The contracting of dental structures has been a strategic move for most dental laboratories and clinics in the world. With the rise in the volume of cases and the pressure on costs, additional providers are reconsidering their approach to metal framework fabrication, either in-house work or outsourcing to a specialized vendor. Dental frameworks are structurally motivated, process motivated, and highly compatible with standardized production, unlike highly esthetic restorations, which is why they are a natural target of outsourcing with proper management.
But outsourcing the dental structures and more so internationally is not merely about pricing. It implies familiarity with the limitations of products, stipulation of technical limitations, creation of reliable working processes, and quality control. With this guide, the dental professionals can reap the benefits of experience through a hands-on framework of outsourcing metal dental frameworks to China, including the why, the how, the risks, and the controls that are necessary to achieve long-term success.
1. What Is a Dental Framework?
A dental framework is the metal framework that provides the mechanical basis of most dental prosthetic restorations. It is primarily applied in removable partial dentures (RPDs), overdenture supported by implants, or some types of hybrid restorations where strength and stability are critical.
In practice, a dental structure has four fundamental purposes:
- Structural support: offers the structural support of the prosthesis
- Force distribution: evenly distributes the occlusals to teeth, soft tissue, or implants
- Retention and stability: determine the clasp design and the course of insertion
- Protection of abutments: reduces piling action on structures
Dentally speaking, dental structures are commonly constructed of either cobalt-chromium (Co-Cr), titanium, or precious metal alloys. Co-Cr has become the current outsourced framework of choice in the world because it is stronger, resistant to corrosion, biocompatible, and cost-effective. Now, frameworks are digitally designed and fabricated with greater consistency and repeatability with the aid of CAD/CAM and metal 3D printing technologies.
To non-professional readers, a dental framework may be likened to a steel frame in a building: the one that is not seen day-to-day but is very important to the stability and functionality of the building over a long period.
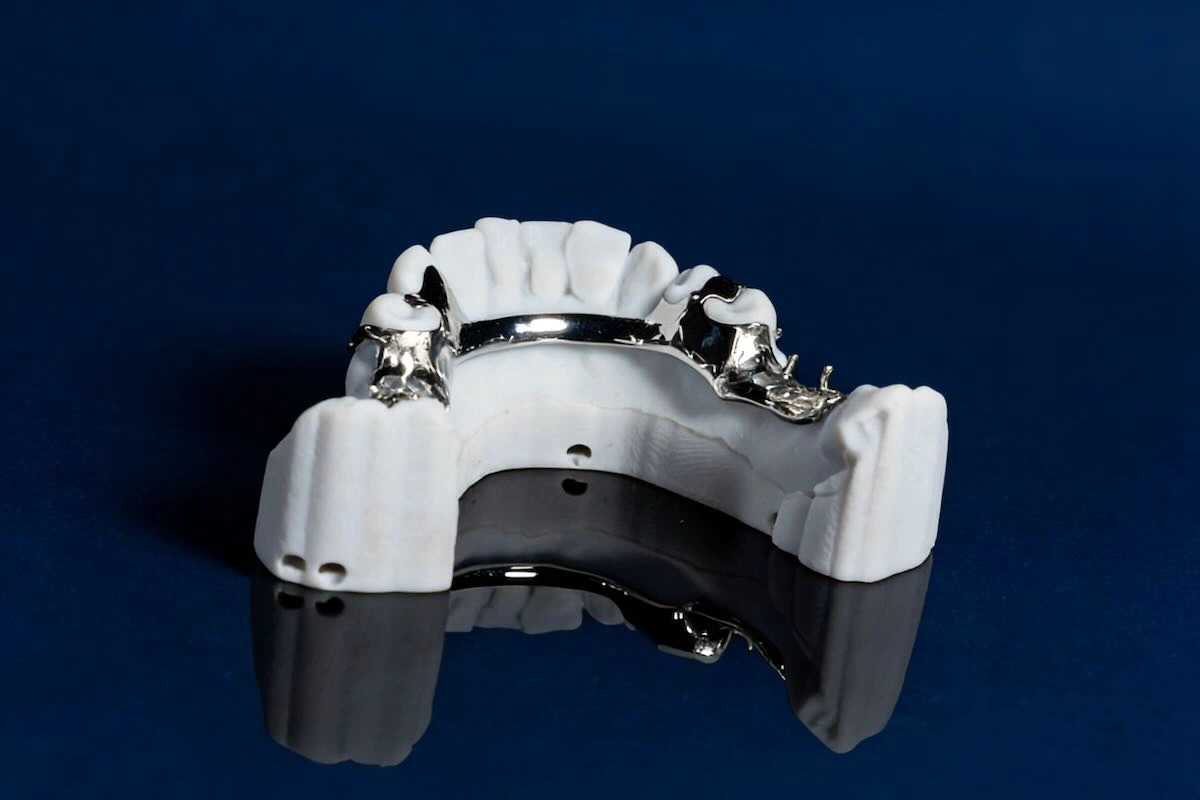

2. Why Are Dental Frameworks Suitable for Outsourcing?
The dental models are especially favourable to outsourcing since they incorporate both high technical standards and labour-intensive production. The manufacturing process is very repeatable once the clinical parameters are well established, i.e., type of major connector, type of clasp, location of undercut, material used, and path of insertion are clearly defined.
