What is more important than the headline figure is whether the schedule is realistic, reproducible, and in accordance with the treatment planning of the clinic as opposed to the best-case scenarios at the occasional.
1) Typical Veneer Outsourcing Timeline
In normal circumstances, veneer outsourcing to China has a well-defined time framework:
- Veneer production: 3–5 working days, this encompasses CAD design, milling or pressing, layering or staining, and final finishing, depending on the chosen material and aesthetic needs.
- Quality control and packing: 1 working day, finished cases are checked internally, documented, and packed to be shipped.
- International shipping: 3–5 working days. The time of delivery will vary depending on the country of delivery, the courier service, and the efficiency of the customs clearance.
2) Total Turnaround Time
The overall turnaround time in most of the routine cases is between 7 and 10 working days, depending on the complexity of the case and logistics. The more complicated aesthetic scenarios or design confirmations can be more time-consuming, and the repeat cases that have parameters established can be faster.
It is also worth mentioning that trustworthy outsourcing partners are concerned about the consistency of the timeline rather than an aggressive promise. Reliable delivery allows clinics and labs to book appointments with certainty, and in the long run, this is more important than short-term, marginally fast delivery.
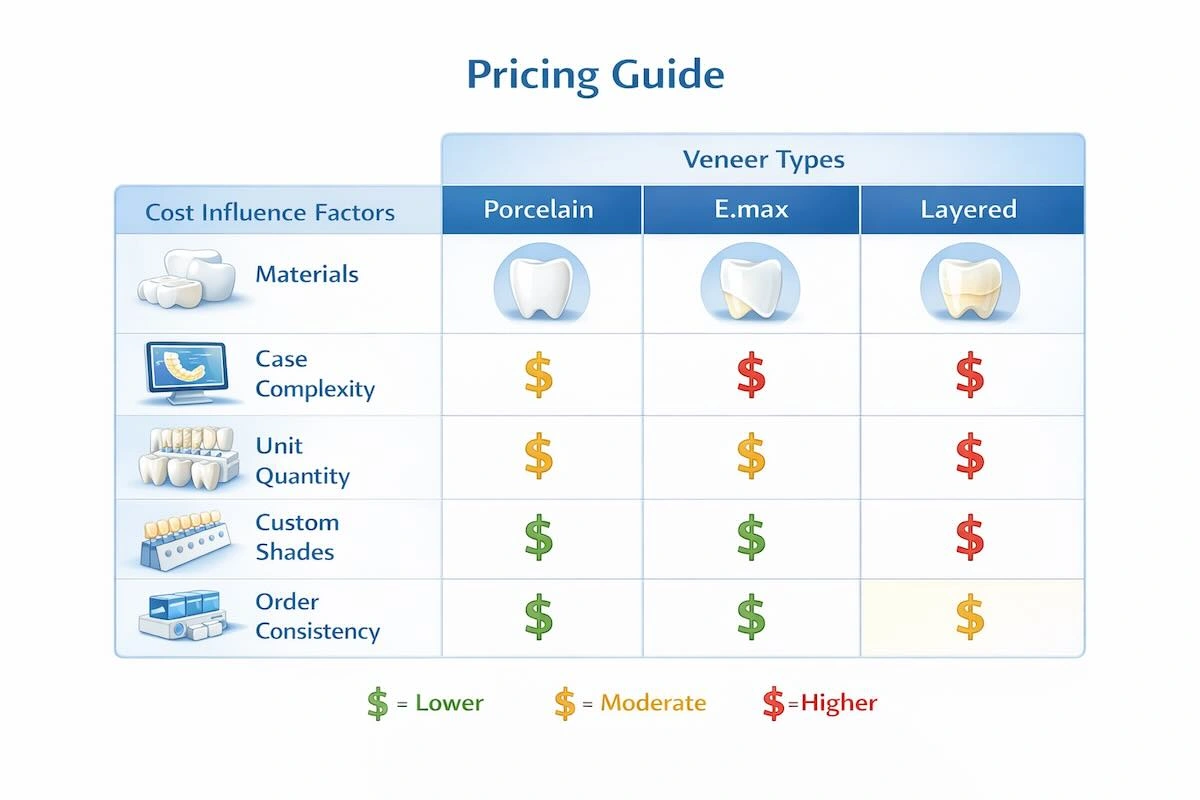
7. Pricing Guide: Understanding Veneer Outsourcing Costs
The issue of pricing is one of the most delicate ones in dental veneer outsourcing, which is usually misinterpreted. Although the material choice can be a significant factor, ultimately, the veneer pricing can be influenced by a complex of technicality, aesthetic needs, and the consistency of production. Learning about the structure of pricing enables clinics and laboratories to compare the offers on a deeper level than just the comparison on the surface.