It is very expensive to keep the production of in-house structures. This also incorporates casting systems or metal printers, CAD/CAM software licenses, scanners, alloy inventory, environmental controls, and ongoing training of technicians. These expenses cannot be easily justified against utilization rates, which is the case with many laboratories. Outsourcing transforms such fixed costs to predictable unit costs, enhancing operational flexibility and financial efficiency.
Workflow positioning is another factor. One of the upstream elements is the dental framework. Its outsourcing does not take away the control of aesthetics, occlusion, or ultimate delivery by the laboratories. The setup of acrylic, arrangement of teeth, its finishing, and its adjustment may also be done locally. It is what renders frameworks as one of the least risky in dental outsourcing than veneers, anterior crowns, or highly esthetic restorations.
Also, the demand for frameworks, in particular, RPD frameworks, is stable and volume-based. This is quite consistent with centralized manufacturing models, where the efficiency, consistency, and quality achieve an increment with increasing volume.
3. Why Outsource Dental Frameworks to China?
The arrival of industrial maturity, cost economy, level of production, and the experience of international service developed over time have all led to China being a preferred destination for dental framework outsourcing.
(1) Maturity in Industry Accrued Through Two Decades
Chinese dental laboratories changed over the last two decades as they have transformed into an automated manufacturing structure with standard procedures and consistent output to global customers.
(2) Efficiency of Structure, but not Dumping Price
Structural efficiency is a strength of China, not short-term low pricing. Achieved through lower labor, centralized acquisition of alloys, and high usage of equipment, competitive pricing is maintained, and investment in CAD/CAM and metal manufacturing technology is carried on.
(3) Scale to promote Consistencies
Big Chinese dental laboratories are helping to do framework cases in large numbers every month. This scale will allow optimizing workflows, specializing technicians, reducing the error rate, and maintaining the turnaround time at a constant level, even during the highest demand.
(4) Established History of cooperation at the international level
The suppliers are already established and know the international prescriptions, material requirements, and documentation standards. Cross-border cooperation is also lessened by the use of English-speaking communication teams.
Collectively, these aspects make China not a low-cost substitute but a full-fledged manufacturing companion that can provide consistent outcomes on a large scale.