Instead of set prices, the prices of veneer outsourcing are usually relative within some ranges depending on the intensity of production and the aesthetic need.
| Veneer Type | Relative Price Level | Primary Cost Drivers |
| Porcelain veneers | Lower–mid range | Standard fabrication workflow, moderate technician time |
| E.max pressed or milled veneers | Mid range | Material cost, CAD/CAM precision, controlled thickness |
| Layered esthetic veneers | Premium range | Extended technician time, multi-layer characterization, and higher QC intensity |
The following are the main factors that affect the price of veneer. The impact of the following factors on outsourcing quotations is the greatest and must be considered together and not separately:
| Pricing Factor | Impact on Cost | Explanation |
| Material type | Medium to high | Different ceramics require distinct fabrication and firing processes. |
| Number of units | Medium | Multi-unit cases benefit from production efficiency and reduced per-unit cost. |
| Esthetic complexity | High | Advanced layering, translucency control, and texture increase technician workload. |
| Custom shade requirements | Medium | Non-standard or highly specific shades require additional matching steps. |
| Case volume consistency | High | Stable, repeat orders allow labs to optimize scheduling and pricing. |
The analysis of quotes using these dimensions will reveal that a price is either naturally justified or naturally suppressed.
Low prices can be an indication of simplification of processes, minimization of QC, and overloading of technicians instead of actual efficiency. The idea of sustainable pricing is an indicator of fair distribution of labor, complete fabrication process, and regulated quality control.
In the case of clinics and laboratories, the objective is not to obtain the lowest unit price, but to obtain value stability, a pricing model that has a positive impact on the provision of high-quality work, predictable turnaround time, and cooperation over an extended period.
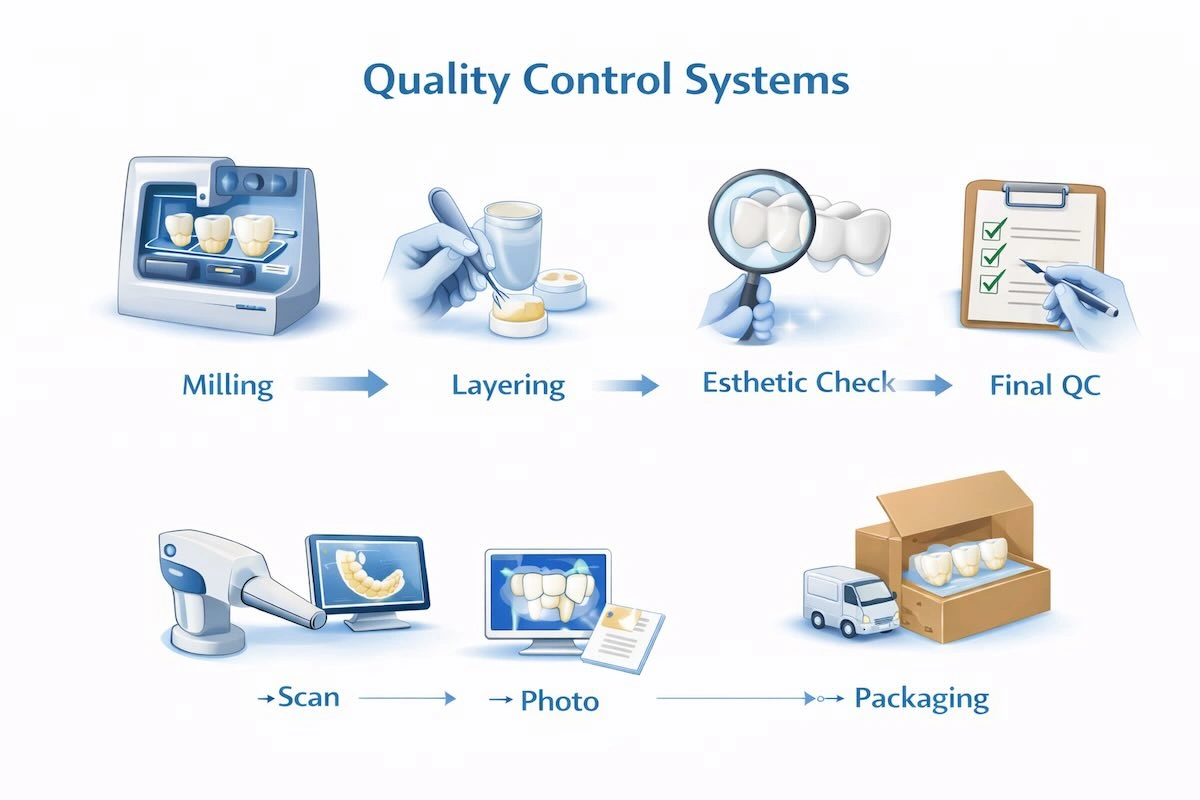
8. Quality Control Systems: Ensuring Consistent Veneer Performance
Successful veneer outsourcing is anchored on quality control. In the absence of a formal QC system, even technically competent laboratories can provide varying results, which is especially dangerous in the case of international customers who are not able to make real-time corrections.