4. What Can and Cannot Be Outsourced?
It is critical to create a clear boundary in outsourcing to ensure that the cooperation is effective, the clients are properly informed, and that both the laboratories and suppliers will be working in a reliable and predictable structure. Knowing well what is safe to outsource will assist in avoiding confusion, wastage of time, and redundant refurbishment, and will actually give clients confidence in what the supplier is able to do.
1) Suitable for Outsourcing
- Removable partial denture Co-Cr frameworks
- Calculated digitally, cast, milled, or SLM printed structures
- Implant bar systems that are founded on verified implants
- Checking structures and test jigs
- High-volume, standardized RPD designs
The cases can be easily outsourced due to their standardization, process-based, and digital workflow compatibility that enables suppliers to deliver quality in a streamlined manner.
2) Less Suitable or Not Recommended
- Cases that have not been fully impressed, have unstable occlusal records, and cases whose margins have not been defined
- Very experimental or unusual designs that have no reference cases
- Cases that need to be delivered within one day or the next day
- When the clinician anticipates a wide-ranging chairside adjustment rather than a premeditated design
Such cases cannot be outsourced because they have a greater variation, there are more chances of error, and they require a quick turnaround. An initial definition of scope protects both parties, minimizes remakes, and makes sure that every case is managed using the right workflow and expertise.
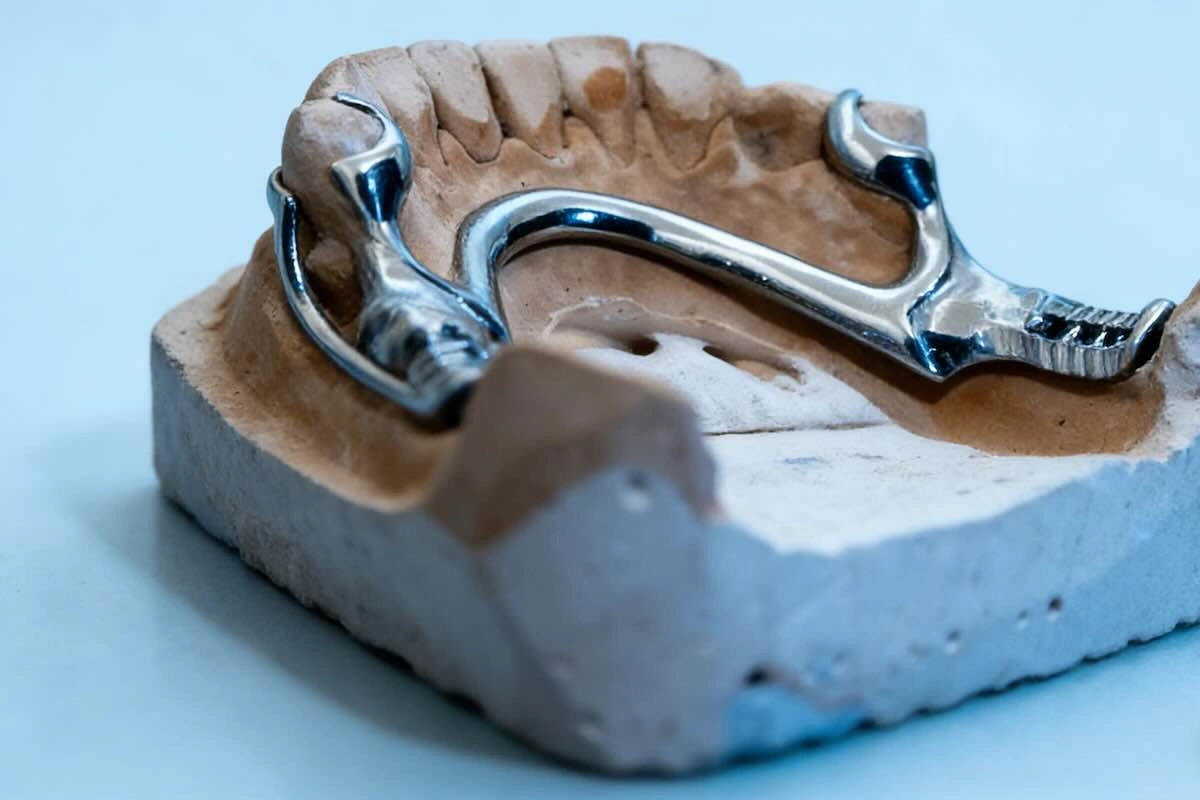

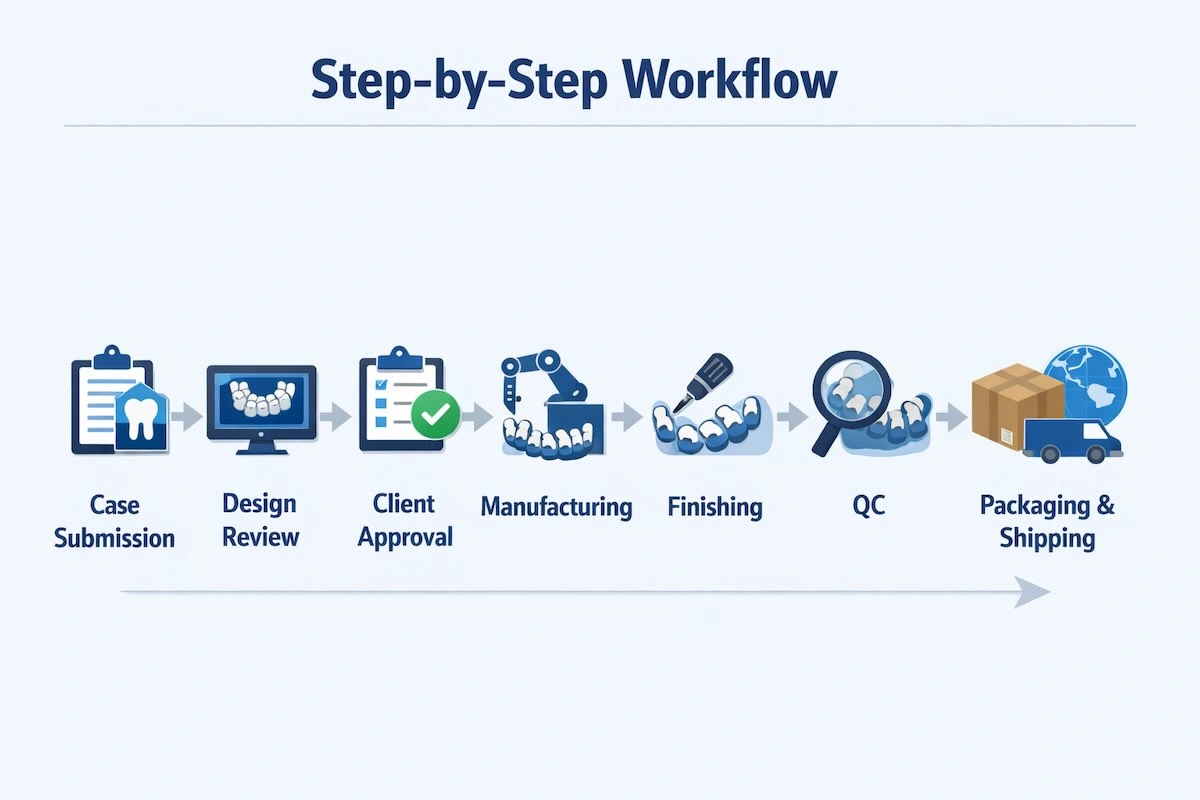
5. Step-by-Step Workflow for Dental Framework Outsourcing
The workflow of outsourcing is the most significant factor of success. An organized and accountable Chinese dental framework vendor has a clear, open procedure that is predictable, reduces remakes, and fits well with the internal business processes of the client. The following is a sequence of steps, which is a reflection of a real-life practice.
Step 1: Case Submission
Clients either provide digital STL files of an intraoral scan or lab scan, or they provide physical models. The full prescription must consist of:
- Clasp types and locations
- Important connector design and relief spaces
- Stress reliever (Co-Cr, titanium, or precious alloys)
- Clearance and finish line tastes
- Special instructions (e.g., changed path of insertion, implant angulation corrections)
Best practices: Each file should be well labeled, with the bite registration and abutment orientation, which decreases the possibility of misunderstanding. Most suppliers insist on a checklist that accompanies the supply in order to verify that all the necessary parameters are supplied.
Step 2: Design Review and CAD Development
The framework design is produced by CAD technicians based on the provided information. Key steps include:
- Checking undercut sites, route of insertion
- Optimizing great connectors and clasp engagement
- Simulation of the distribution of the occlusal force to avoid stress concentration
- Improving the fit of implant bars or verification jigs to the intended angulation of implants
Industry experience: Experienced suppliers tend to apply an automated system of interference detection and the simulated digital fit before review by the client. This minimizes remakes due to little undercut errors or connector conflicts.
Step 3: Client Approval
The client is sent design previews (3D views or screenshots) to confirm the design.
- Clients inspect the framework fit, the positions of the clasps, major connectors, and any modifications requested
- A request for annotated revision or formal approval is saved
Why this matters: This is a very important control point. One slip in this direction will lead to expensive remakes. In most professional labs, the policy is that without signed approval, no production can be done.
Step 4: Manufacturing
Upon approval, structures are constructed with the approach appropriate to the situation:
- Casting: Casting in the traditional lost-wax method of common RPD frameworks
- Milling: High-precision designs, Subtractive CAD/CAM milling
- SLM / 3D printing: To be used in complex bars or implant-supported frameworks that are personalized
Pro tip: Digital workflow makes sure that each unit is similar to the approved CAD design. Production repeatability leads to a decrease in variation, as well as to a better fit, particularly when production volumes are high.
Step 5: Finishing and Polishing
Manufactured frameworks are subjected to:
- Surface finishing to eliminate artifacts of casting or printing
- Tension of the clasp to make sure it engages
- Passive fit check on the physical model or the 3D-printed model
Practical note: Trial fitting on the model is done by the experienced labs before shipment, and this leaves the possibility of adjustment at the chairside to a minimum.
Step 6: Quality Control
QC teams inspect each framework for:
- Against CAD design, dimensional accuracy
- Material integrity, porosity, and surface consistency
- Correct traceability labeling and documentation
- Adherence to customer-related needs
Industry standard: A significant number of suppliers have multi-stage QC, such as CAD cross-checks, visual inspection and mechanical testing where necessary. Transparency is provided to the client through documentation.
Step 7: Packaging and Shipping
Completed frameworks are:
- Labelled and arranged individually on a per-client prescription basis
- Packaged protectively to prevent deformation during transportation
- Using QC reports, tracking data, and following instructions
To keep the logistics frameworks delivered on time, it is important to choose reliable logistics and arrange shipments well in advance to not interrupt the clinical process of the client.
The next step in this workflow is that, rather than being a risky process with a black box nature, it is a predictable expansion of the client’s internal production. Appropriate implementation in every phase, in particular, submission, design approval, and QC, is what distinguishes between successful outsourcing relationships and those that produce several re-remakes and delays.
6. Turnaround Time for Dental Framework Outsourcing
One of the most widespread issues in relation to the outsourcing of dental frameworks to the international arena is the turnaround time. In the case of frameworks that are produced in China, the following schedule can be subdivided:
(1) Design and Approval: 1–2 working days
Fast feedback at the approval phase is imperative. Timely feedback from clients ensures manufacturing is not held up, and obviously, clearly marked-up designs or STL files will mean less back-and-forth clarification process.
(2) Manufacturing and Finishing: 3–5 working days
Most frameworks can be made in this window depending on the complexity and method of production (casting, milling, or SLM printing). In high-volume laboratories, the workflows tend to be standardized, which enables several cases to be run simultaneously and enhances efficiency, but not the quality.
(3) International Shipping: 2–4 working days
The shipping time varies with the courier, clearance at customs, and destination. A lot of professional suppliers organize their work with the help of stable logistics partners, give them tracking data, and plan the shipment to reduce the number of delays.
In normal circumstances, the majority of the cases are received within 7-10 days of working days after being submitted. Turnaround consistency is based on online submissions, timely client endorsements, and consistent logistics alliances. To further minimize variability, certain labs provide priority processing or batch scheduling of large customers or emergencies to enable predictable targeting of the clinic business processes.
Knowing these time aspects and having proactive communication, clients will be able to plan case schedules more precisely, prevent last-minute rush, and provide acceptable integration of outsourced structures into the daily clinical activities.

7. Pricing Guide: Understanding Cost Structures for Dental Framework Outsourcing
The cost of dental outsource systems is determined based on several parameters, such as the type of material used, the complexity of the design, the production type, and the quantity of orders. Price comparison without taking these variables into consideration is likely to give deceptive results.
The Chinese laboratories that are reputable are not based on low prices but on cost-effectiveness. Transparent pricing normally encompasses all the key production processes, and clients can assess the overall landed cost rather than individual unit prices.
An average cost breakdown may be disaggregated in the following way:
| Cost Component | Description | Typical Considerations |
| Design & CAD Development | Digital framework design, verification, and client approval | Complexity of framework, number of revisions, STL file processing |
| Material | Co-Cr, titanium, or precious alloy | Alloy type, weight, and market fluctuations |
| Manufacturing | Casting, milling, or SLM printing | Machine utilization, complexity, post-processing effort |
| Finishing & Polishing | Surface refinement, clasp adjustment, model verification | Time-intensive manual steps may vary per case |
| Quality Control | Dimensional and material inspection, documentation | Multi-stage QC for high-volume and complex cases |
| Shipping & Documentation | Standard international delivery and handling | Customs clearance, tracking, and insurance |
In long-term relationships with suppliers, one can expect more stable prices, volume discounts, and priority scheduling. This supports the essence of strategic partnership as opposed to transactional sourcing with certain predictability in costs and production schedules.