(1) Multi-Stage QC Process
In the highest-level offshore labs, QC starts as soon as the milling or pressing takes place and will proceed to all phases of production. Early verification is done to make sure that margins, fit, and occlusal relationships are as specified before commencing layering or glazing. This preventive measure minimizes the chances of downstream errors.
(2) Esthetic Verification
Upon making the base veneer, the esthetic analysis is done to make sure that the surface texture, translucency, and incisal edge features meet the clinical and patient expectations. Each case is examined by senior technicians in uniform lighting conditions to ensure consistency.
(3) Objective Measurements
Visual assessment is augmented with data by digital scanners, verification jigs, and shade-matching tools. Such a combination of objective measurements and technician judgment yields a strong, predictable system of quality control, minimizing remakes and providing consistency among different cases.
(4) Risk-Based Inspection
In high-value cases or complex cases, extra review cycles are implemented. This risk-oriented QC makes sure that the cases that have higher aesthetic or functional requirements are handled at the necessary level, whereas the regular cases are handled at a high level of efficiency.
(5) Documentation and Reporting
All the QC findings are recorded and included with the completed case of veneer. The detailed reporting is also a source of transparency as well as a source of continuous improvement and traceability.
A multi-level QC system will convert veneer outsourcing into a potentially dangerous threat into a foreseeable and high-quality solution that will allow clinics to be certain about the result of their work in terms of both functionality and aesthetics.
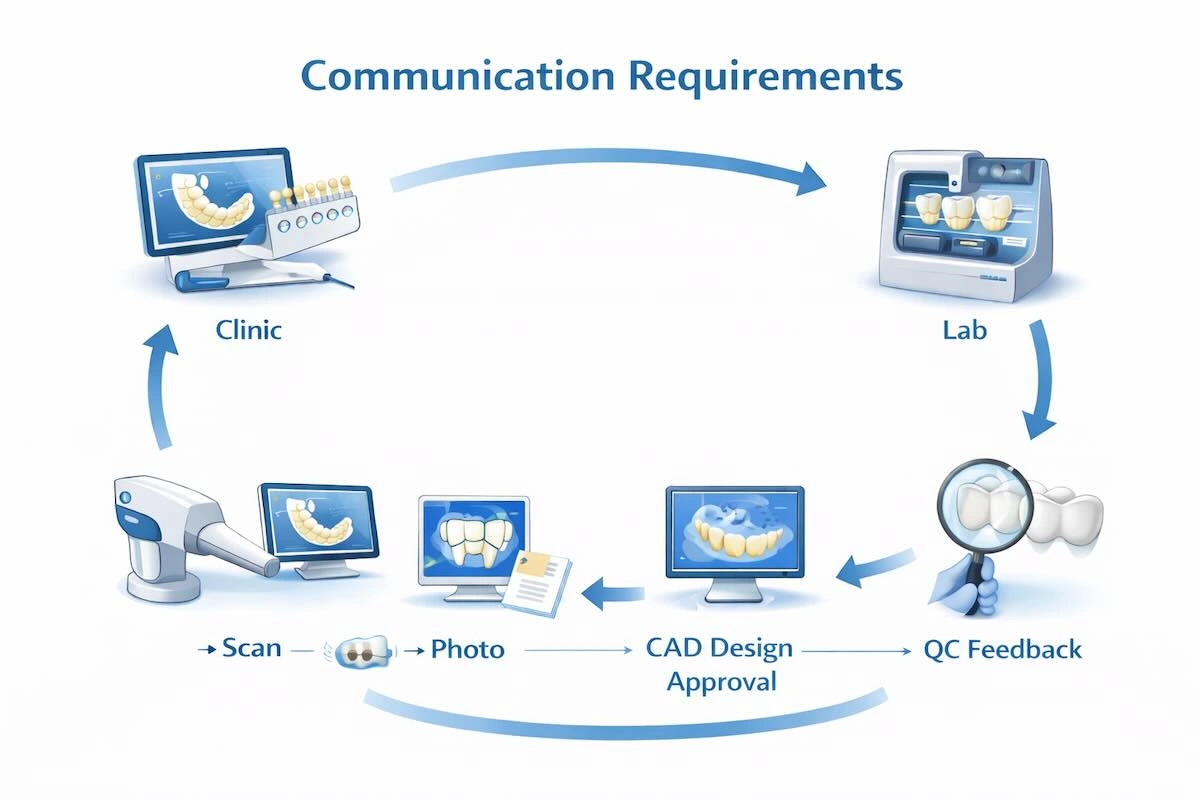
9. Communication Requirements: Reducing Misunderstandings and Remakes
One of the most important factors of successful veneer outsourcing is effective communication. The delays, remakes, and patient dissatisfaction can be caused by misunderstandings in submitting the cases, confirming the design or delivery instructions. As such, it is important to define a well-organized communication process that could sustain quality and efficiency in all international partnerships.