Rule of thumb: When seeking quotes, insist on a breakdown of each cost element. This is to enhance the comparison of the suppliers and avoid hidden charges in the workflow.
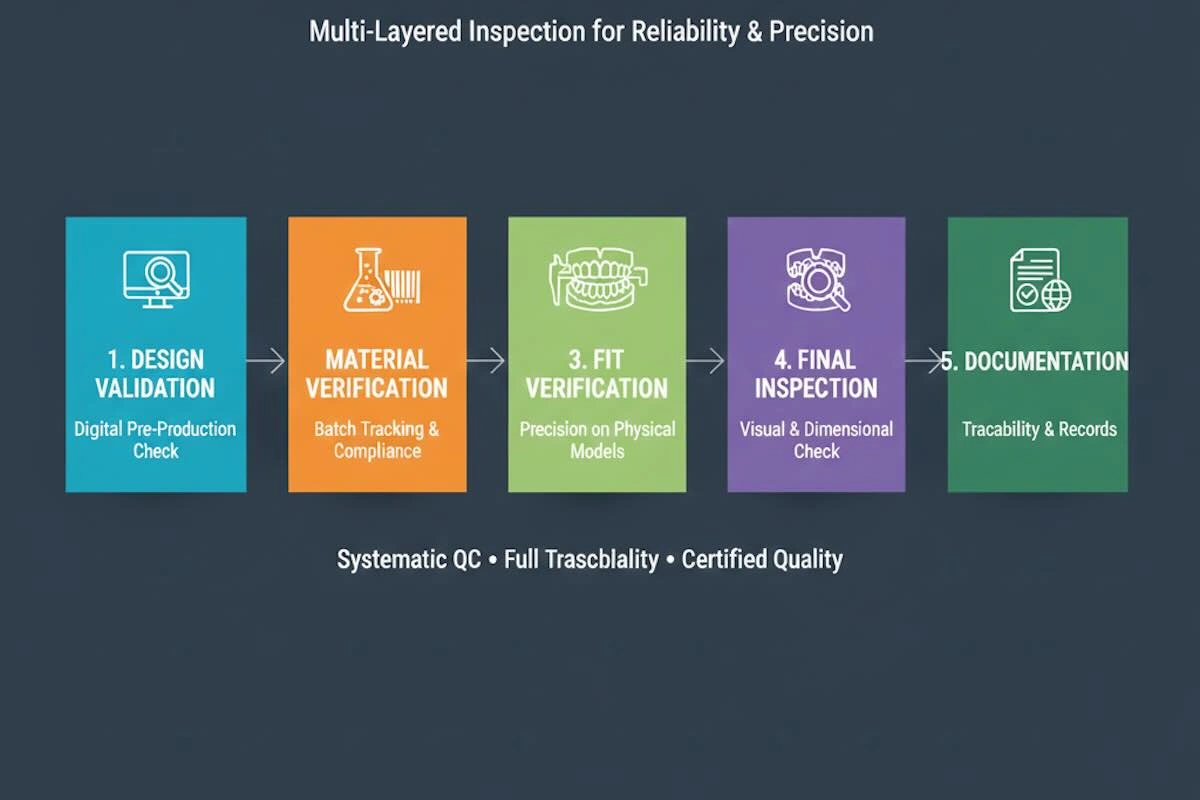
8. Quality Control Systems for Dental Framework Outsourcing
A successful B2B dental framework outsourcing is based on quality control (QC). Mature Chinese laboratories use multi-layer QC systems, which ensure that there are minimal errors, consistency, and adherence to client requirements. With international clients, the QC documentation is transparent, and as significant as the inspections per se because it gives the client confidence in the trustworthiness of the outsourced operations.
(1) Design Validation
All framework designs are examined before the start of production with reference to the prescription made by the client. CADs and STLs are verified to include:
- The right direction of insertion and the location of the clip
- Significant connector and relief area congruence
- Correct occlusal and stress distribution
Impact: This is because early identification of design faults will save expensive remakes, and the constructed structure will be correct on the first attempt.
(2) Material Verification and Batch Tracking
The suppliers use batch tracking, where the quality of the materials is verified before fabrication. This includes:
- Checks on weight consistency and alloy composition
- Traceability of Co-Cr, titanium, or precious metal batches
- Regulatory and client auditing documentation
Impact: It eliminates the utilization of defective or inconsistent material, and this gives it mechanical strength and biocompatibility.
(3) Fit Verification on Models
Models are trial-fitted on physical or 3D-printed models before being finished. Checks include:
- Passive fitting of connectors and clasp
- Contact points and occlusal clearance
- Corpus callosum with implant positions or abutment teeth
Impact: Decreases the chairside adjustment time and enhances the comfort of the patient to guarantee clinical happiness.
(4) Final Visual and Dimensional Inspection
QC teams are involved in:
- Surface inspection of casting defects, porosity, or roughness
- CAD specifications in dimensional measurement
- Confirmation of a complete prescription request
Impact: and verifies that all frameworks satisfy accepted standards, which guarantee predictable quality in a variety of cases.
(5) Documentation and Traceability
Every case is accompanied by QC reports, which describe:
- Inspection results
- Material batch numbers
- Deviations and remedial measures
Impact: The transparency and confidence of the international clients have been achieved, as well as accountability and repeat quality on the part of the supplier.