To begin with, the clinics should submit full and precise case information. These comprise intraoral scans or impressions of high-resolution, clear photographs of the margins of the preparations, occlusal records, and accurate references of shade. In complicated esthetic situations, further annotations or diagrams can assist the laboratory to gain insight into subtle design intent. A detailed submission of the cases would make sure that the laboratory would possess enough data to plan and realize production correctly.
Subsequently, on the design stage, digital CAD images or virtual aesthetic sketches are provided to the client by the laboratory. This will enable the technicians to ensure that the parameters of functionality and aesthetics are met before the start of fabrication. Feedback and approval will be provided promptly to reduce the subjective interpretation, hence they will avoid errors and redundant remakes. Moreover, the stage of communication establishes preconditions not only of the clinic but also of the laboratory concerning possible restrictions or changes.
Then, it is necessary to have a constant feedback loop post-case delivery. Clinics are supposed to give positive notes on the fit, shade, or aesthetic results that can be recorded by the laboratory and applied in future cases. In the long run, the practice will help the laboratory to fit certain client preferences, enhance predictability, and simplify production in the case of repeat cases.
Finally, organized communication, including the case submission process, post-delivery feedback, etc., not only reduces the misunderstandings and remakes but turns outsourcing into a predictable, efficient, and reliable process for international clients.
10. Risks and Mitigation Strategies
All outsourcing deals across borders have risks involved, but it is possible to mitigate them through systematic knowledge and take significant exposure. The category of risks associated with veneer outsourcing may be divided into four broad categories, which are clinical, technical, logistical, and operational risks.
- Clinical risks: Incorrect preparation, margin ambiguity, or occlusal instability can be considered clinical risks. Mitigation entails complete case filing and pre-production feasibility.
- Technical risks: Refer to misinterpretation of the design, material failure, or aesthetic variation. The mitigation is based on the standard workflow of CAD/CAM, highly competent technicians, and multi-level quality control.
- Logistical risks: Shipment delays, customs clearance, and handling errors fall under the logistical risks. These mitigation measures comprise trustworthy international couriers, protective shipping, and real-time monitoring of shipments.
- Operational risks: Poor communication, poor case documentation, or overcommitting with suppliers are some of the operational risks. Standardized communication protocols, clear documentation templates, and a stable production schedule will be required to mitigate the situation.
Dynamic risk management changes outsourcing into a liability that can be scaled and utilized as a dependable aspect of the clinical operations.

11. How to Choose the Right Supplier
The choice of an appropriate veneer outsourcing company is not just a matter of price comparison. The potential suppliers should be assessed in several important dimensions so that clinics can guarantee the quality and reliable results:
- Technical Capability: The lab must be skilled in CAD/CAM design, milling and pressing technology, esthetic layering, and glazing. This helps in taking care of the functional and cosmetic requirements.
- Quality Assurance: Multi-step QC verification, comprehensive reporting, and traceable documentation are necessary to avoid remakes and ensure consistency.
- Communication Infrastructure: Organized, timely, and English-fluent communication that prevents misunderstanding and creates a harmonious cooperation is essential.
- International Experience: Confirmed knowledge of the US, EU, UK, or Australian markets means that they understand the aesthetics, regulatory compliance, and international logistics.
- Reputation and Track Record: Partners who have a record of staying within the same case histories, have repeat clients, and favorable reviews have higher chances of providing predictable outcomes.
To find a high degree of predictability and professional assistance, those clinics that prefer to have such elements, suppliers such as Bestodental represent the best example of such qualities by integrating sophisticated technology, professional technicians, and strong quality control measures.
12. Who Should Outsource—and Who Should Not
The problem of veneer outsourcing to a clinic or lab is important to determine the consistency of results and cost-efficiency of the business. Knowledge of the kind of practices that are most advantageous, as well as those that might be problematic, can prevent the pitfalls and have a successful outsourcing relationship.