9. Communication Requirements to Avoid Remakes
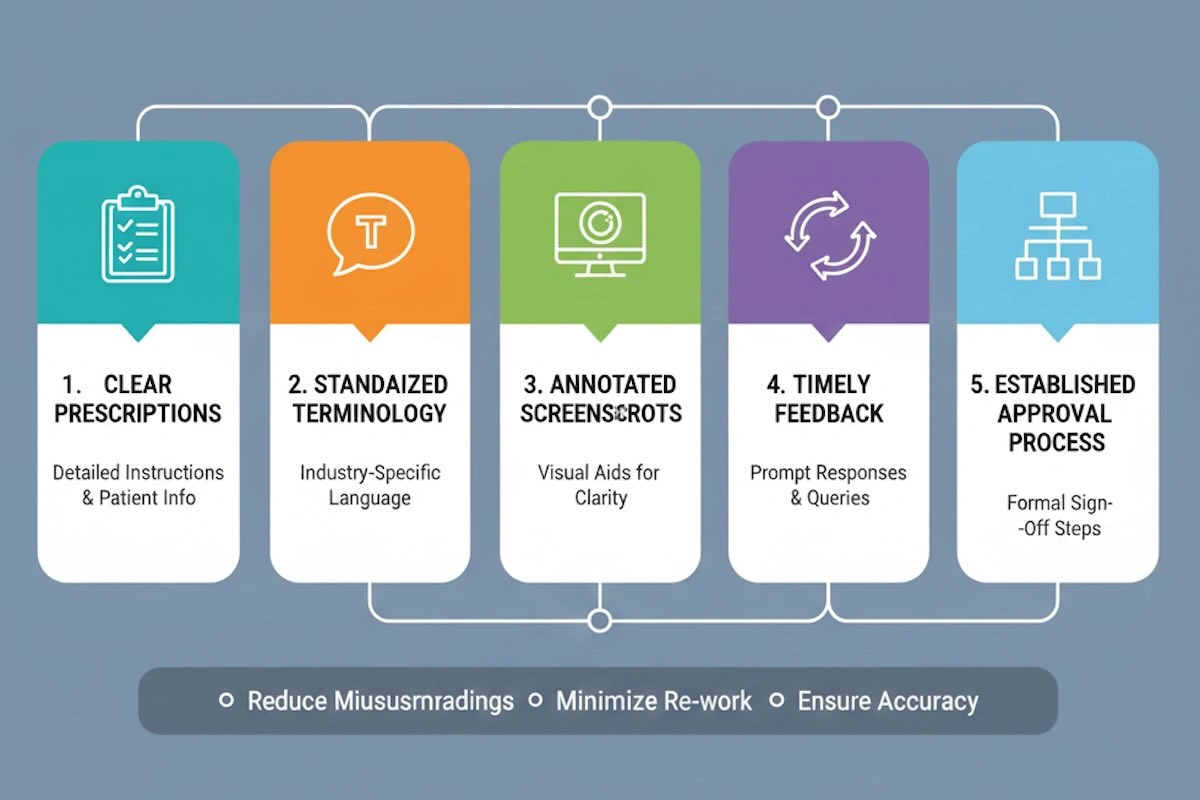
Communication is considered to be one of the most neglected aspects of effective dental framework outsourcing. Standardized and clear communication is essential to make sure that the designs, specifications, and expectations are correctly understood and the remaking and delays are minimized. The most important communication practices are listed below:
- Clear Prescriptions: Give comprehensive guidelines with regard to clasp types, large connectors, material selection, and special design. Do not be vague or make assumptions.
- Standardized Terminology: Consistent terminology should be used in framework components and dental anatomy. This minimizes misunderstanding between the foreign customers and Chinese engineers.
- Annotated Visuals: Add shots, STL previews, or highlighted images with signs of changes or important areas. Pictorial references assist the technicians in having a feel of subtle requirements.
- Timely Feedback: Accept or demand changes at the early stages of design. Late feedback may bring bottlenecks in production and increase turnaround time.
- Determined Communication Protocols: Identify responsible approval, acceptable response times, and revision limitations. The standardization of roles and procedures helps to avoid misunderstanding and contradictory orders.
- Documentation of Decisions: Note down approvals, alterations, and clarifications. This makes it traceable and gives a point of reference in case of any discrepancy in the manufacturing process.
Communication will help to streamline outsourcing as a reactive and problem-solving process to a predictable and controlled working process, eliminate mistakes, and improve the quality of the delivered frameworks.
10. Risks and Mitigation Strategies
Dental framework outsourcing has some risks, but these risks can be managed systematically as long as proper planning is done. Identifying the possible pitfalls and mitigation plans of these pitfalls are some of the factors that the clients can continuously stay in predictable quality and schedule.
| Risk | Potential Impact | Mitigation Strategy |
| Design Misinterpretation | Poor fit, repeated adjustments | Pilot cases, detailed digital/physical prescriptions, annotated screenshots |
| Material Inconsistency | Reduced strength, clinical failure | Batch tracking, certified alloy suppliers, material verification before production |
| Logistics Delays | Missed deadlines, clinic scheduling issues | Reliable couriers, pre-scheduled shipping, tracking updates, buffer days |
| Communication Gaps | Workflow confusion, remakes | Dedicated account managers, fixed protocols, timely feedback, and documented approvals |
| Unexpected Clinical Requirements | Production disruption, high-cost rush orders | Realistic scheduling, contingency planning, and early case review |
Professional outsourcing doesn’t avoid risk but manages it proactively through structured workflows, proactive communication, and continuous feedback loops. By understanding and addressing these factors, clients can integrate outsourcing as a reliable extension of their in-house workflow rather than a source of uncertainty.