(1) Veneer outsourcing will best fit in clinics and laboratories that:
- Process moderate to high volumes of elective cases of esthetics: Clinics that have a regular flow of cases will find outsourcing to be advantageous since the labs will be able to schedule the production at the best and be cost-efficient without loss of quality.
- Have consistent, standardized preparation and design procedures: The use of standardized preparation and design processes minimizes errors in interpretation and makes offshore laboratories consistently able to replicate results.
- Demand cost reduction without affecting aesthetic quality: Outsourcing is also very economical in terms of cost savings than in-house production, and yet the quality of veneers is of high quality, given the clarity of cases.
- Able to deliver all digital information and organized directions: The laboratories can produce veneers with minimum adjustment or remakes when clinics have the capability of producing the correct scans, photographs, occlusal records, and shade specifications.
(2) Outsourcing may not be ideal for practices that:
- Relied on emergency or same-day delivery: Cross-border processes demand manufacturing and delivery, thus emergent cases are challenging to handle without risking delays or quality loss.
- Often deal with very experimental or one-off aesthetic designs with no definite allusions: Offshore laboratories are based on the visual and technical references; the most subjective or experimental design has a greater risk of interpretation and possible remakes.
- Absence of digital workflows or standard documentation: The lack of systems with regular digital documentation or guidelines causes ambiguity among technicians, which leads to more errors and overhead in communication.
- Cannot allocate staff to verify or communicate potential issues during design or QC stages: Outsourcing demands cooperation; in case the clinic is not able to review the design or answer questions in time, cases may be delayed or have quality discrepancies.
The analysis of internal capabilities on the same basis will help clinics and laboratories make a wise decision, targeting their outsourcing activities in cases where it provides predictable quality, efficiency, and financial gain.

13. Outsourcing Dental Veneers FAQs
Workflow, quality, cost, and timelines are some of the practical questions that are posed by clinics and laboratories when thinking about dental veneer outsourcing. The frequently used questions are answered in the following FAQs, which make the decision-making process effective.
Q1: How much volume of cases should be outsourced without quality being compromised?
A1: A majority of the laboratories can manage both single-unit and multi-unit cases, but it is simpler to maintain quality consistency with moderate and predictable volumes. Huge batches are to be planned to make sure that technicians pay attention and quality control is maintained.
Q2: How should I be able to guarantee the aesthetic outcome is as expected by the patients?
A2: It is very important to offer good scans, detailed photos, accurate shade guides, and reference cases. When dealing with complicated aesthetic items, it is best to give the CAD designs or digital mock-ups approval before they are made into actual items to reduce subjectivity.
Q3: What are the protocols of remakes in case veneers are not fitting/matching?
A3: Organized remake procedures are applied in professional laboratories. Problems identified on QC or upon receipt are remedied quickly and in most cases with no further delay in distributing further, which ensures continuity in the treatment plans of patients.
Q4: What is the international shipping done to preserve the fragile veneers?
A4: Veneers are well packed and sent through a safe courier. All shipments are tracked, and professional labs develop packaging to reduce the risks during transit.
Q5: Will the workflow outsourcing be able to be integrated into my current digital systems?
A5: The vast majority of professional laboratories work with the standard intraoral scan formats, STL files, and popular CAD software, and they can be easily integrated into the digital flow of your clinic.
Q6: What is the duration of the lab to respond to design or feasibility questions?
A6: The design confirmation and feedback on feasibility are usually returned within 24-48 hours, based on the complexity of the case. Timely reaction prevents production delays and makes treatment schedules predictable.
Q7: Are there any additional expenses that I need to know about?
A7: Transparent labs will give complete quotations at the beginning, including material, production, QC, and shipping. There are no extra charges that are typically imposed unless the client demands additional esthetic work, custom shades, or expedited shipping.
These are the main questions that can be answered to guide the clinics and laboratories to outsource with a sense of security, which will allow a seamless working process, time predictability, and quality results.

14. Conclusion
Outsourcing dental veneers to a reputable Chinese lab may provide cost-effectiveness, technology, and reliability in providing esthetic outcomes. The success is determined by the clarity of the submissions of the cases, the organized communication, and the strict quality control. With the right choice of lab with strong QC systems and well-established communication, the clinics can reduce remakes, guarantee a consistent turnaround time, and have repeatable, high-quality results.
For practices that are interested in finding a reliable partner in the complex or high-volume cases, there are labs such as Bestodental that offer proven expertise, high-level technology, and reliable services, so outsourcing is a viable and scalable option.