11. How to Choose the Right Dental Framework Supplier
Choosing the appropriate supplier is not just an issue of price comparison. There are several points that decision-makers have to consider:
- Capacity to Produce: Does the supplier manage your case volume without hitches?
- Digital Capabilities: Does the lab facilitate CAD/CAM processes, STL-based Design and high-tech manufacturing processes like SLM or milling?
- Transparency of Quality Control: Does the organization have documented QC processes that are traceable and communicated to clients?
- Responsiveness to communication: Does the supplier respond in time, have a clear approval policy, and communicate in English?
- Long-term Cooperation Awareness: Does the supplier have the ability to increase with your practice or laboratory in the long run?
Compared with other suppliers like Bestodental, this company distinguishes itself with scalable production capacity, highly trained technicians, and consistent English-speaking communication teams, as well as multi-stage documentation of QC. This allows them to provide predictable quality at scale, and they are suited to long-term strategic alliances, not one-off or short-term outsourcing experiments. This is supported by the fact that their record with international clients is very high, and therefore, they can easily fit in the flow of the clients without distorting their clinical accuracy and reliability.
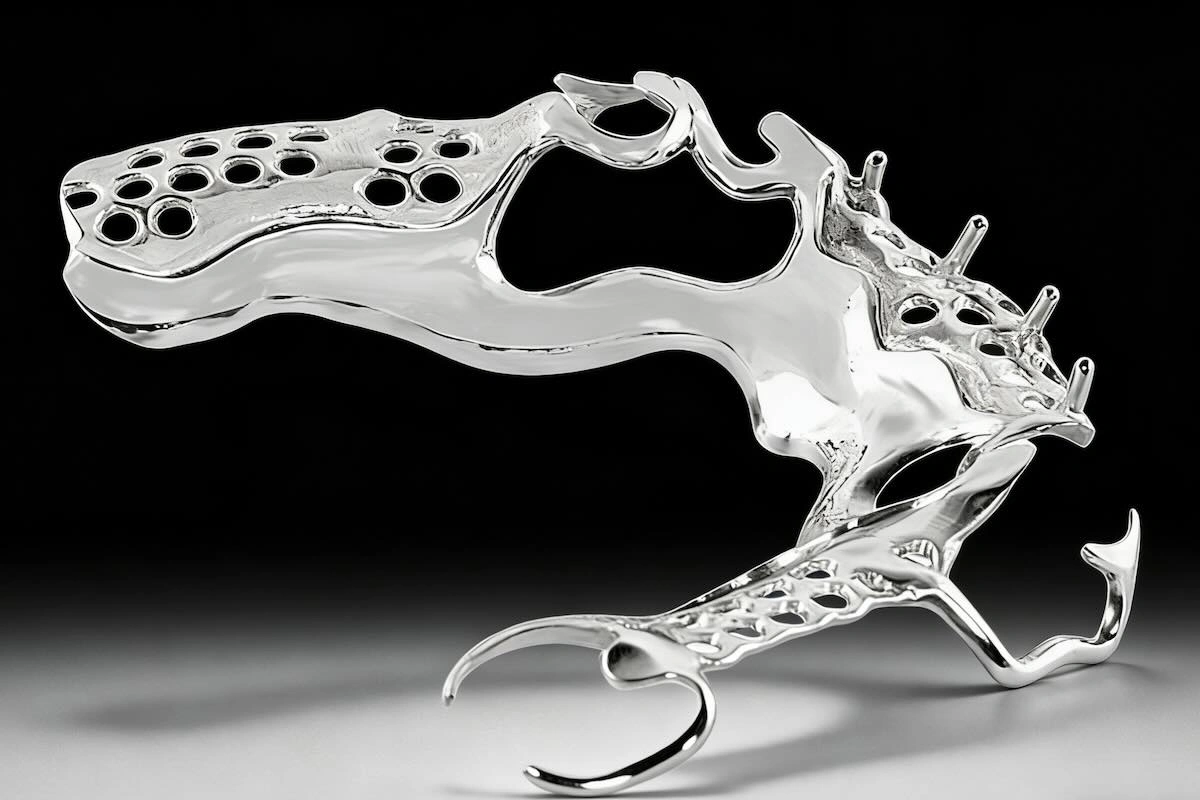

12. Who Should and Who Should Not Outsource Dental Frameworks?
To know when it is appropriate to outsource, it is important to have a clear picture of how (volume and strategic) your laboratory works.
1) Who Should Outsource
- Laboratories whose RPD or implant framework volumes are beyond internal production capacity.
- Labs with little metal fabrication equipment or those with old equipment.
- Labs or clinics that are looking to be cost-effective without affecting quality.
- Organizations interested in dedicating internal resources to aesthetic finishing or services that directly interact with patients.
- Laboratories that wish to capitalize on digital processes and high-precision production without spending large amounts of money on infrastructure.
2) Who Should Not Outsource
- Laboratory-scale single-application labs that only do highly custom or experimental designs with the necessity of continuous iteration.
- Labs that require the same-day turnaround or very high turnover on a case-by-case basis.
- Chairside practices include a high frequency of unexpected changes that cannot be planned.
- Labs that do not have a specific workflow of communication and design approval because it involves remakes.
- Labs that are keen on having full in-house control on all the steps that are involved in the production process, because of either regulatory or branding factors.
Having a clear strategic fit ensures that outsourcing is a sound extension of your operations rather than a source of time wastage, remakes, or stress on operations.
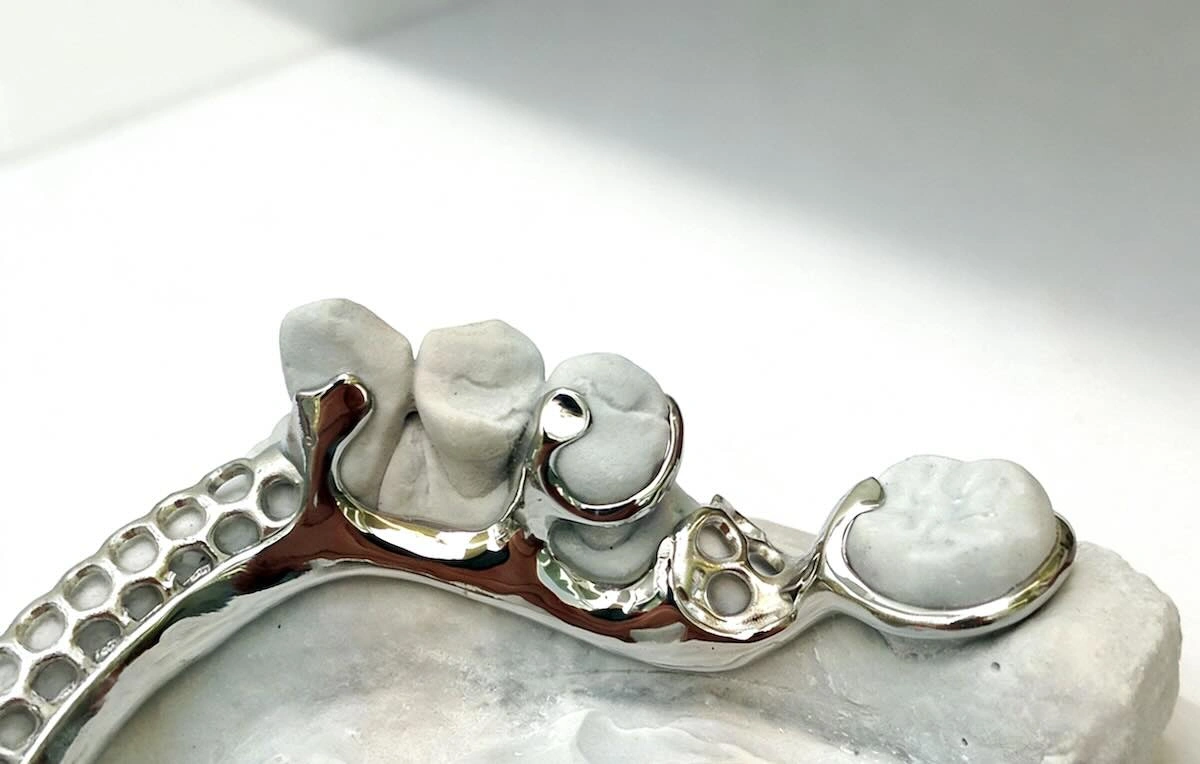

13. Dental Framework Outsourcing FAQs
Dental frameworks outsourcing leaves a lot of practical questions. The common and technical issues that international clients have are detailed in the following FAQs:
Q1: What should I do to make sure that the outsourcing frameworks are accurate in a digital form?
High-resolution STL scans, bite registrations, and detailed prescriptions are used to make sure that outsourced frameworks are congruent with clinical needs, followed by production, using CAD-based design validation and pilot cases.
Q2: What are the quality certifications/ material standards I should expect?
Co-Cr, titanium, or precious alloy frameworks are supplied by reputable suppliers with material certificates, batch traceability, and documented QC procedures that comply with ISO 13485 or other standards.
Q3: Is it possible to outsource some workflow steps and retain finishing?
Yes. Most laboratories also outsource the metal framework and do the acrylic work, articulation, or esthetic finishing in-house, and can add the internal expertise.
Q4: What is the number of pilot cases to be recommended before scaling outsourcing?
The majority of the laboratories test the suppliers using 5-10 pilot cases, which enables optimization of the workflow, communications alignment, and quality verification before authorizing a large number of cases.
Q5: What can I do to avoid international outsourcing workflow communication-related mistakes?
Determine standard procedures in approving the designs, utilize marked-up screenshots or STL previews, appoint accountable persons, and plan timely feedback. Each decision should be properly documented to avoid misinterpretation and remakes.
14. Conclusion
The outsourcing of dental framing work to China has evolved over the years into a full-blown and dependable solution for international dental labs and practices. When appropriately controlled and managed, outsourcing to a country like China offers cost-effectiveness, scalability, and quality.
Involvement with any organizational entity that aims to reach operational stability and achieve strategic growth will find that working with a professional Chinese dental laboratory is more than simply an expenditure consideration—it’s a strategic one. Using suppliers that are proven and successful at production and communication will help dental labs expand their reach and allow dental labs to continue to be relevant within the increasingly difficult global market.